Advantages:
- Improved exposure
- Sparing of quadriceps muscle bellies
- Surgical scar that doesn’t interfere with subsequent total knee arthroplasty
Patient position: Supine with a roll under the knee to allow knee flexion
Tourniquet: Not used unless required
- Tight tourniquet can prevent medial retraction of quadriceps
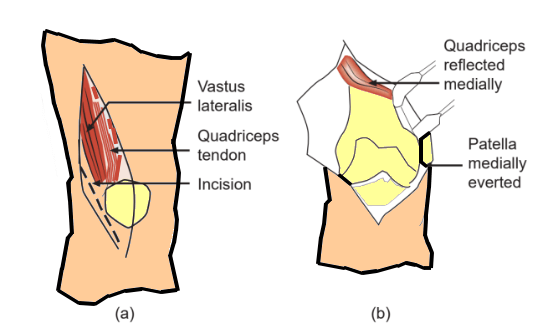
Incision:
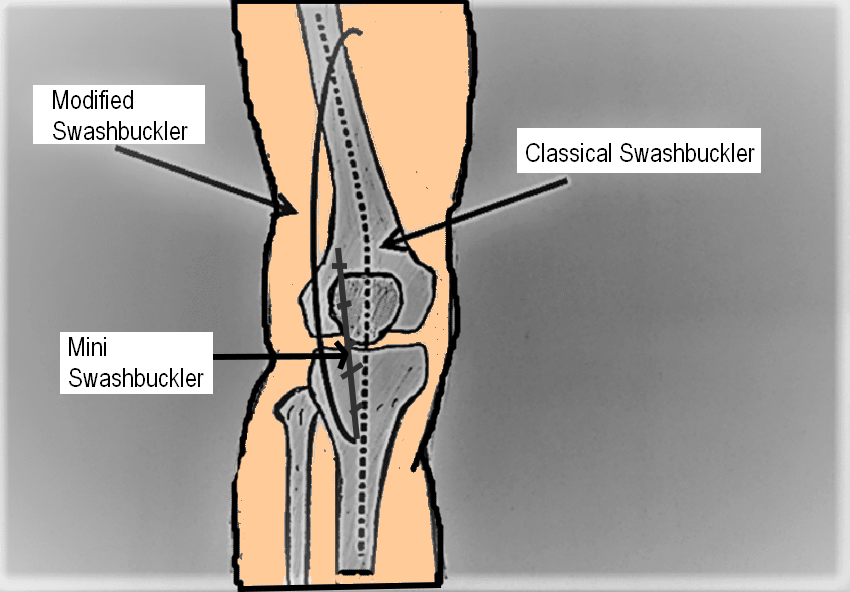
- Classical Swashbuckler (Starr et.al.): Incision starts at tibial tuberosity & extends directly cephalad to the apex of patella. It then extends proximal toward the lateral intermuscular septum.
- Modified Swashbuckler: Incision starts at lateral aspect of tibial tuberosity & continues proximally maintaining 2 cm distance from lateral border of patellar tendon. Then it extends proximal from the base of patella aiming for the posterior depression of vastus lateralis until anterolateral aspect of thigh is reached, about 5 fingerbreadths from the patella. Further, the incision can be extended proximally along anterolateral thigh as per the requirement.
- Mini Swashbuckler (Beltran et.al.): 12-15 cm incision from the lateral edge of tibial tubercle upwards to the superolateral margin of patella
Superficial dissection:
1. Fascia is incised in line of incision & sharply dissected off the vastus lateralis muscle laterally to its inclusion with the iliotibial band, to expose the quadriceps muscle.
2. Iliotibial band & quadriceps fascia are retracted laterally, continuing dissection down to linea aspera.
Deep dissection:
1. Knee capsule is incised immediately along the lateral aspect of patellar ligament.
2. Lateral subvastus arthrotomy:
- Classical Swashbuckler: Dissection is taken directly along the lateral margin of patella, leaving a small cuff of tissue for eventual repair.
- May undermine the lateral supply to anastomotic patellar ring
- Modified Swashbuckler: Arthrotomy is done with a minimum margin of 2 cm from the lateral border of patellar tendon
- Preserves the integrity of the peripatellar vascular anastomotic ring
3. Proximally develop interval between lateral intermuscular septum & vastus lateralis: At the superolateral margin of patella, the dissection extends laterally towards the lateral intermuscular septum & the vastus lateralis muscle is elevated off the intermuscular septum.
Bone exposure:
1. Place a retractor under the vastus lateralis & medialis, exposing the distal femur & displacing the patella medially.
- 4 sequential steps to improve exposure in mini-Swashbuckler approach (less invasive & allows visualization of 87% of articular surface compared to classical Swashbuckler approach & allows access to all critical areas of the knee joint):
- Patellar tendon is bluntly swept off the retro-patellar fat pad with finger dissection, and an Army–Navy retractor placed to protect the tendon
- Entire fat pad and synovial reflection is excised en-bloc to the level of the inter-meniscal ligament, taking care to protect the menisci and the inter-meniscal ligament
- Complete release of the retinaculum distally to the tibial tubercle
- Superior retinaculum is released proximally enough to gain access to the suprapatellar pouch
2. Identify & ligate the perforating branches of profunda femoris artery (located every 3-4 cm approximately 1 cm lateral to femoral cortex)
Inter-nervous plane:
Between –
- Vastus lateralis (innervated by Femoral nerve) And
- Iliotibial band (innervated by Superior and Inferior gluteal nerve)
Closure:
- Allow intact vastus lateralis muscle to fall back against the lateral intermuscular septum.
- Quadriceps fascia along with lateral parapatellar arthrotomu
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Skin
References and Further readings:
- Raja BS, Gowda AKS, Baby BK, Chaudhary S, Meena PK. Swashbuckler approach for distal femur fractures: A systematic review. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021 Nov 19;24:101705. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101705. PMID: 34900578; PMCID: PMC8636817.
- Khalil, M. A., Farid, W., & Gad, S. (2015). Swashbuckler approach and surgical technique in severely comminuted fractures of the distal femur. Current Orthopaedic Practice, 26(3), 269–276. doi:10.1097/bco.0000000000000226
- Touloupakis G, Ghirardelli S, Theodorakis E, Antonini G, Violante B, Indelli PF. A modified anterolateral swashbuckler approach for distal femoral fractures: description and outcomes. Acta Biomed. 2022 Mar 14;93(1):e2022005. doi: 10.23750/abm.v93i1.12091. PMID: 35315401; PMCID: PMC8972876.
- Beltran, M. J., Blair, J. A., Huh, J., Kirby, J. M., & Hsu, J. R. (2013). Articular exposure with the swashbuckler versus a “Mini-swashbuckler” approach. Injury, 44(2), 189–193. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2012.10.021
- Campbell’s Operative Orthopaedics – 14th edition

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.