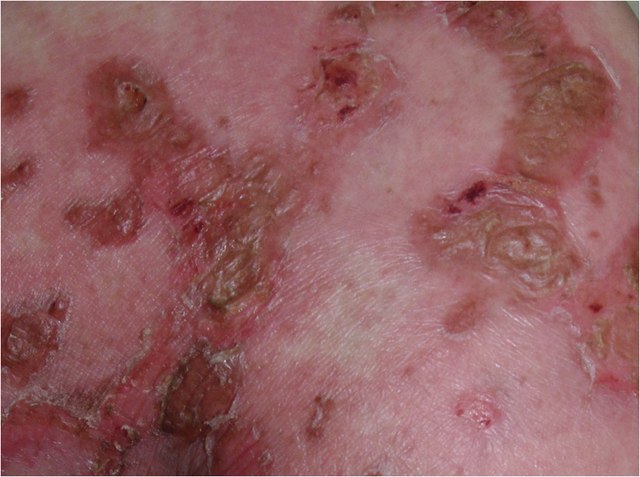
Glucagonoma is an alpha-cell tumor of pancreas. Mnemonic: 6 D’s 1. Diabetes 2. Dermatitis (Necrolytic migratory erythema) 3. Declining weight 4. Diarrhea 5. Deep vein thrombosis 6. Dilated cardiomyopathy
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
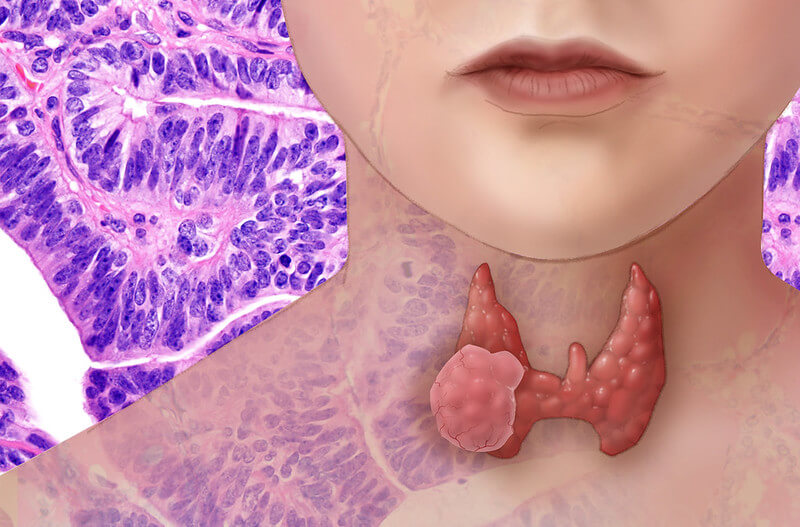
Thyroid Tumors : Mnemonics
Papillary carcinoma Follicular carcinoma Medullary carcinoma Mnemonic: MENACED Anaplastic carcinoma
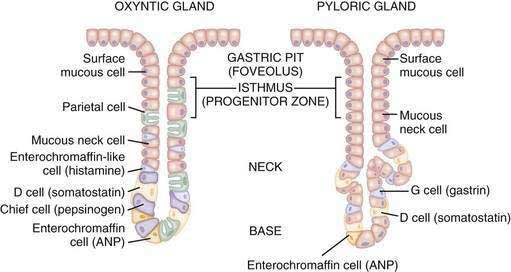
Gastric Acid Secretion in Parietal cells: Mechanism
Key player: H+/K+ ATPase or “proton pump” (in canalicular membrane of parietal cells) a. Hydrogen ions are generated within the parietal cell from dissociation of water. The hydroxyl ions formed in this process rapidly combine with carbon dioxide to form bicarbonate ion, a reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase. b. Bicarbonate…
ABG Interpretation Made Easy
Normal values Step 1: pH Step 2: pCO2 Step 3: HCO3- Step 4: Determine compensation If there is metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, determine if there is appropriate respiratory compensation: No respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 = Measured pCO2 Respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 ≠ Measure pCO2 Step 5: Delta ratio ΔAG /…
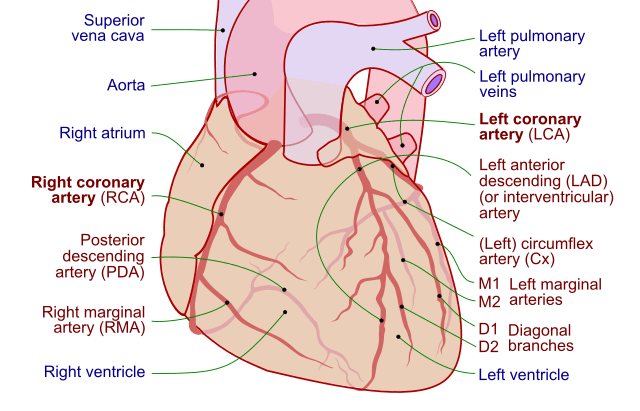
Coronary Arteries : Mnemonic
Right coronary artery (RCA) Course: Branches: Mnemonic: TRaP Me IN Large: Small: Left coronary artery (LCA) Course: Branches: Mnemonic: LaTe PAD Large: Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery – Small: Arterial supply of conducting system of heart 1. RCA: SA node, AV node, AV bundle 2. LCA: Right bundle branch of…
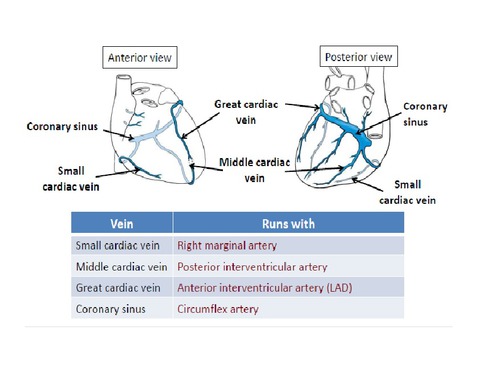
Venous Drainage of Heart : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: CAT 1. Coronary sinus (50%): Drains blood from left side of heart → Thebesian valve → Right Atrium 2. Anterior cardiac veins (20%): Drain blood from right side of heart → Right Atrium 3. Thebesian veins/Venae cordis minimi (30%): Drain deoxygenated blood from endocardium and myocardium → Respective chamber…
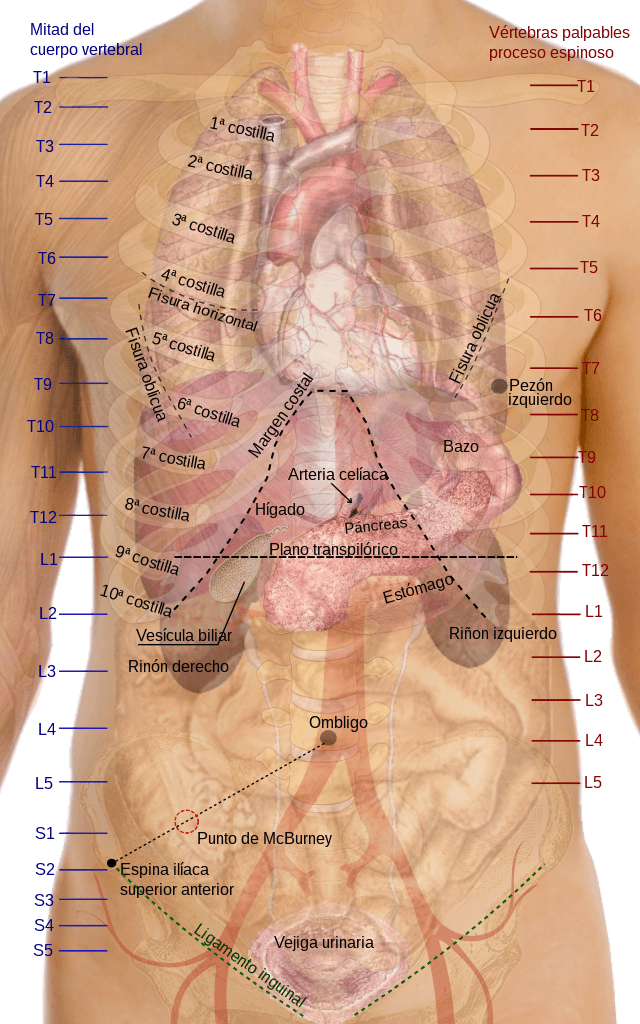
Transpyloric Plane : Mnemonic
Synonyms: Addison’s plane Definition: An imaginary horizontal line (halfway between suprasternal notch and pubic symphysis) through the L1 vertebra, a line that is important when performing radiographic imaging studies. Structures lying in transpyloric plane: Mnemonic: TRANSPYLORIC
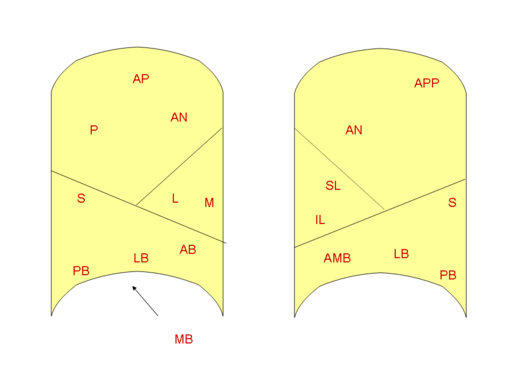
Bronchopulmonary segments : Mnemonic
Features of Bronchopulmonary segments: Right Lung Mnemonic: A PALM Seed Makes Another Little Palm (from top to bottom) 1. Superior lobe: 2. Middle lobe: 3. Inferior lobe: Left Lung Instead of lateral and medial segment as described in middle lobe of right lung, the left lung lingula has: Some books…