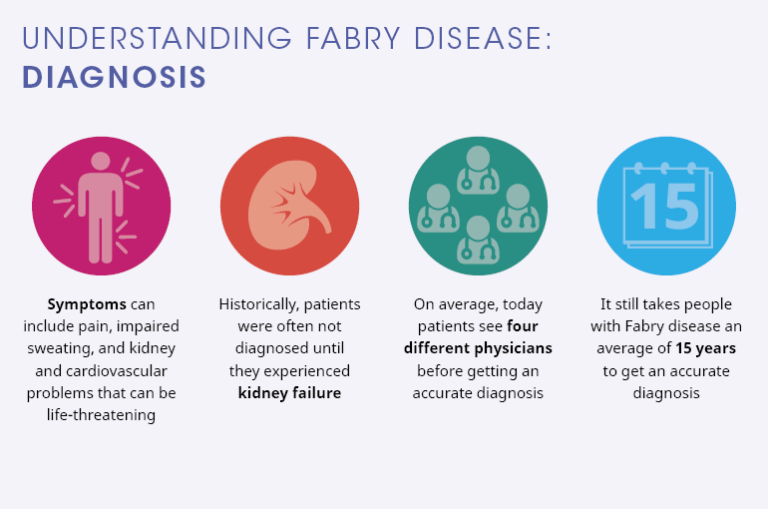
Mnemonic: FABRY CX 1. Febrile episodes, Foam cells 2. Angiokeratomas, Alpha galactosidase A deficiency 3. Burning pains in hands and feet 4. Renal failure 5. Youth death 6. Cardiovascular disease, Ceramide trihexoside accumulation 7. X-linked recessive inheritance Further reading:
Tag: Biochemistry
Tay Sach’s Disease : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: SACHS GO 1. Spots in macula (Cherry red spots) 2. Ashkenazic jews 3. CNS degeneration 4. Hexosaminidase A enzyme deficiency 5. Storage disorder 6. GM2 ganglioside accumulation 7. Onion skin appearance of lysosomes Further reading:
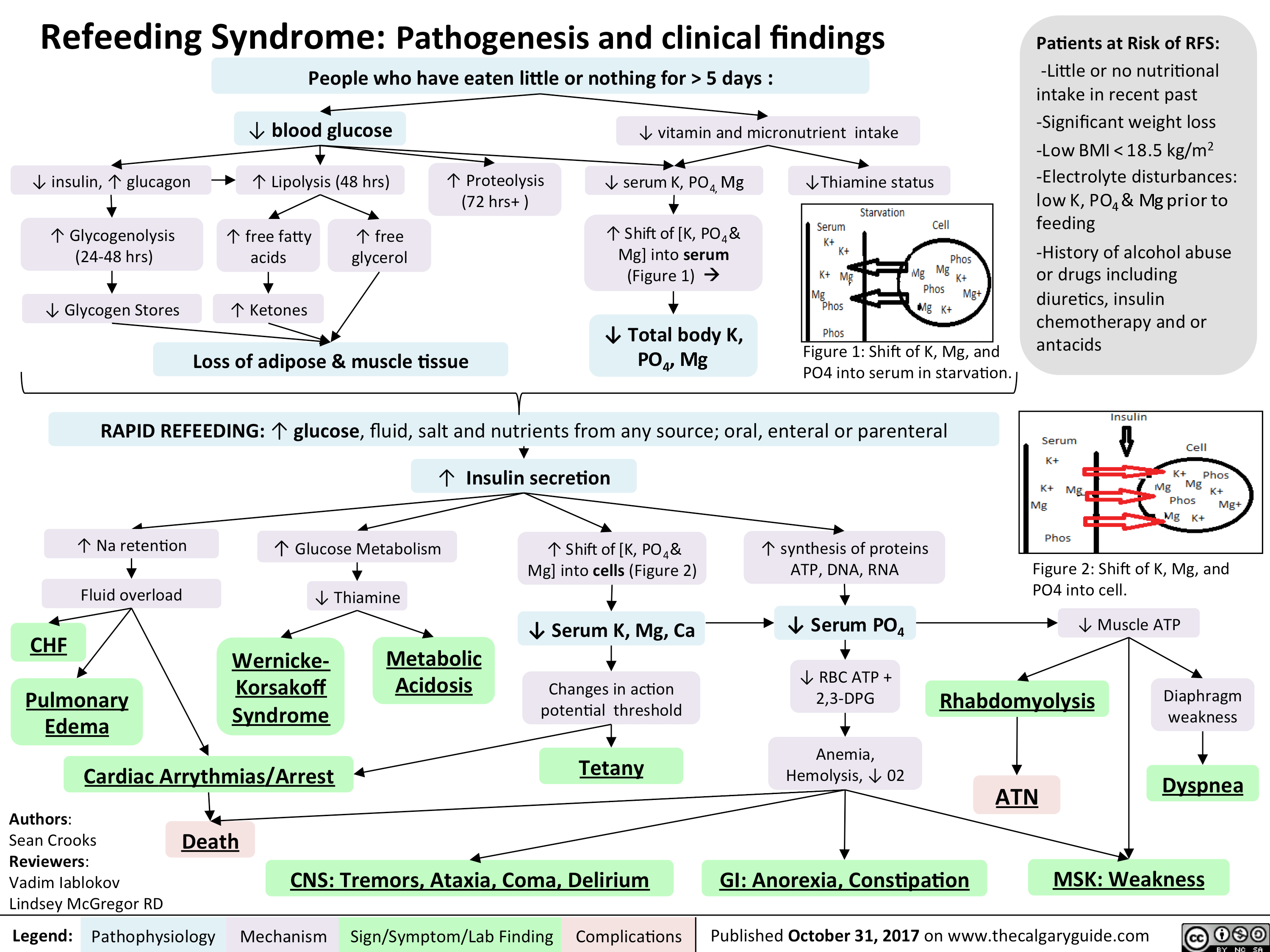
Refeeding Syndrome : Mnemonics
Risk factors Mnemonic: ABCD Pathophysiology Mnemonic: PPM Malnourished (depleted intracellular Phosphate, Potassium, Magnesium) → Refeeding → Increased glucose load → Insulin spikes → Drives PPM into cells → Hypophosphatemia (major abnormality), hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia Prevention If patient hasn’t not eaten for >5 days, aim to refeed at <50% energy and protein…
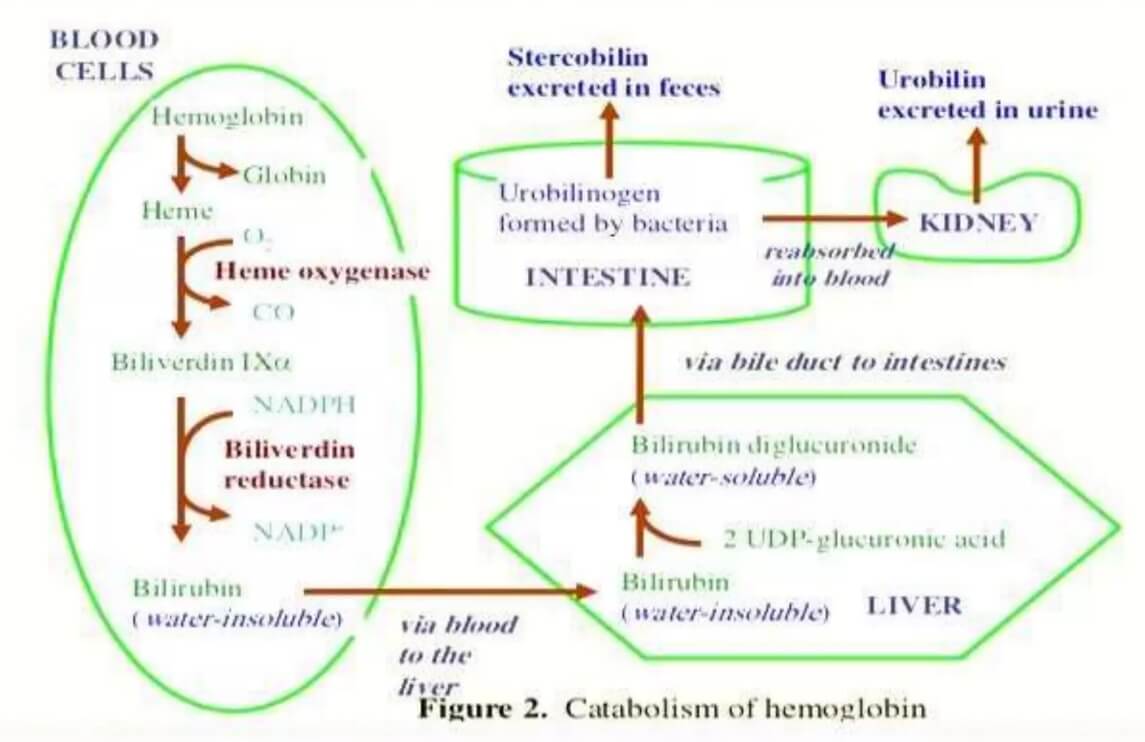
Bilirubin Metabolism and Disorders
Bilirubin Metabolism Mnemonic: ABCDE 1. Aged RBCs (80-85%) 2. Breakdown to Biliverdin and Bilirubin (in reticuloendothelial system) 3. Circulation 4. Delivery to liver (Conjugation) 5. Excretion and Enterohepatic circulation Unconjugated Vs Conjugated Bilirubin Unconjugated bilirubin Conjugated bilirubin Van den Bergh reaction Indirect Direct Solubility Water insoluble; Lipid soluble Water soluble;…
ABG Interpretation Made Easy
Normal values Step 1: pH Step 2: pCO2 Step 3: HCO3- Step 4: Determine compensation If there is metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, determine if there is appropriate respiratory compensation: No respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 = Measured pCO2 Respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 ≠ Measure pCO2 Step 5: Delta ratio ΔAG /…
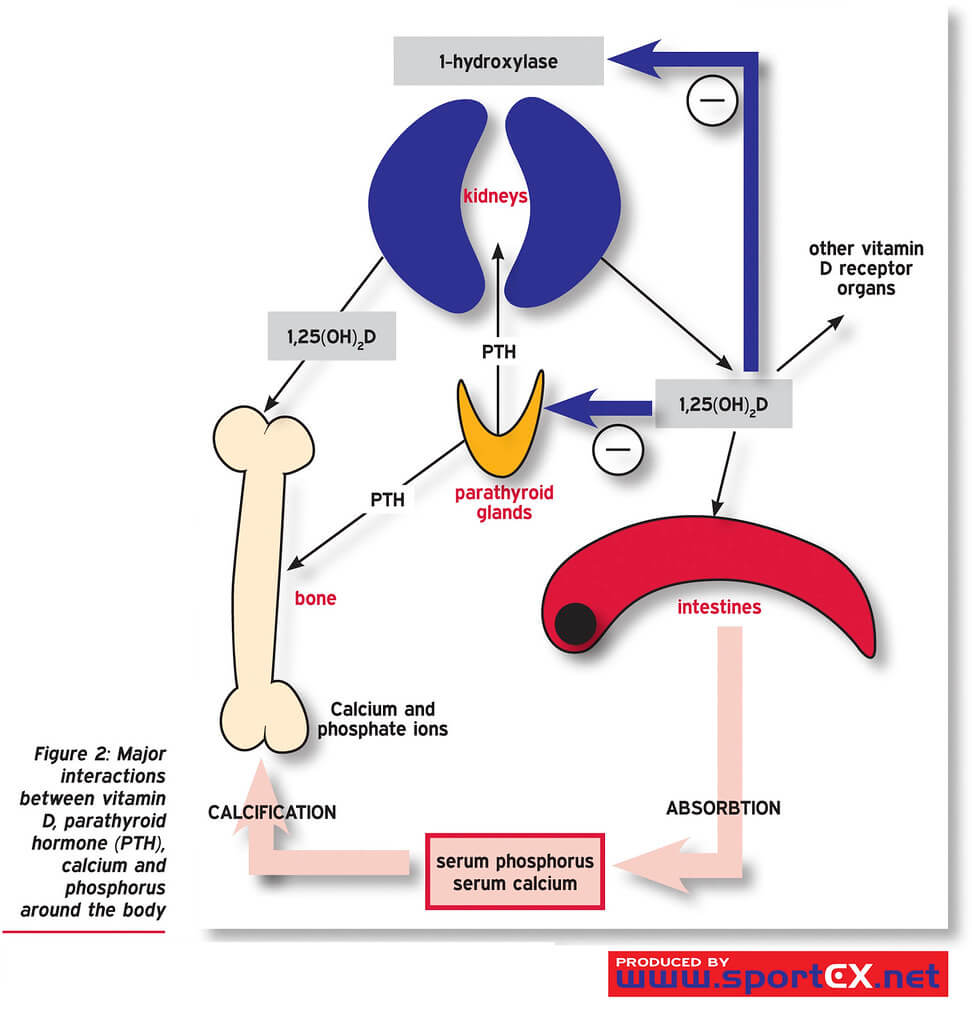
Calcium Metabolism
Functions Mnemonic: Six ‘C’s Contraction of muscles (Coupling of excitation-contraction) Conduction in nerves Cardiac function Coagulation in blood (Co-factor) Communication (intracellular messengers) for hormones, autacoids and transmitters Cementing (mineralization) of bone – Compressive strength Distribution Average young adult = 1200 gm calcium 99% in bone as calcium hydroxyapatite 1% in…
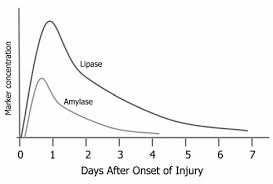
Amylase and Lipase in Acute Pancreatitis
Test Rise Peak Return to baseline Lipase 4-6 hours 48 8-14 days Amylase 2-4 hours 24-48 5-7 days Serum lipase elevation has a better diagnostic value as compared to serum amylase due to its superior specificity. Amylase has a low molecular weight and as a result can easily pass through…
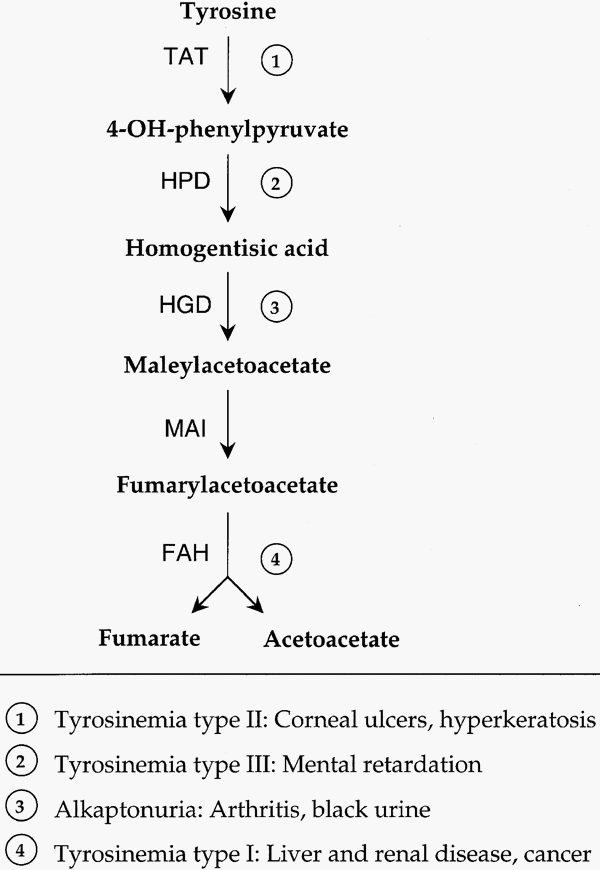
Tyrosinemia Enzymes : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: FAHeem TATtooes because of Histrionic Personality Disorder (HPD) Tyrosine is necessary for biosynthesis of catecholamines, thyroid hormones and melanin pigment. 1. Tyrosinemia type I (Tyrosinosis/Hepatorenal tyrosinemia): Enzyme defect: FAH (Fumaryl-acetoacetate hydroxylase) Last enzyme in the cycle Cabbage like odor Hepatocellular carcinoma Renal tubular acidosis Peripheral neuropathy 2. Tyrosinemia type II…