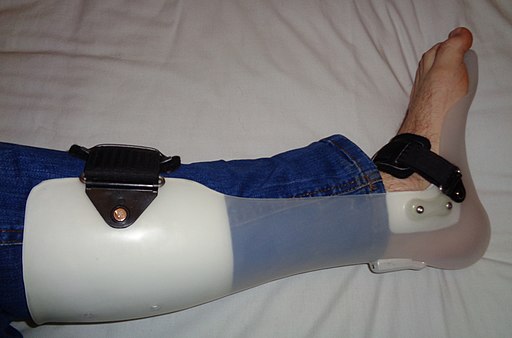
Foot drop can result from: L5 radiculopathy Lumbar plexopathy Sciatic neuropathy Peroneal neuropathy Causes Disc herniation, Spinal canal stenosis Pelvic surgery, hematoma, prolonged labor Hip surgery, Injection injury Compression/trauma Motor Weakness includes muscles and hip abductors Weakness includes hip abductors and anal sphincter Weakness includes tibial and hamstring muscles Weakness…
Tag: Internal medicine

How to check an Error in ABG ? ABG analysis
Sometimes, clinicians might find ABG result not matching with the patient condition. These results might arise from technical errors in machine and there are certain points which can be used to check the error. How to Check whether ABG result is Right or has Error? X= 24X PaCO2/HCO3 Y= 80-…
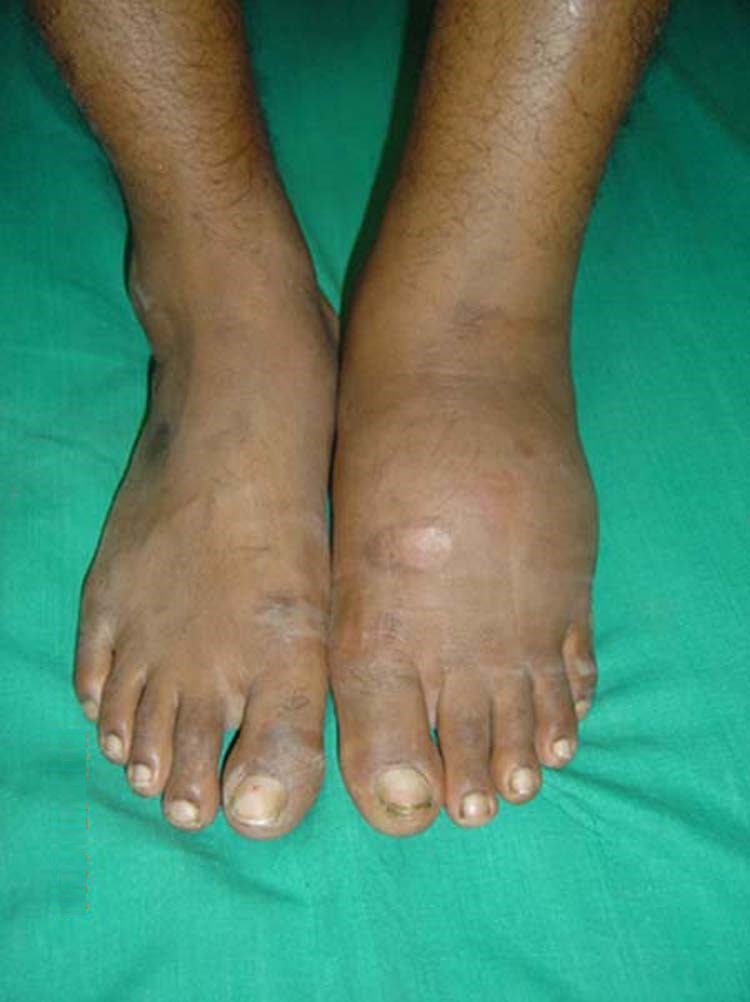
Charcot Arthropathy : Mnemonics
Causes of Charcot Arthropathy Mnemonic: 10 S 3 Theories of Charcot Arthropathy a. Neuro-traumatic: Damage to sensory feedback → Repeated microtrauma → Release of proinflammatory cytokines → Bone resorption b. Neuro-vascular: Change in vascularity caused by dysregulation of vasomotor and trophic nerve supply c. Neuro-inflammatory: Abnormal persistence of inflammatory response…
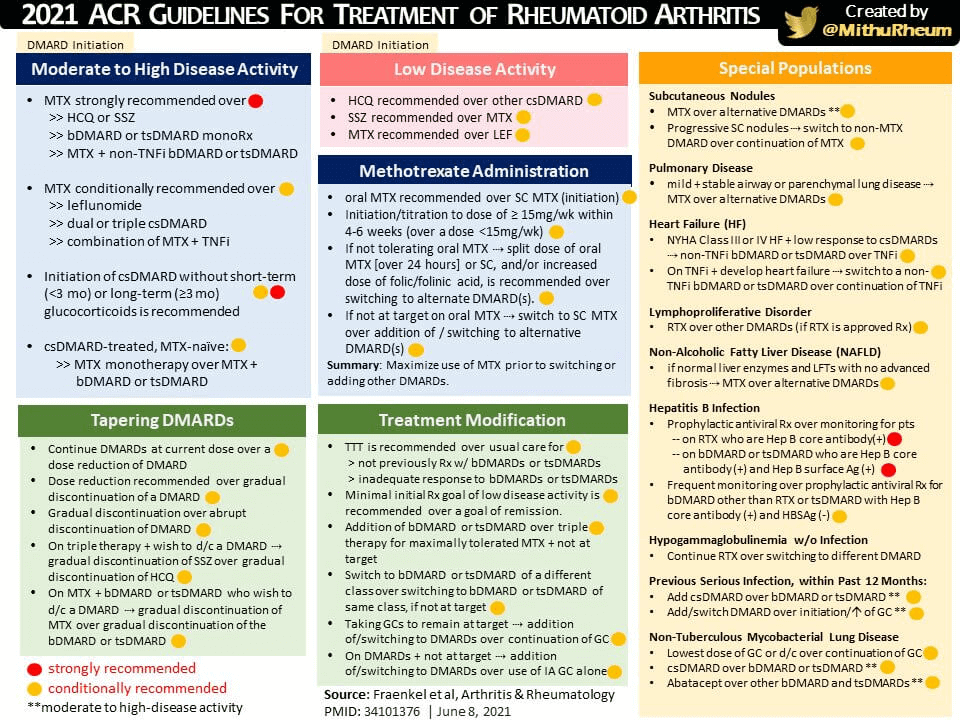
Rheumatoid Arthritis – ACR 2021 Guidelines: Summary
Among various methods of measuring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis, we will be discussing Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI). CDAI = TJC(28) + SJC(28) + PGA(10) + EGA(10) Interpretation of CDAI: CDAI Score Range Disease Severity ≤ 2.8 Remission > 2.8 – 10.0 Low > 10.0 – 22.0 Moderate >…
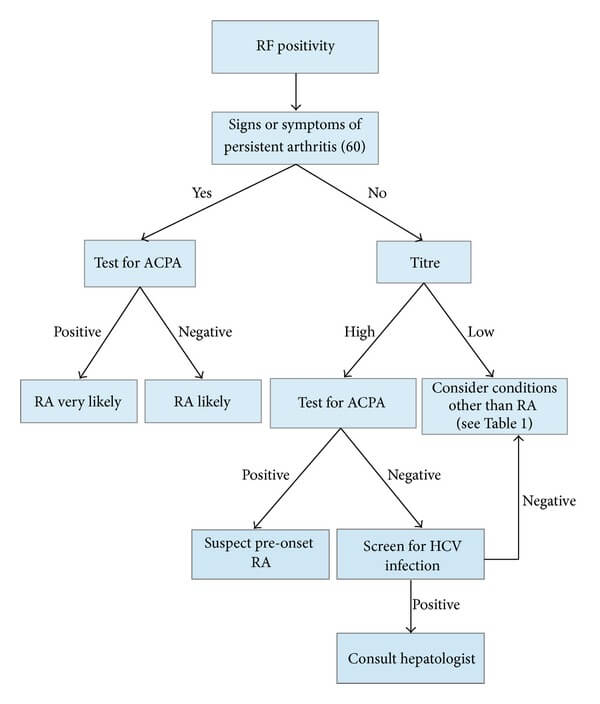
Approach to Rheumatoid Factor Positive test
Rheumatoid factor (RF; also mistakenly called RA factor) is an auto-antibody (commonly IgM and rarely IgG or IgA) directed against the Fc portion of IgG. Increase in both IgM and IgA RFs is almost exclusively observed in patients with RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis). Clinical Significance of Rheumatoid Factor 1. A positive…
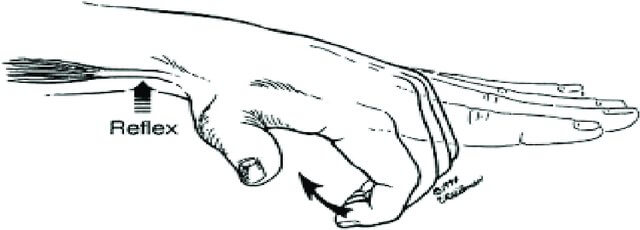
Inverted Reflexes
An inverted tendon reflex refers to the elicitation of the movement opposite to that normally seen when the reflex is elicited. Mechanism of Inverted Reflexes A lesion which simultaneously affects: This leads to 2 components: Mechanisms of hyperactive response: Types of Inverted Reflexes 1. Inverted supinator reflex: 2. Paradoxical triceps…
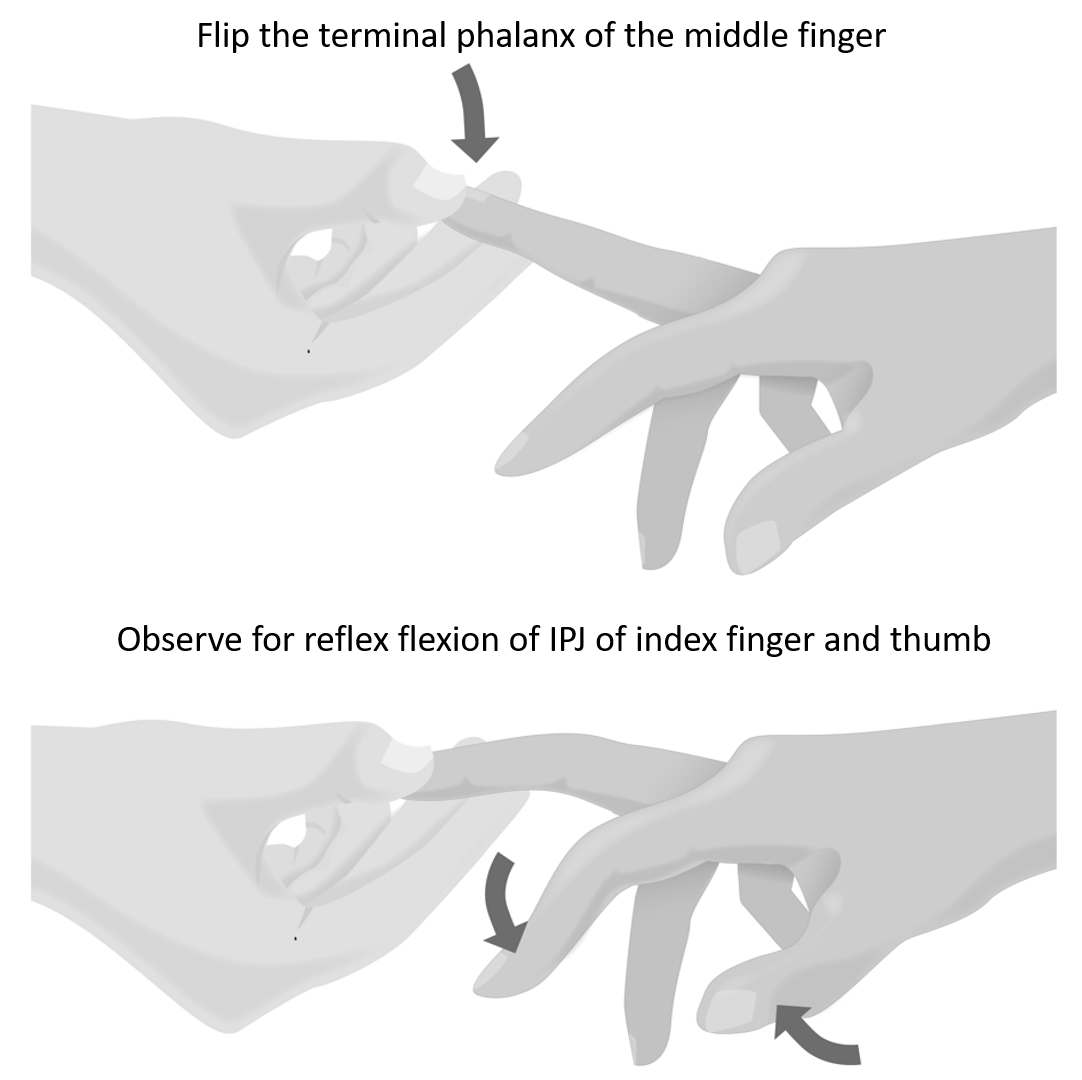
Hoffmann’s Sign
History Method of Eliciting Hoffmann’s Reflex Mechanism of Positive Hoffmann’s Reflex Sudden stretch of the finger flexors causes involuntary finger flexor contraction due to activation of a monosynaptic stretch reflex. Exaggeration of the reflex is caused by hyperreflexia in the setting of upper motor neuron dysfunction. Upper motor neuron lesions…

Friedreich’s Ataxia : Mnemonic
Friedreich’s ataxia is a hereditary spinocerebellar degenerative disorder named after German neurologist, Professor Nicholaus Friedreich. Mnemonic: FRIEDREICH’S Ataxia 1. Foot deformity (progressive cavo-varus), Frataxin expression reduced 2. Recessive (autosomal), Repeat of trinucleotide GAA (chromosome 9) 3. Iron accumulation in mitochondria 4. Extensor plantar response 5. Dysarthria (within 5 years of…