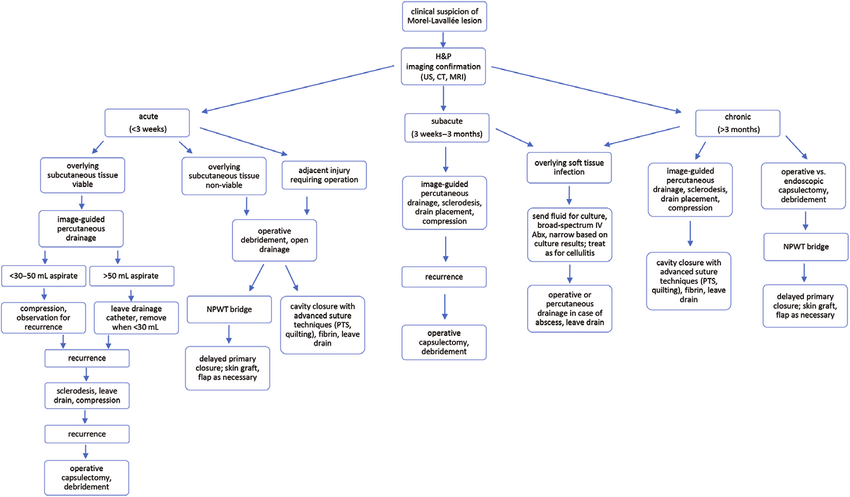
Definition: Post-traumatic closed degloving injury, in which the skin and subcutaneous tissue is detached from the underlying fascia by a shearing force which can disrupt perforating vessels and nerves, creating a potential space that fills with blood, lymph, debris and fat (necrotic and/or viable). Clinical features: The diagnosis can be…
Author: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MS Orthopedics
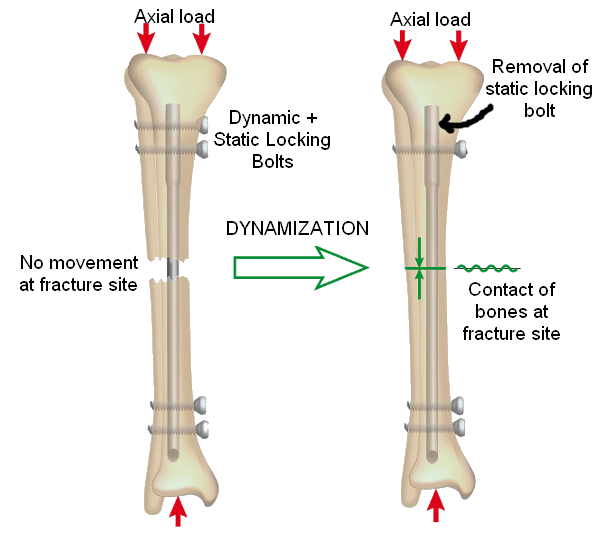
Intramedullary Nail Dynamization
Dynamization of intramedullary nail is the process of converting a static interlocking nail (provides better fixation & rotational control) to a dynamic locking nail (allows axial loading of fracture to stimulate bone healing). Dynamization converts a bridging mode of fixation to the splinting mode. Timing of Dynamization: Dynamization should be…
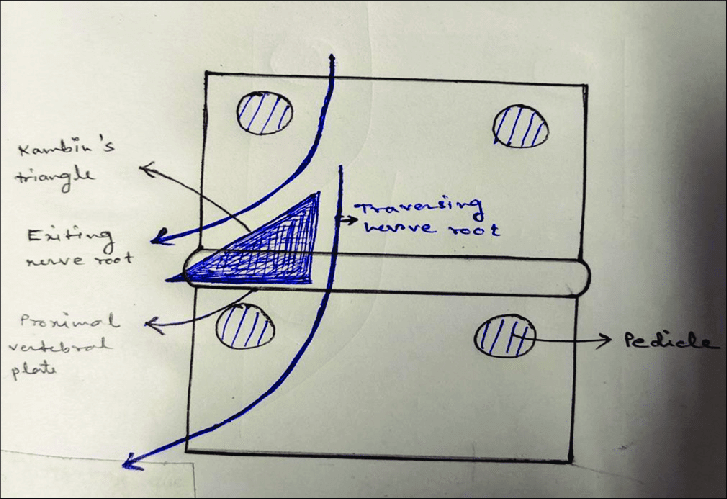
Kambin’s Triangle or Prism
There is confusion regarding the borders of Kambin’s triangle across the literature. Kambin originally described the borders of this triangular working zone as: Though it was named as a “triangle” it was described with 4 borders with 2 triangles (in AP view and Lateral view) which gives a 3D structure…
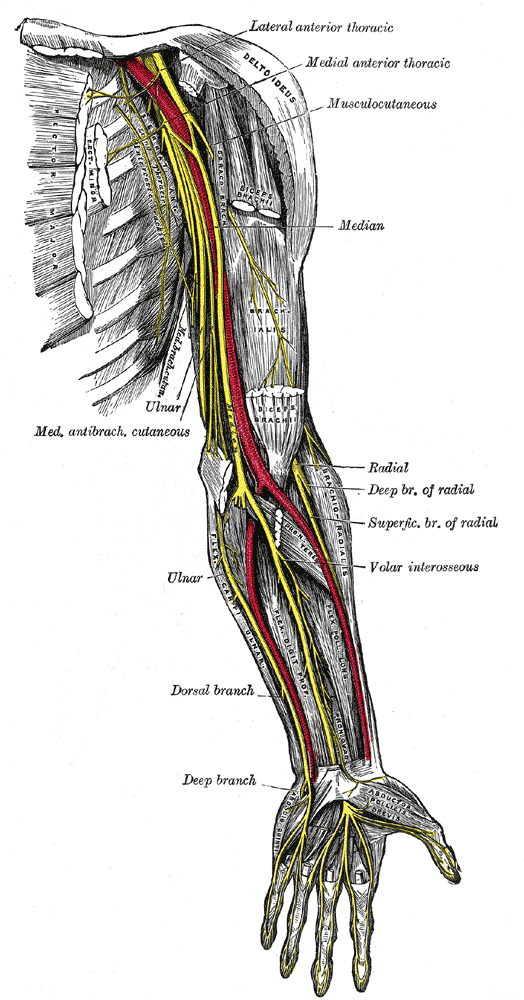
Lateral and Medial Pectoral Nerve : Mnemonic
Mnemonics a. Lateral is Less and Medial is More. b. Major receives 2 innervations and Minor receives 1 innervation. Hence, Lateral pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major. Medial pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major and minor. The lateral pectoral nerve and the medial pectoral nerve form…
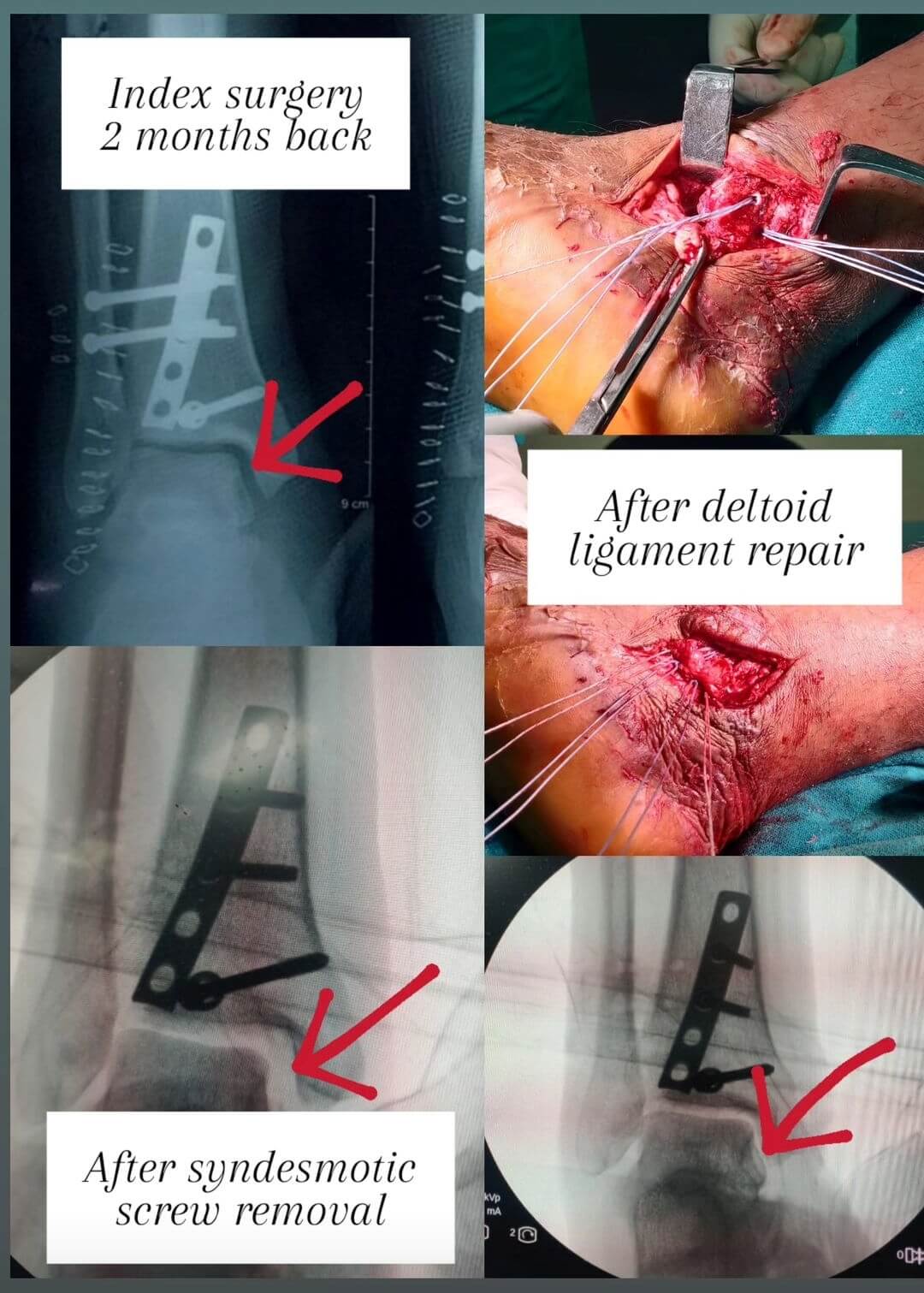
Deltoid Ligament : Anatomy, Clinical tests and Acute Injury
Deltoid ligament is the complex of medial collateral ligaments of the ankle joint. 2 layers of Deltoid Ligament a. Superficial layer: Originates from anterior and inferior aspects of medial malleolus fanning out & sending 3 bands to – b. Deep layer: Originates on posterior border of anterior colliculus, intercollicular groove…
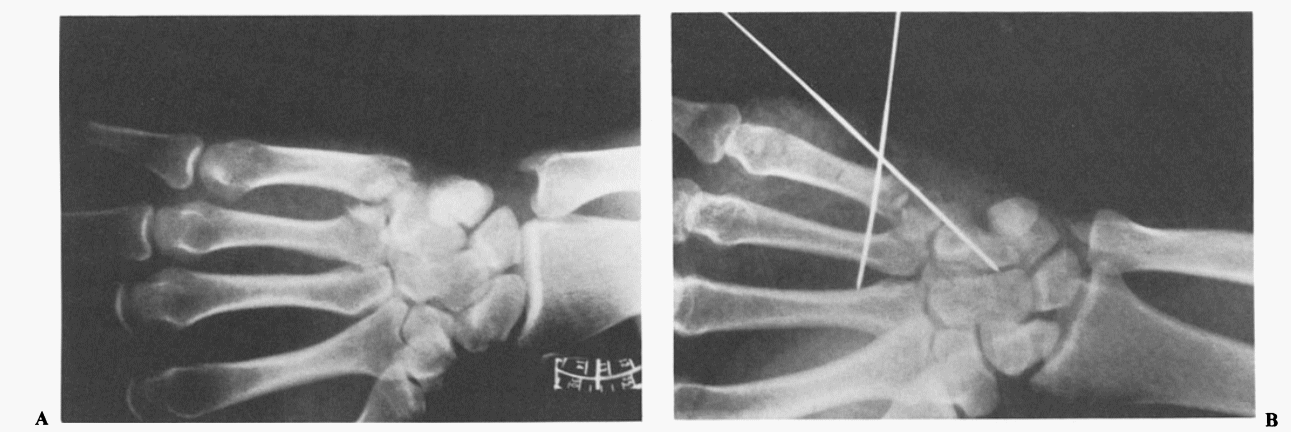
Reverse or Baby or Mirrored Bennett’s Fracture
Definition: The fracture-dislocation at the base of the fifth metacarpal analogous to Bennett’s fracture of the thumb Mechanism of injury: Muscle pull and displacement: Consequences of unreduced fracture-dislocation: Possible associations: X-ray views: Treatment: 1. Closed reduction and internal fixation with K-wires 2. Open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires or…
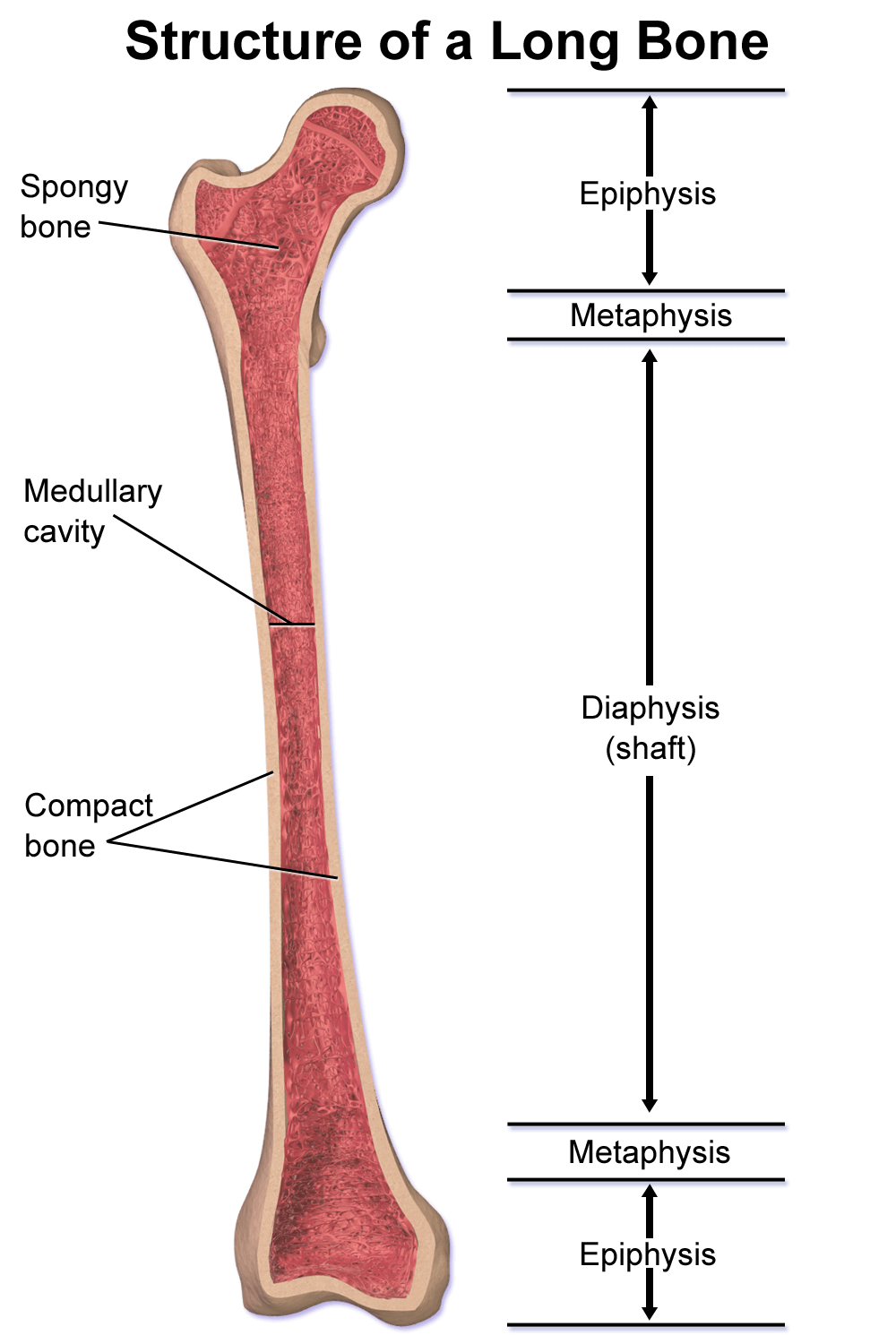
Metaphyseal lesions : Differential Diagnoses
Lesions Age Demographics Site Presentation Imaging Treatment Comments Acute Osteomyelitis Bimodal (<2 years and 8-12 years) M:F = 2:1 Distal femur, Proximal tibia Pain, refusal to bear weight, erythema, warmth, fluctuance, tenderness Lags 2 weeks behindDestruction of bone, periosteal reaction (lamellated, hair on end), new bone formation 1. Antibiotics2. Surgical…
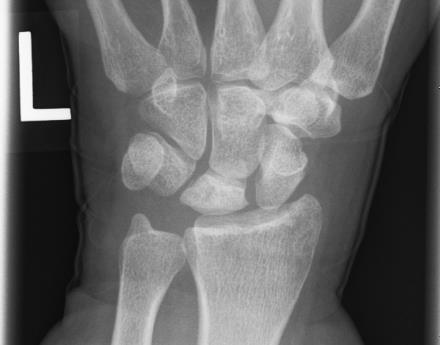
Kienbock’s Disease : Mnemonic Approach
Etiology Mnemonic: RSTUV Lichtman Classification and Management Stage Description Treatment Mnemonic: ABCD Mnemonic: ABCD I Abnormal MRI (decreased T1 intensity; variable T2 intensity) or scintigraphy Analgesics + immobilization II Bone sclerosis ± Bone breaks (fracture lines) Bony procedures:1. Negative or Neutral ulnar variance: Joint levelling procedure (Radius shortening osteotomy; Ulnar…