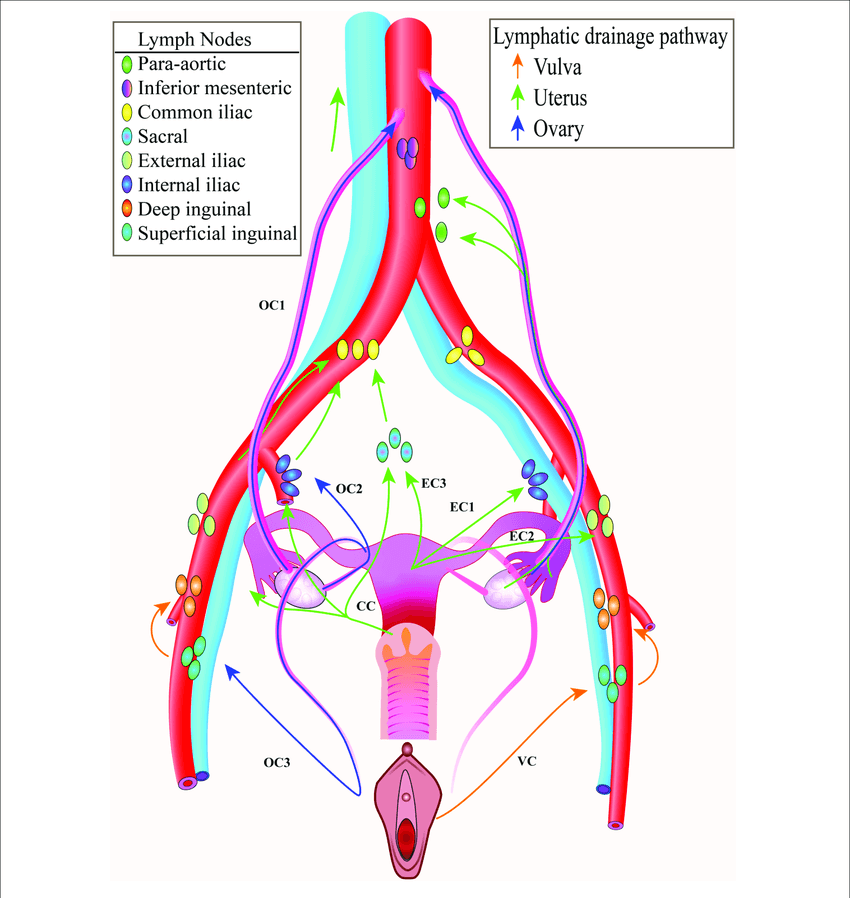
1. Para-aortic (lumbar) nodes: Gonads (derive blood supply from kidneys) 2. Inferior mesenteric nodes: As of blood supply – to the structures derived from hindgut 3. Common iliac nodes: Receives external and internal iliac nodes; Drains into para-aortic nodes 4. Superficial inguinal nodes: Everything that can be touched with fingers…
Tag: ObGyn
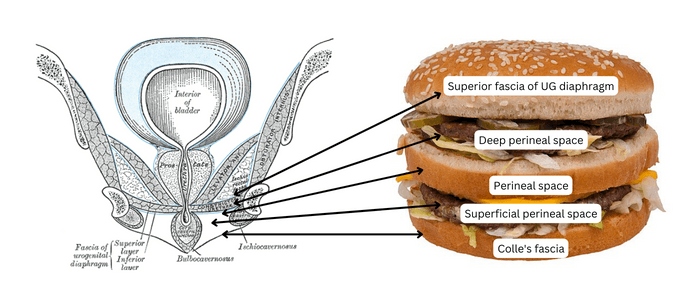
Superficial and Deep Perineal Space or Pouch
Superficial and deep perineal space is located in the urogenital triangle, the boundaries of which are: Analogy: Remember a big mac. It has 3 layers of BUN and 2 hamburger PATTIES. Posteriorly, all 3 Fascias are attached to the perineal body, closing the spaces. Superficial Perineal Space Mnemonics: 1. Superficial…
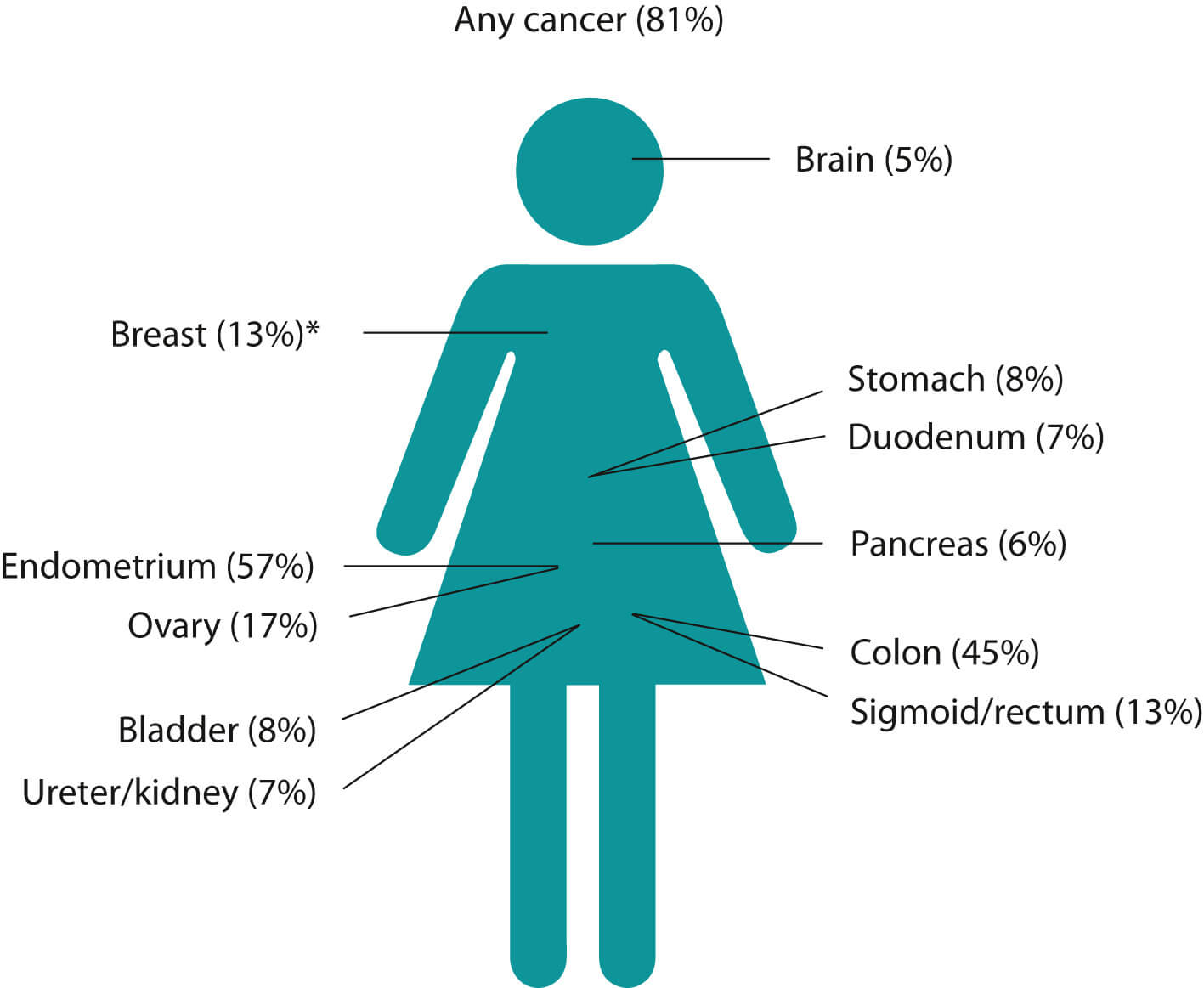
Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC) : Mnemonics
Inheritance: Autosomal Dominant (AD) Cause: Microsatellite instability (MLH1, MSH2 mismatch repair gene mutation) Types: Amsterdam II Criteria for Diagnosis Mnemonic: 3-2-1-0 rule Colorectal cancers: More likely to be mucinous and right-sided Treatment: Total colectomy with ilio-rectal anastomosis Annual screening: Age 25 onwards or beginning no later than 5 years before…
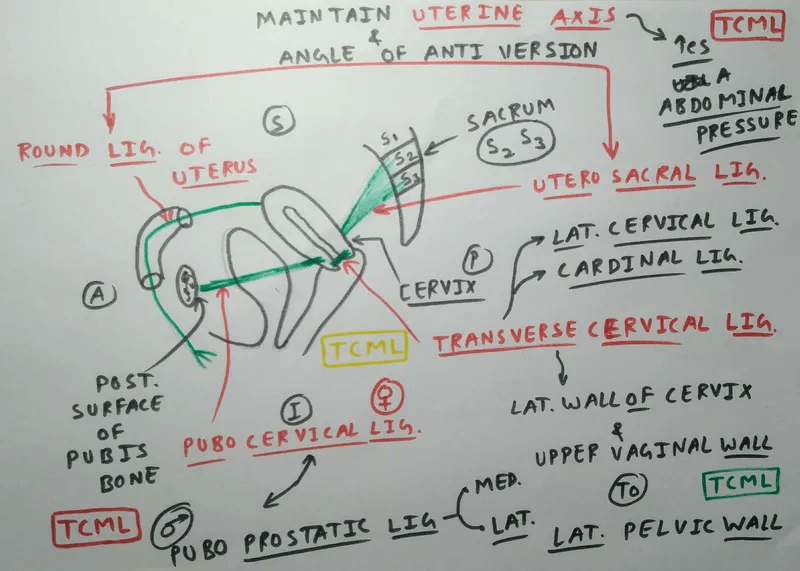
Supports of Uterus : Mnemonic
Primary Supports 1. Mechanical Support Mnemonic: 3 A 2. Muscular/Active Support Mnemonic: Muscle PULLs 3. Ligamentary Support Mnemonic: Ligaments hold uterus like CUP Cardinal ligament + Pubocervical ligament = Triradiate ligament Secondary supports (Peritoneal folds) Mnemonic: RUB

Aberdeen Knot
To end continuous suture, either a square knot, surgeon’s knot or an Aberdeen knot is required. The Aberdeen knot has been shown to be superior to a surgeon’s knot. Recommendations on number of throws: Technique/Steps:
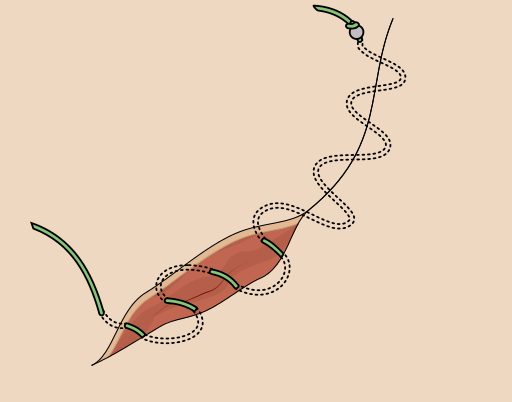
Running subcuticular suturing
1. Start with a buried knot at distal apex of the wound. 2. Take a bite deep to the epidermis that should curve parallel to the skin surface and exit in the same plane approximately 5-10mm along the wound, taking care to stay at the same level. 3. Continue step…
Heart Disease in pregnancy
Mortality risk associated with pregnancy Group I – Mortality <1% Group II – Mortality 5-15% Group III – Mortality 25-50% Commonest in Pregnancy Valvular heart disease: Mitral stenosis Congenital heart disease: ASD Cyanotic congenital heart disease: Fallot’s tetralogy (TOF) Predictors of Cardiac Events during Pregnancy N – NYHA Class >II…
Apt Test in Newborn: Maternal vs Neonatal Blood
We had few cases of suspected GI bleeding, admitted or referred to our NICU. One was case of Hematochezia and other was case of fresh blood in vomitus. Both babies were born to mother with Antepartum hemorrhage. The general condition of the babies were fine, and the vitals. There was…