A) HISTORY Besides chief complaints, other portion of history is similar to the one you prepare in internal medicine. 1. Description of symptom (SOCRATES): S – Site (Unilateral or Bilateral) O- Onset C – Character R – Radiation (if applicable) A – Aggravating and relieving factors T – Timing and…
Tag: Clinical examination
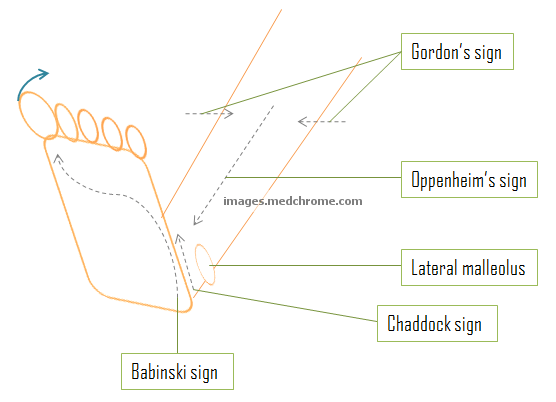
Pathological reflexes – Variations of Babinski
Normally, the pathological reflexes are not evident because they are suppressed by cerebrum at brainstem or spinal cord level by 6 months of age. Importance: Up-going (dorsiflexion) toe can be elicited at various sites and all indicated Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) lesion. Use a blunt-pointed object like fingernail or tip…
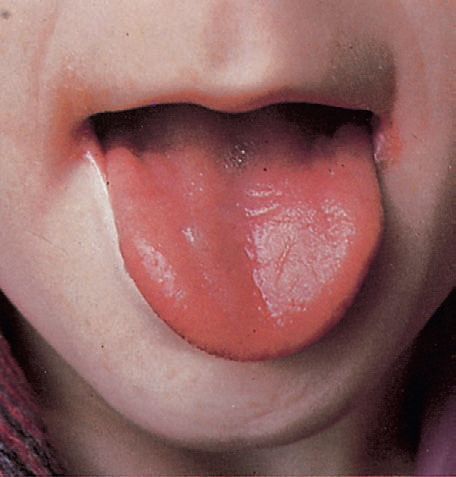
Hematological Signs – Angular Stomatitis and Atrophic Glossitis
ANGULAR STOMATITIS/CHEILITIS Definition: Maculopapular and vesicular lesions grouped on the skin at the corners (or ‘angles’) of the mouth and the mucocutaneous junction. It is made worse by licking the lips. Causes: 1. Oral candidiasis 2. Poorly fitting dentures 3. Bacterial infection 4. Less common Nutritional deficiencies (especially riboflavin, iron and pyridoxine) Iron…
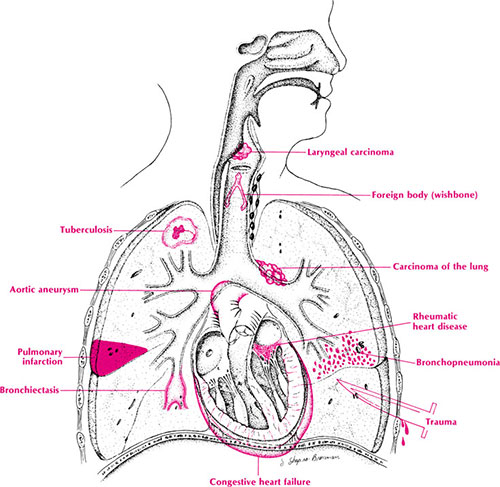
Hemoptysis – Examination and Evaluation
Synonym: Haemoptysis Definition of Hemoptysis Simple definition: Expectoration of blood or bloody sputum Hemoptysis is defined as the expectoration of blood from the respiratory tract, a spectrum that varies from blood-streaking of sputum to coughing up large amounts of pure blood. True hemoptysis is expectoration of blood from the lower respiratory tree, below…
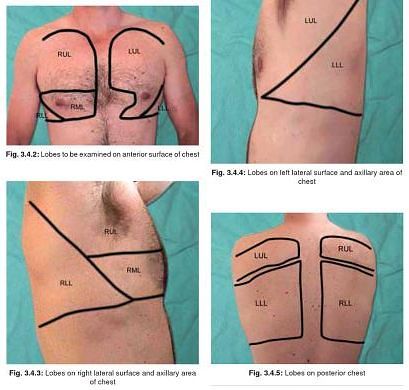
Respiratory Examination – Relevant Anatomy and Physiology
1. Division of Airway: Extrathoracic (Upper) airway: Nose to Upper trachea Intrathoracic (Lower) airway: Lower trachea to Alveoli and lungs Note: Vocal fold is also regarded as the demarcating line between upper and lower respiratory tract 2. Angle of Louis: Junction of body of sternum to manubrium (2nd costal cartilage…
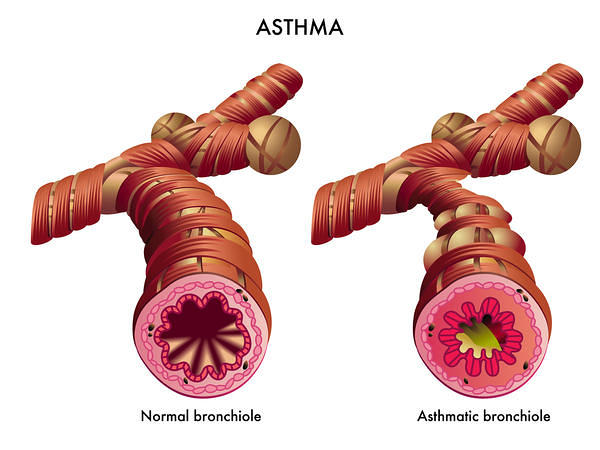
Respiratory Examination – Noisy Breathing
GRUNTING Definition: A short, explosive, moaning or crying sound heard on expiration (Child and neonates) Cause: Any cause of respiratory distress Mechanism: In attempt to increase FRC which helps to keep narrowed or collapsing airways open, creating a longer time for alveolar gas exchange STERTOR Definition: Non-musical, low pitched, snoring…

Examination of Hands
History: Hand dominance and occupation? Injury? Pain? Paresthesia? Impaired function? Swelling? Position: Place the patient’s hands on pillow Look: SEATS a. Shape or Deformity: – Wrist: Radial deviation: RA Ulnar deviation and flexion deformity: Spastic hemiplegia (CP) Wrist drop (also finger drop): Radial nerve injury Prominent dorsal ulnar and radial…
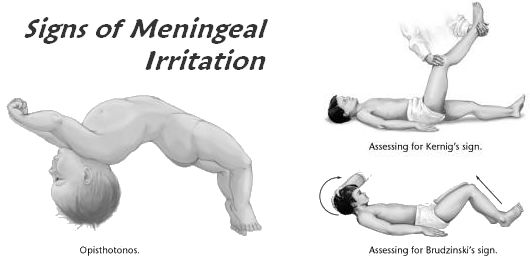
Meningeal signs
Meningitis refers to the inflammation of leptomeninges and underlying subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Meningism or meningismus is a morbid state characterized by a meningitic syndrome (a triad of headache, photophobia and nuchal rigidity) without intracranial inflammation. Some authors, have also used the term “meningism” or “meningismus” to describe the characteristic signs…
