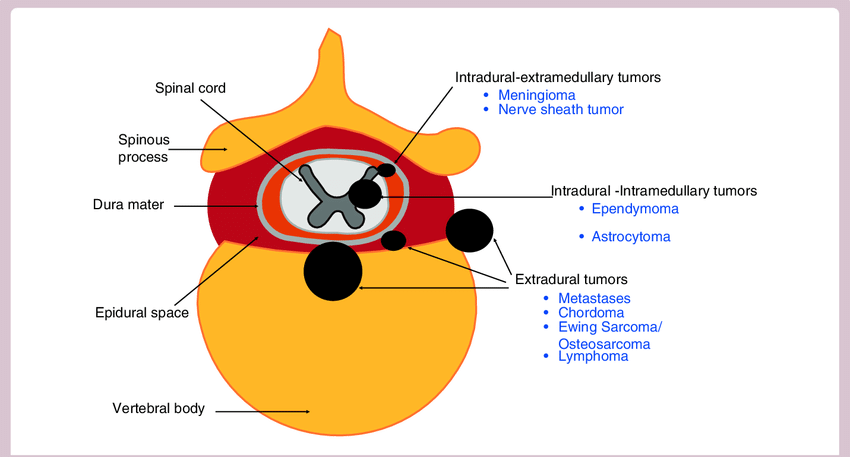
Intradural Intramedullary Spinal Tumors Mnemonic: I HEAL Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumors Mnemonic: MNM Extradural Spinal Tumors Lesions outside the thecal sac are categorized as extradural lesions. Remember that everything that isn’t in the thecal sac is extradural, including discs, bones, nerves, and blood vessels.
Tag: Orthopedics
Section Editor: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MBBS, PGY1 Orthopedics
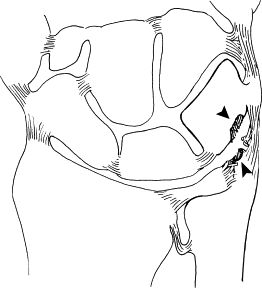
Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome
Definition: Impaction of triquetrum against the ulnar styloid causing chondromalacia, synovitis and ulnar-sided wrist pain Pathology: Etiology: Clinical features: 1. Asymptomatic 2. Ulnar-sided wrist pain, aggravated by wrist extension and specific positioning (having hands on hip or back pockets) 3. Potential history of trauma to distal radius or ulna, surgery…
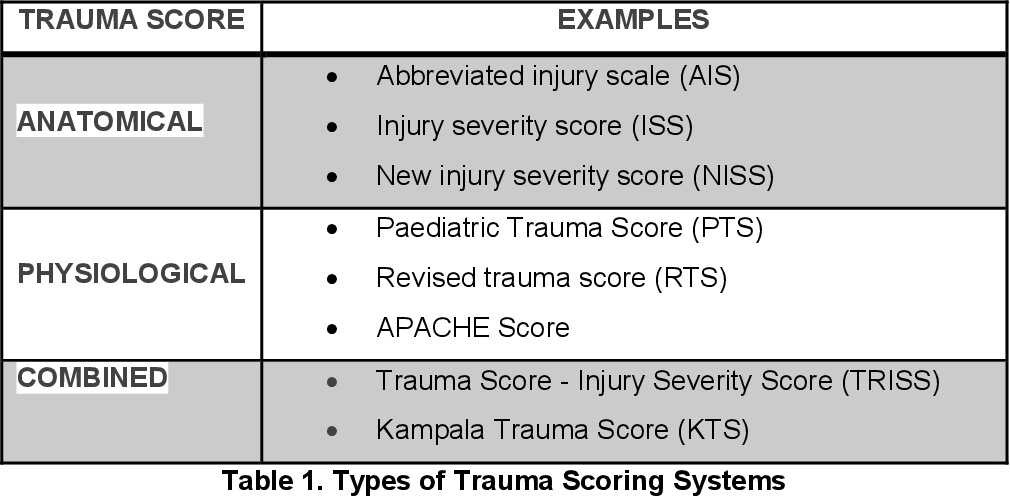
Trauma Scoring Systems
Scoring systems Score type Brief description Score interpretation Revised trauma score (RTS) Physiologic RR + SBP + GCS Each parameter is scored 0-4 (Total range = 0-12) Lower score indicates more severe injury (RTS 12 = <1% mortality; RTS 0 = >99% mortality) Score <11 – transfer to trauma center…
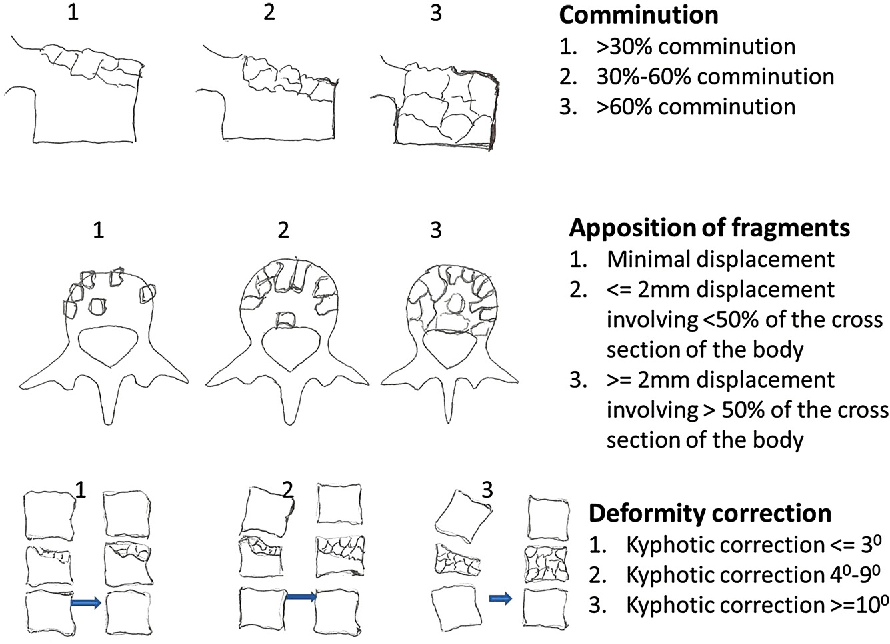
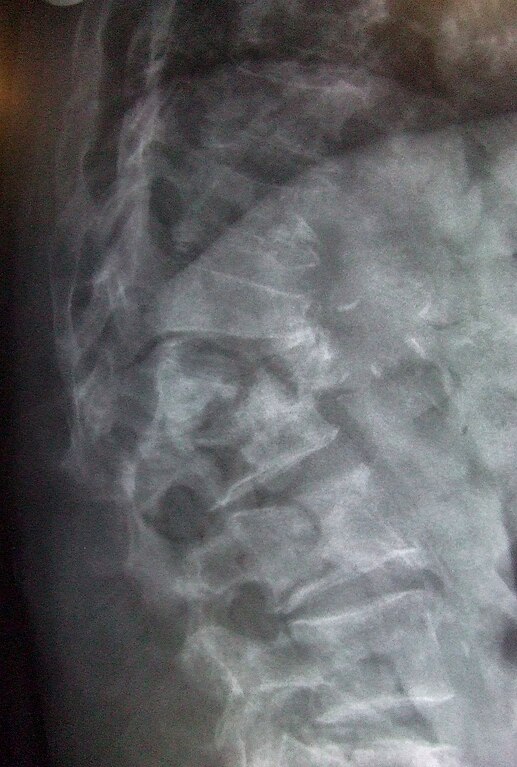
McCormack Load Sharing Classification (LSC)
McCormack classification aims to predict the need for anterior stabilization in addition to posterior fixation in cases of thoracolumbar burst fractures. It considers 3 factors for scoring: Principle: Application of load-sharing principle of long bone fixation (load sharing between implant system and host bone) to surgical treatment of acute thoracic…
TLICS vs SLICS
Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity (TLICS) and Subaxial Cervical Spine Injury Classification System (SLICS) are based on 3 components of injury: TLICS score and SLICS score provide a scoring system to guide management: Characteristics TLICS SLIC 1. Injury morphology (Radiographs, CT) a. No abnormality 0 0 b. Compression 1 1…

Rheumatoid Thumb – Nalebuff Classification
Type Description Treatment 1 Boutonniere (most common) Synovectomy with extensor hood reconstruction; MCP fusion or arthroplasty 2 Boutonniere with CMC subluxation (uncommon; Type 1 + Type 3) Same as type 1 and type 3 3 Swan neck deformity (2nd most common) Splinting vs CMC arthroplasty; MCP fusion 4 Gamekeeper deformity…
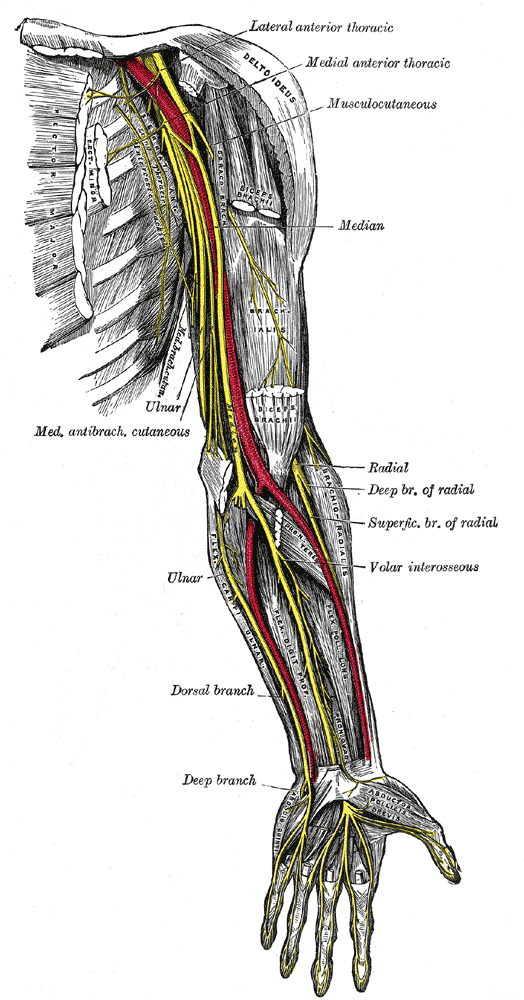
Lateral and Medial Pectoral Nerve : Mnemonic
Mnemonics a. Lateral is Less and Medial is More. b. Major receives 2 innervations and Minor receives 1 innervation. Hence, Lateral pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major. Medial pectoral nerve passes through and supplies Pectoralis major and minor. The lateral pectoral nerve and the medial pectoral nerve form…
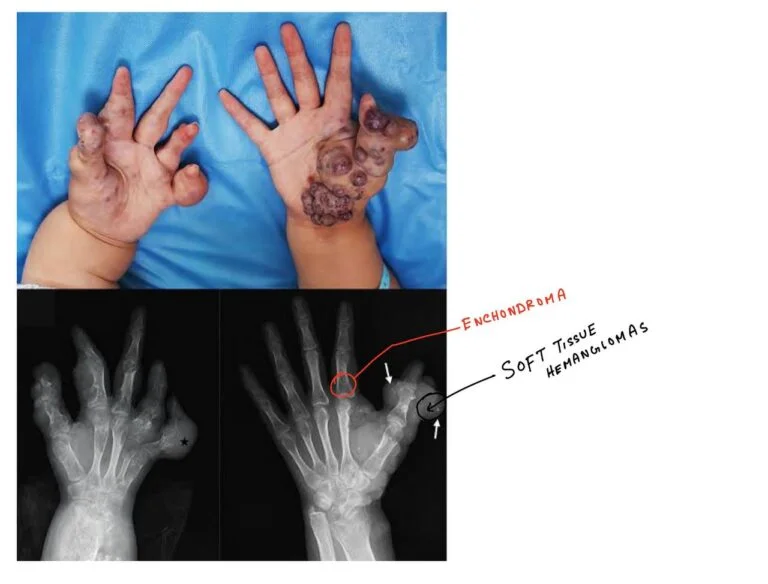
Ollier’s Disease and Maffucci Syndrome : Mnemonic
Ollier’s disease Maffucci syndrome