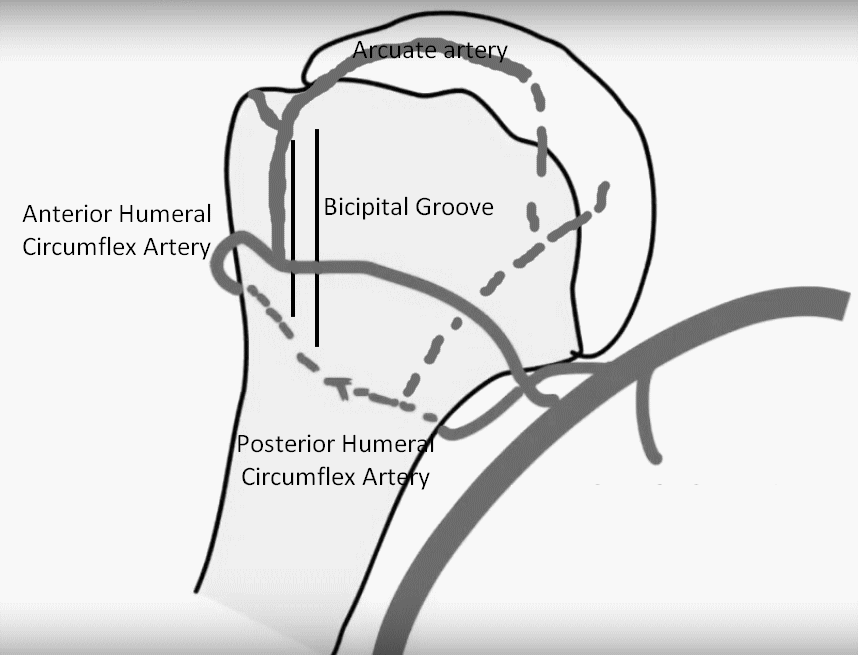
Anterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (AHCA) Origin: Axillary artery Course: Along the inferior border of subscapularis Gives anterolateral ascending branch which courses along lateral aspect of bicipital groove entering the humeral head and becoming arcuate artery Continues posterolaterally to anastomose with Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (PHCA) Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (PHCA)…
Tag: Musculoskeletal system
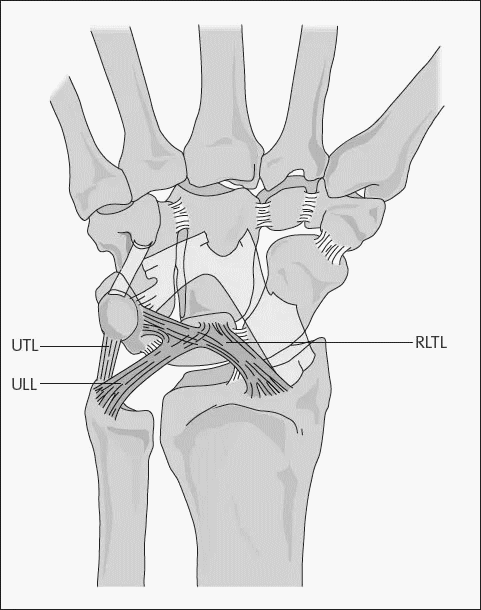
Wrist Ligaments
a. Interosseous: Extend deeply, directly between two bones Radioscapholunate (RSL) aka Ligament of Testut (neurovascular conduit to SL ligament) Scapholunate (SL) and Lunotriquetral (UL) – volar, dorsal and proximal fibrocartilaginous membrane components Capitohamate (CH) b. Palmar-proximal V: Converge as an “upside-down V” from the radius/ulna to lunate Radio-luno-triquetral (RLT) –…
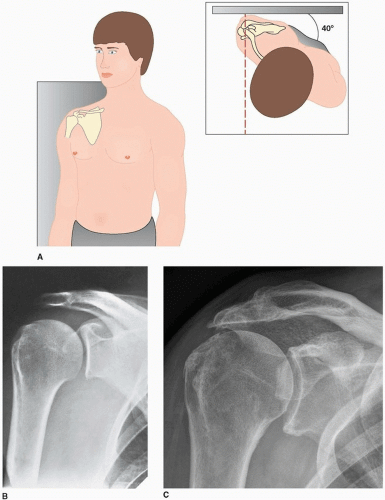
Shoulder X-ray views
Shoulder X-ray views AP Shoulder: in plane of thorax AP in plane of scapula: Angled 45 degrees lateral Scapular Y lateral: Erect with opposite shoulder rotated 40 degrees out and beam centered on spine of scapula (shoulder dislocations and scapula fractures) Supraspinatus outlet view: Scapular Y view with beam caudally…
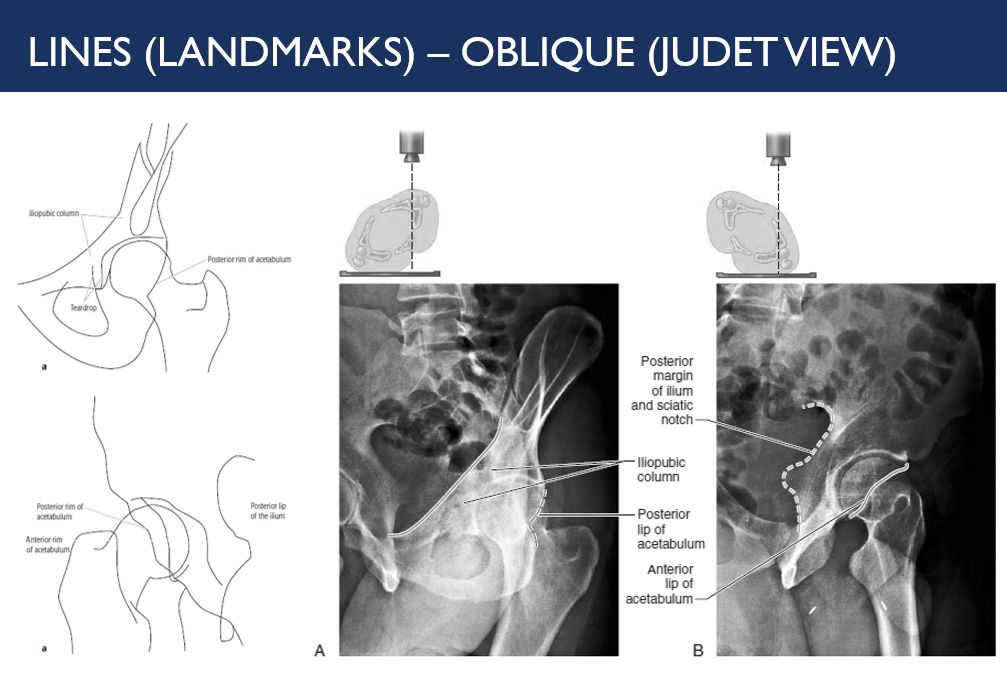
Pelvis X-ray : Simplified Approach
Views AP pelvis: patient supine and the x-ray beam oriented 90 degrees to the patient’s long axis, passing through the patient from anterior to posterior Pubic symphysis and coccyx in straight line in middle of screen with 1-3cm between superior pubic symphysis and tip of coccyx Greater and lesser trochanters…
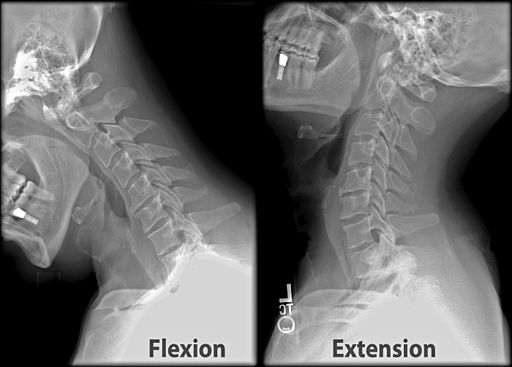
C-spine X-ray : Mnemonic Approach
Mnemonic: ABCDEF For images of the particular Cervical spine (C-spine) X-ray findings and views mentioned below, please refer to the links at the end of the article or use web-search. Adequacy Skull base, C1-C7 and upper T1 must be visible 3 views: True lateral, AP, Odontoid (Open mouth) +/- Swimmer’s…
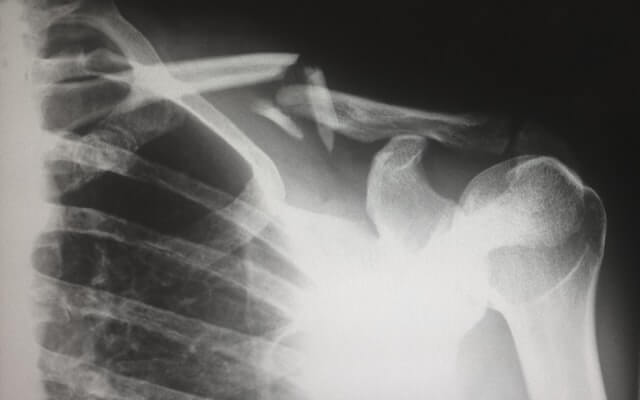
Complications of Fractures
This is a tabulated compilation for complications of fractures in general which can be immediate, early or delayed and local or generalized/systemic. This topic is commonly tested in exams. Local Systemic Immediate 1. Soft tissue injuries (Skin, Nerve, Vessels, Muscle-tendon) 2. Physeal injury 3. Hemarthrosis 4. Local visceral injury 1….
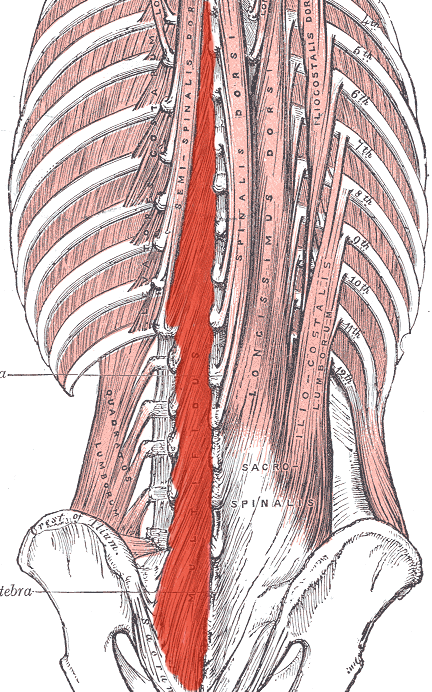
Muscles of Back – Simplified
A. Superficial Group (Appendicular group) Arise from vertebral column and attach to shoulder (assist in movement of limbs) a. Most superficial: Trapezius (From external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae and spinous process C7-T12) Latissimus dorsi (From spinous process T7-T12, thoracolumbar fascia and iliac crest) b. Covered by trapezius: Levator scapulae (From…
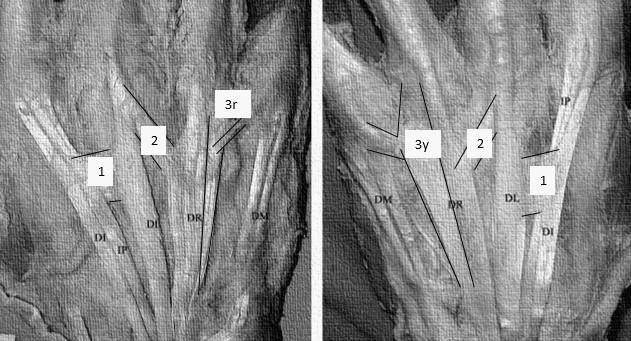
Juncturae Tendinum
Synonyms: Connexus intertendinei, Intertendinous connections Plural: Juncturae tendinae Location: Intermetacarpal spaces in dorsum of hand between the extensor digitorum tendons Morphologic types: The usual pattern is that it gets thicker from radial to ulnar side. Type 1: Thin filamentous (square, rhomboidal or triangular) – present only in 2nd metacarpal space…