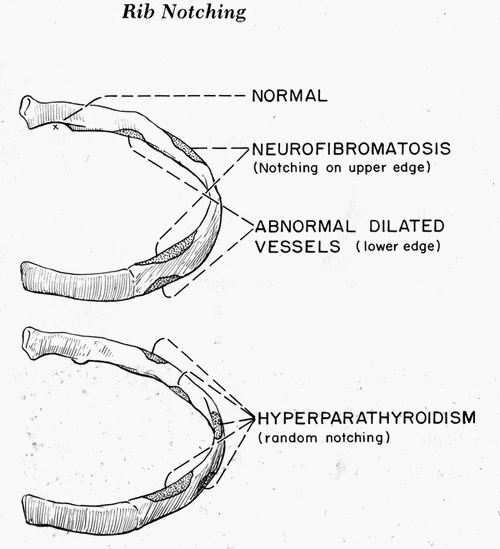
Normal Rib Notching A small notch near the costo-vertebral joint is normal, so pathologic rib notching is more likely if the notching is more lateral. Types of Pathological Rib Notching 1. Superior rib notching 2. Inferior rib notching (more common) Inferior Rib Notching (Roesler’s sign) Mechanism: Enlargement of one or…
Tag: Radiology
Silhouette and Cervico-thoracic sign
Synonyms: Obscured margin sign, Loss of outline sign Silhouette refers to the shadow and derived it’s origin from shadow papercuts done by Etienne de Silhouette. Principle of Silhouette sign On a normal Chest X-ray the well-defined borders of the heart and the domes of the diaphragm are visualised because the adjacent…
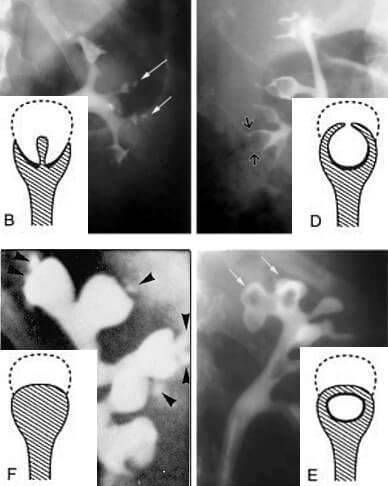
Ball-on-Tee, Lobster Claw and Signet Ring Sign – Renal papillary necrosis
Synonym: Necrotizing papillitis In renal papillary necrosis, part or all of necrotic renal papilla sloughs and may fall into the pelvicalyceal system, which may remain there (and get calcified) or may be voided down the ureter (often causing obstruction). The renal medulla and papillae are vulnerable to ischemic necrosis because…
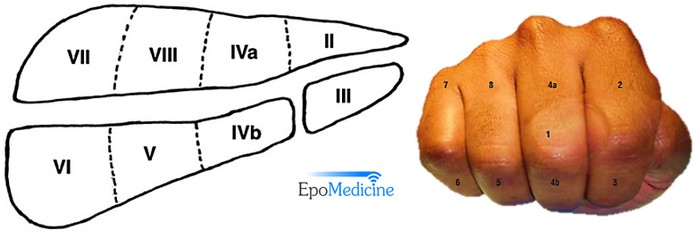
Liver Segments Explained with Mnemonic
Couniaud divided liver into 8 functional segments, each of which is supplied by it’s own portal triad (composed of a portal vein, hepatic artery and a bile duct). Hepatic veins divide the liver in saggital plane: 1. Middle hepatic vein: Divides the liver into right and left functional lobe. 2….
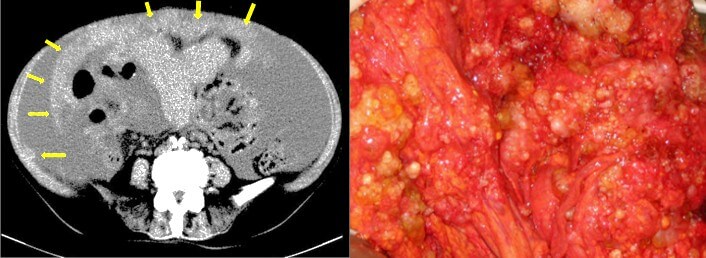
Omental Cake
Definition of Omental Caking Thickening of the omentum resulting from localized or diffuse infiltration of omental fat by soft tissue density mass is referred as “omental caking”. It is a radiological sign, which is often identified in CT scan. Involved Anatomical Structure in Omental Caking Greater Omentum – an extension of…
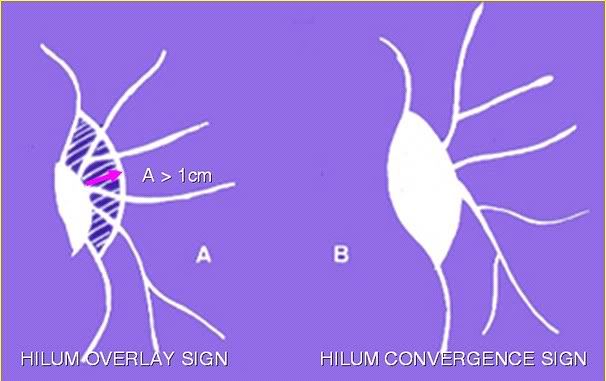
Chest Xray – Approach to hilum
Hilum in human anatomy refers to the depression where structures such as blood vessels and nerves enter an organ. The structures contributing to hilar shadows in a Chest X-ray are: Major: Pulmonary artery and veins Minor: Fat, Lymph nodes and Bronchial walls Normal Hilum: Position: Left hilum is slightly higher…
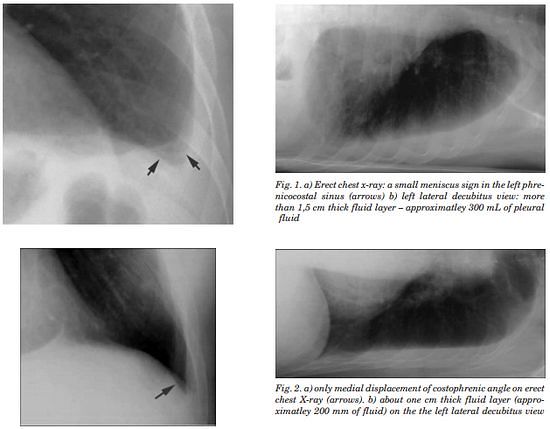
Chest X-ray – Pleural Effusion
Pleura is a mesothelial lined sac that envelopes the lungs and comprises of 2 membranous walls i.e. visceral pleura and parietal pleura that encloses pleural space filled with pleural fluid. Pleural space contains about 0.3 ml/kg body weight of pleural fluid. The pleura is not visible on a normal CXR…
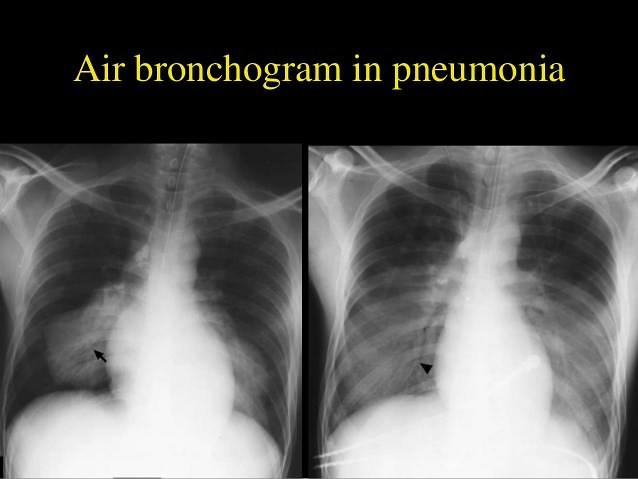
Chest X-ray: Alveolar vs Interstitial Disease
Interstitium is the scaffolding that supports the alveolar walls and surrounds both the alveoli and the terminal bronchioles. Neither alveoli nor interstitium is visible on a chest X-ray when normal. It is necessary to analyze whether the pattern of diffuse opacification in the lung field is alveolar or interstitial. Terms:…