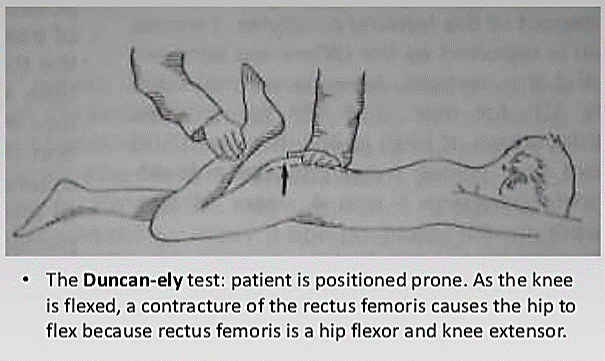
Rectus femoris is the only Quadriceps muscle that cross the hip joint and act as a hip flexor and knee extensor. When the rectus femoris is shortened/tightened, it tends to pull the pelvis forward into anterior pelvic tilt and also forces the knee into hyperextension. Ely’s test: Patient is positioned…
Tag: Clinical examination
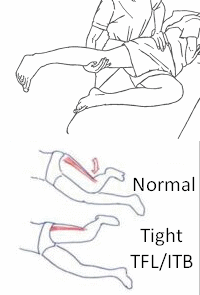
Ober’s Test
Tensor fascial latae (TFL) originates from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) outer surface, outer lip of anterior iliac crest and deep surface of fascia latae, continues down in thigh as Iliotibial band (ITB) and inserts to the ipsilateral Gerdy’s tubercle. TFL plays role in flexion, medial rotation and abduction…

WIPERS mnemonic for starting patient examination
A useful approach before examining any patient, using the mnemonic WIPER. 1. Wind up clothes above elbow, Withdraw all jewelry and Wash your hands. 2. Introduce yourself. 3. Purpose and Permission – explain purpose and gain verbal consent (permission) to proceed with the examination. 4. Expose the patient as needed….
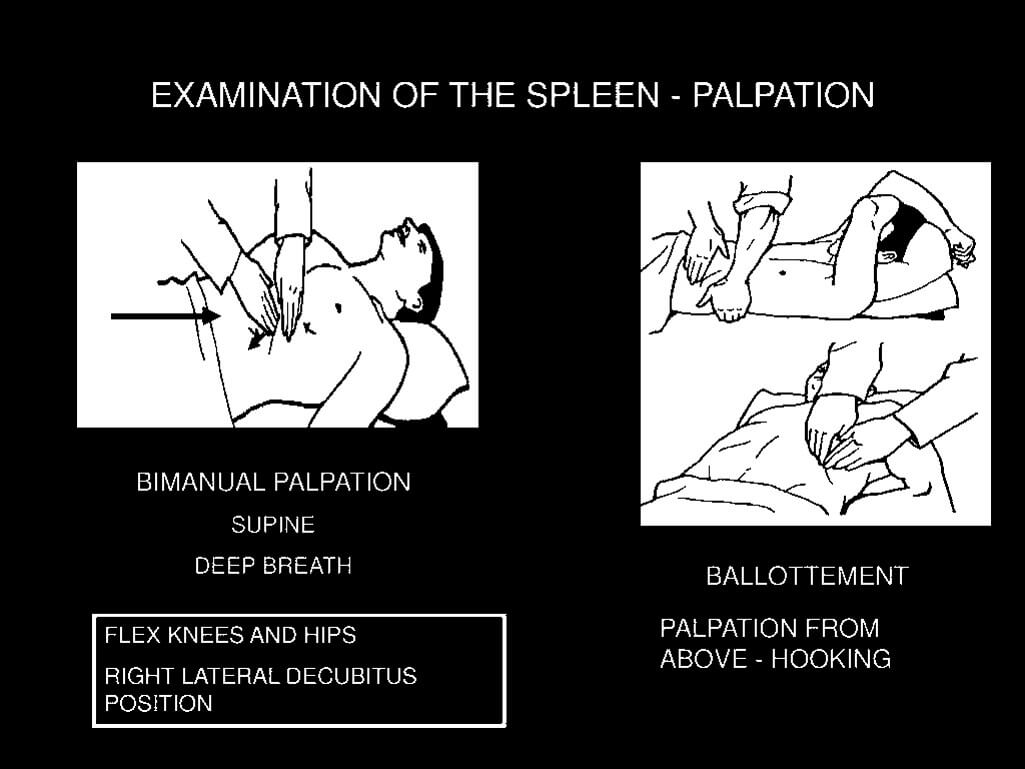
Splenomegaly : Examination techniques and Clinical Approach
ANATOMY OF SPLEEN Histologically: FUNCTIONS OF SPLEEN Spleen is the largest lymphoid organ organ and serves following functions – An increase in these normal functions may result in splenomegaly EXAMINATION OF SPLEEN 1. Palpation: If history suggest splenomegaly but is not palpable: Roll the patient on to the right lateral…

Paraplegia in Extension and Flexion
Paraplegia in extension and paraplegia in flexion occur only after the spinal shock has ceased. Paraplegia in extension indicates an increase in the extensor muscle tone owing to the overactivity of gamma efferent nerve fibers to muscle spindles as the result of the release of these neurons from the higher…
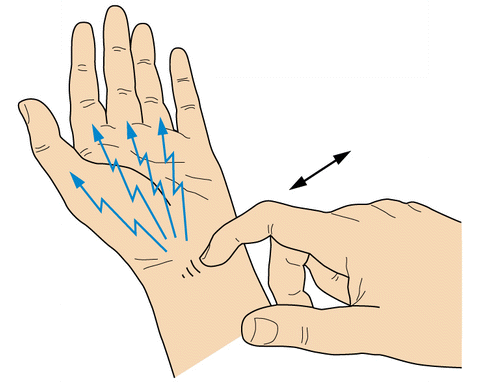
Tinel Sign
Synonyms: Hoffman-Tinel test, Tinel’s sign, Nerve percussion test Definition: “pins and needle feeling” elicited by tapping on a nerve proximally, with resulting paresthesia experienced in the corresponding distal cutaneous distribution of an injured peripheral nerve. Eliciting tinel sign: With gentle percussion by a finger or percussion hammer along the course of…

Constructing Differential Diagnoses : Mnemonic
Think of VITAMINS ABCDEK V: Vascular (bleed or blocked), or anything related to hematology I: Infective or Post-infective T: Trauma or mechanical factors such as obstructions or pressure. A: Autoimmune-related or Allergy M: Metabolic I: Idiopathic or Iatrogenic N: Neoplasia S: Social reasons – child abuse and social deprivation A:…
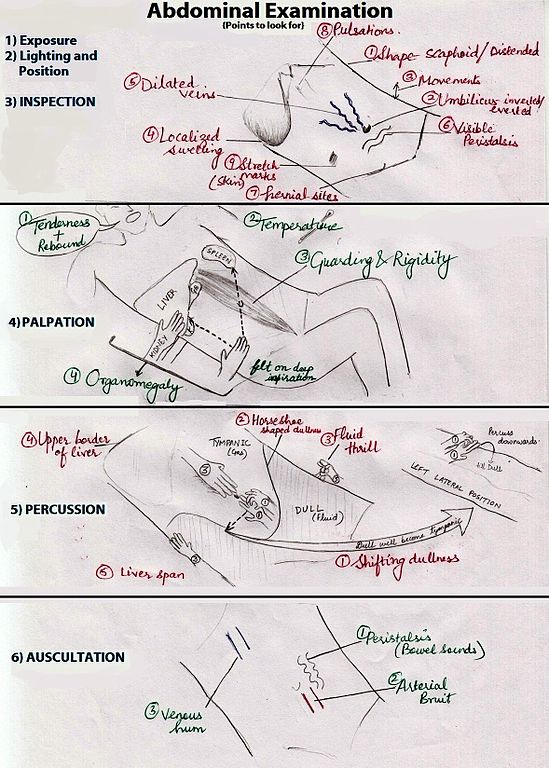
Common mistakes in Per Abdominal examination
1. Forgetting to Expose abdomen adequately: Before examination, patient should ideally be exposed from the nipples to mid thigh. Failure to do so may lead to missed findings during examination e.g. Hernia 2. Abdominal symmetry and movement: Abdominal symmetry and movement should be examined tangentially and from leg end. Comment…