Chronic paronychia is an inflammatory recalcitrant disorder affecting the nail folds. It can be defined as an inflammation lasting for more than 6 weeks and involving one or more of the three nail folds (one proximal and two lateral). Surgical management is only indicated in cases of chronic paronychia, which…
Tag: Plastic surgery
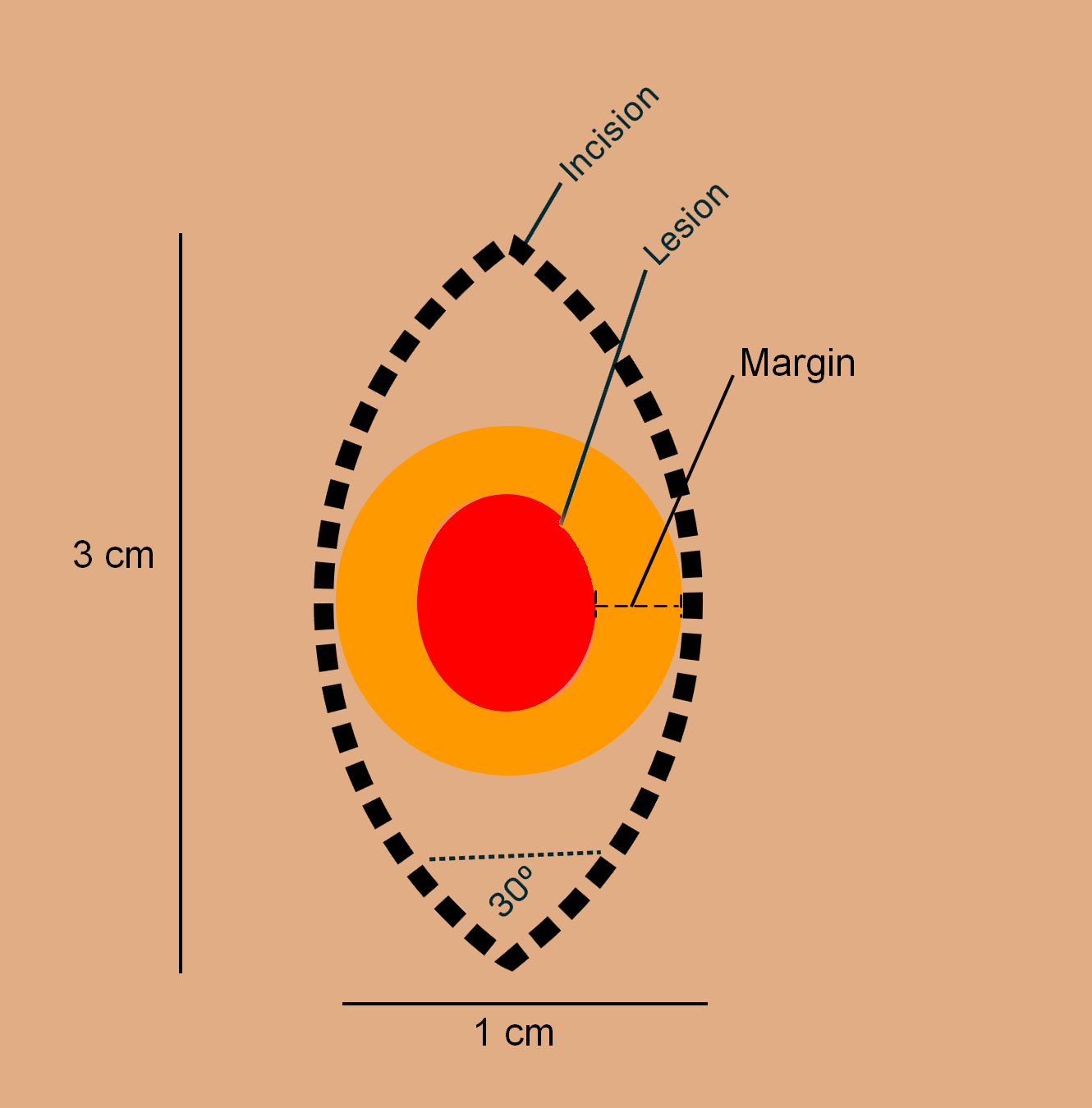
Geometry and Margins of Elliptical Excision
Ends of ellipse (Apical angles): Dimension of ellipse: Axis of ellipse: Margin of excision: Lesion type Surgical margin Uncertain Consider shave or punch biopsy to delineate prior to elliptical excision or start with 1- to 2-mm margins to avoid unnecessary tissue removal. Benign Visible lesion removed BCC 3–5 mm SCC 3–6 mm…
Hypertrophic Scar vs Keloid
Hypertrophic scars and keloids are both raised, firm scars formed from excess fibrinogen production and collagen during healing. Mnemonic: BAD SCARS Mnemonic Basis Hypertrophic scar Keloid B Behavior Natural regression No spontaneous regressio A Acuteness Appears in weeks Appears over months to years D Demographic All races affected More prevalent…
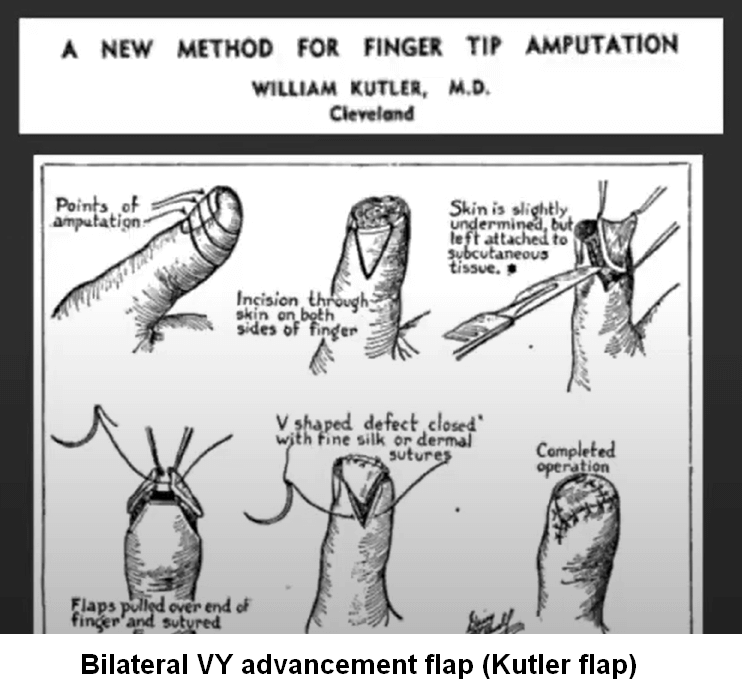
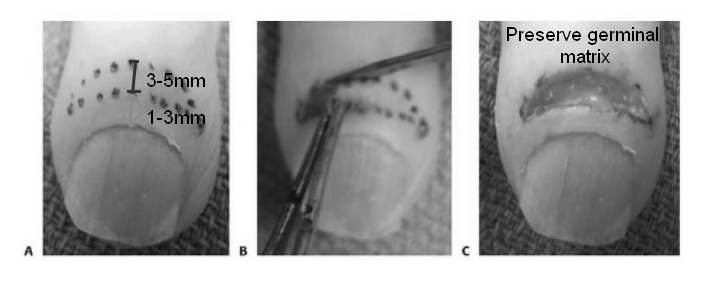
Bilateral V-Y (Kutler) flap for finger stump closure
Indications Classically, this flap is indicated in patients with transverse or volar oblique amputations. In actuality, the patient in whom this flap is useful generally will have an amputation where there is more tissue on the radial and ulnar margins of an amputation and exposed distal phalanx. Limitations Generally, the…

Aberdeen Knot
To end continuous suture, either a square knot, surgeon’s knot or an Aberdeen knot is required. The Aberdeen knot has been shown to be superior to a surgeon’s knot. Recommendations on number of throws: Technique/Steps:
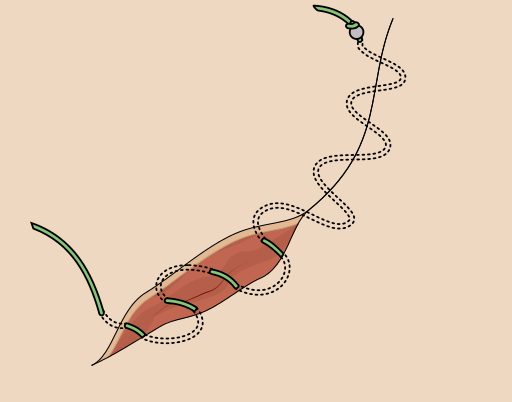
Running subcuticular suturing
1. Start with a buried knot at distal apex of the wound. 2. Take a bite deep to the epidermis that should curve parallel to the skin surface and exit in the same plane approximately 5-10mm along the wound, taking care to stay at the same level. 3. Continue step…
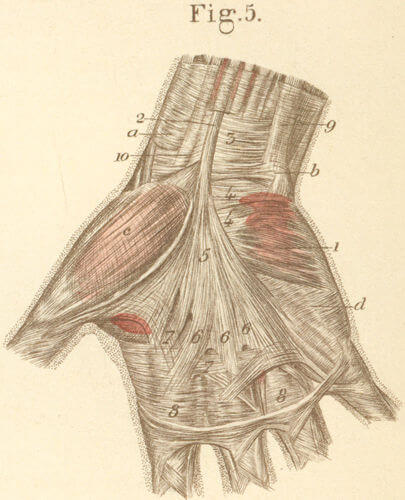
Palmar Aponeurosis or Fascia
5 components a. Central aponeurosis It is triangular in shape with apex originating at the level of flexor retinaculum as a continuation of palmaris longus and thins and fans out distally. It has 3 dimensional fiber orientation: longitudinal, transverse and vertical 1. Longitudinal: Gives 4 pre-tendinous band (PTB) in the…
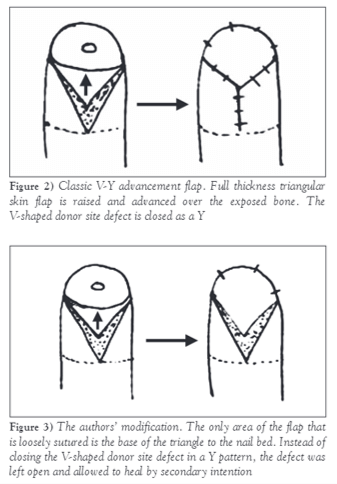
Volar V-Y advancement flap for fingertip amputations
Indications Contraindications Advantages Disadvantage Tension (maximum tension occurs in mid portion of the defect) especially with large defects Blood supply of flap Oblique terminal branches of the digital arteries arising from the trifurcation of distal interphalangeal joint (a subcutaneous pedicle flap) Technique References: