K: Kids (Induction agent of choice in children) E: Emergence reaction (floating sensations, vivid dreams and hallucination; reduced using benzodiazepines), Enantiomers (S-Ketamine and R-Ketamine) T: Thalamo-cortical dissociation with limbic system causing dissociative anesthesia A: Analgesic, Amnesic, Antidepressant, All routes (IV, IM, PO, Intranasal, Epidural, Intrathecal) M: Meals – can be…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.

SCFE : Mnemonic Approach
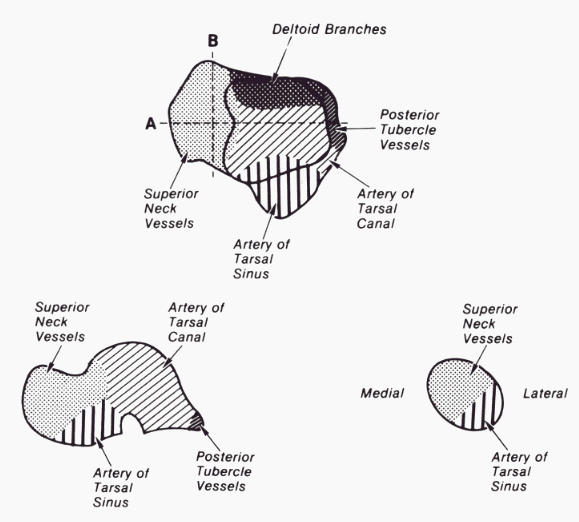
Approach to a limping child General points Classification Management depends on 4 factors which can be remembered using the mnemonic SCFE. Stability and Severity a. Loder classification: b. Severity: Severity Southwick angle on frog-leg lateral view (Difference of head-shaft angle from normal side) Wilson slip % on AP or frog-leg…
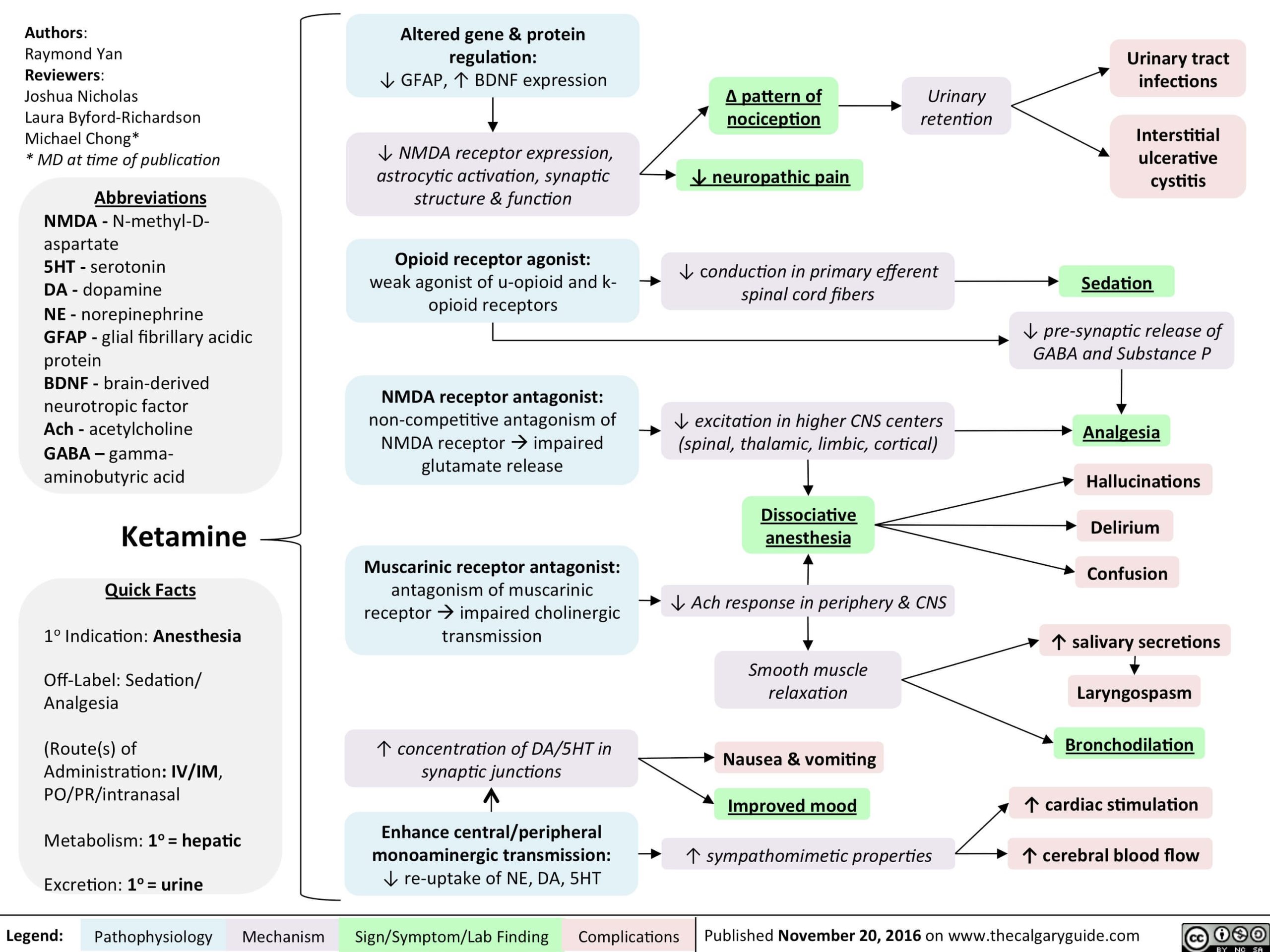
Talus Anatomy : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 0 : Attachments of muscles and tendons 1 : Sinus and Canal 2 : Processes and Tubercles 3 : Parts 4 : Blood vessels: 5 : Articulating surfaces
Management of Skeletal Tuberculosis – Principles
Classification Stage/Type Pott’s spine (Kumar’s) Pott’s paraplegia (Tuli) Hip and Knee Hip (Shanmugasundaram) I Predestructive (Straightening, spasm, hyperemia) Negligible (Objective plantar extensor response or ankle clonus) Synovitis (ROM 75-100%/Haziness, rarefaction)– Hip: FAbER, Apparent lengthening Normal (C) II Early destructive (Diminished space, paradiscal erosion, K<10) Mild (Subjective neuro-deficit but walks with…
Clavicle Fractures : Last Minute Revision
1. 80-85% are mid-shaft fractures (other 10-15% are lateral 3rd and 5% are medial 3rd fractures) because of: 2. Deforming forces: 3. X-ray views: 4. Allman classification: Dameron and Rockwood classification for lateral 1/3 pediatric fractures: Type I: Mild strains of ligaments or periosteal tears Type II: Complete disruption of…
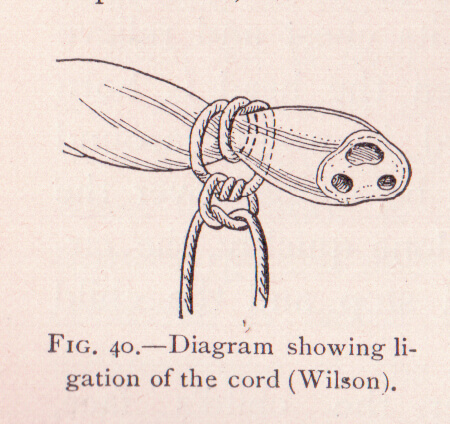
Lesions of the Umbilical Cord in Newborn
Anatomy of Umbilical Cord Umbilical cord is a connecting link between fetus and placenta through which fetoplacental circulation occurs. It is formed from allantois carrying vessels from Fetus to Chorion and passing abdominal stalk. It is around 50 cm long and contains 2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein surrounded by…
Heart Disease in pregnancy
Mortality risk associated with pregnancy Group I – Mortality <1% Group II – Mortality 5-15% Group III – Mortality 25-50% Commonest in Pregnancy Valvular heart disease: Mitral stenosis Congenital heart disease: ASD Cyanotic congenital heart disease: Fallot’s tetralogy (TOF) Predictors of Cardiac Events during Pregnancy N – NYHA Class >II…
Apt Test in Newborn: Maternal vs Neonatal Blood
We had few cases of suspected GI bleeding, admitted or referred to our NICU. One was case of Hematochezia and other was case of fresh blood in vomitus. Both babies were born to mother with Antepartum hemorrhage. The general condition of the babies were fine, and the vitals. There was…