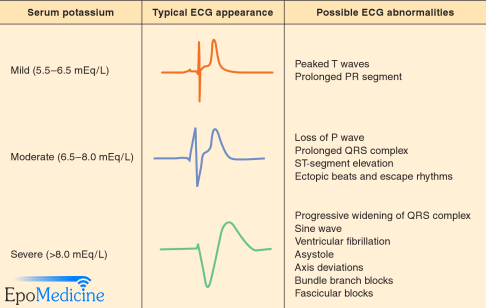
Mnemonic: C BIG K D Calcium gluconate (Cardiac stabilizer) It is generally accepted that calcium should be given when there are ECG changes associated with hyperkalaemia. Calcium gluconate 10% 10-30 ml IV (1-3 gm) over 5-10 minutes (Can be repeated after 5 minutes if ECG changes persistent) 0.5 ml/kg in…
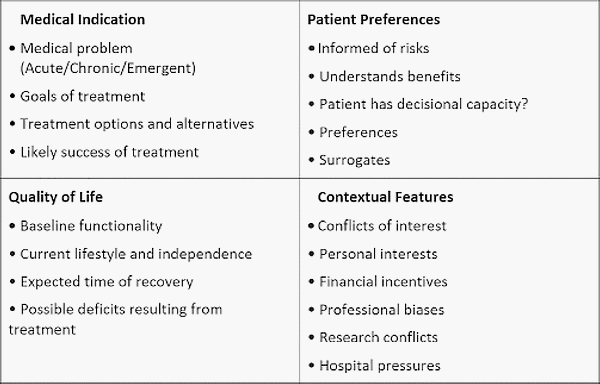
4 Box Model for Clinical Decision Making
Remember the 4 Cs: Clinical indication (Principle of Benevolence and Non-maleficence) Choice of patient (Principle of respect for Autonomy) Contextual features (Principle of Loyalty and Fairness) Condition (quality) of life (Principle of Benevolence, Non-maleficence and respect for Autonomy) A 5th box can be added: Catholic perspective Example: Clinical indications 18…
Complications of Fractures
This is a tabulated compilation for complications of fractures in general which can be immediate, early or delayed and local or generalized/systemic. This topic is commonly tested in exams. Local Systemic Immediate 1. Soft tissue injuries (Skin, Nerve, Vessels, Muscle-tendon) 2. Physeal injury 3. Hemarthrosis 4. Local visceral injury 1….
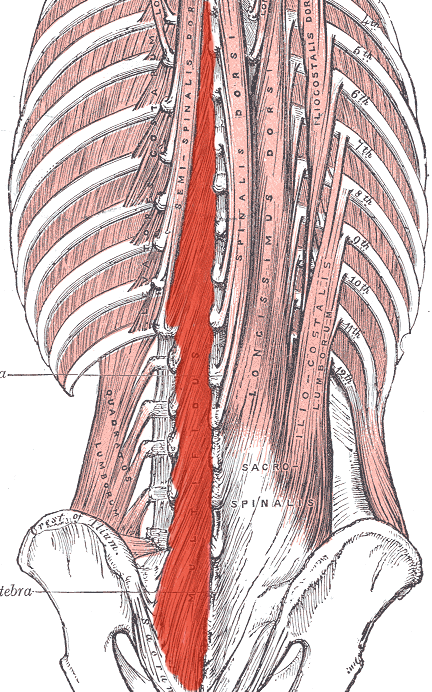
Muscles of Back – Simplified
A. Superficial Group (Appendicular group) Arise from vertebral column and attach to shoulder (assist in movement of limbs) a. Most superficial: Trapezius (From external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae and spinous process C7-T12) Latissimus dorsi (From spinous process T7-T12, thoracolumbar fascia and iliac crest) b. Covered by trapezius: Levator scapulae (From…
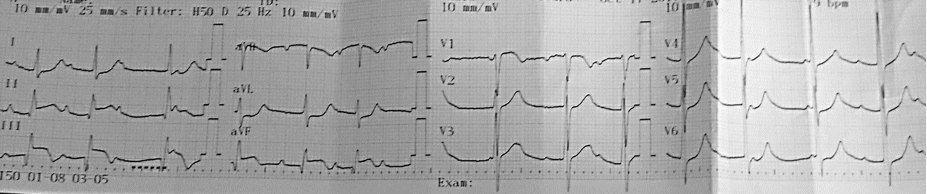
GRACE, HEART and TIMI score Mnemonics : Cardiac Chest Pain Risk Stratification
GRACE Score Mnemonic: GRACE A. Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events B. Renal: Creatinine C. Age D. Cardiac: Heart rate Systolic blood pressure Cardiac arrest at admission Killip class: I – No CHF II – Basal rales and/or JVD III – Pulmonary edema IV – Cardiogenic shock E. ECG and…
Use of Thyroid Function Test in Adult, Non-pregnant patients
The presentation attached below covers approach to management of thyroid disorders and appropriate use of thyroid function test (TFT) during diagnosis and follow-up of patients with thyroid disorders. Few MCQs for self-assessment 1. Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism should be considered for LT4 therapy if the patient has:A. A family history…

Medical Poems About Doctor, Patient and Illness
This is a collection of short poems written by me at different situations and times about medical professionals, patients and illness. Delusion of Immortality In Cotard syndrome, patients often declare to be dead, but this may also be the pathology of immortality. When reason is demolished by illness, disturbing paradoxes…
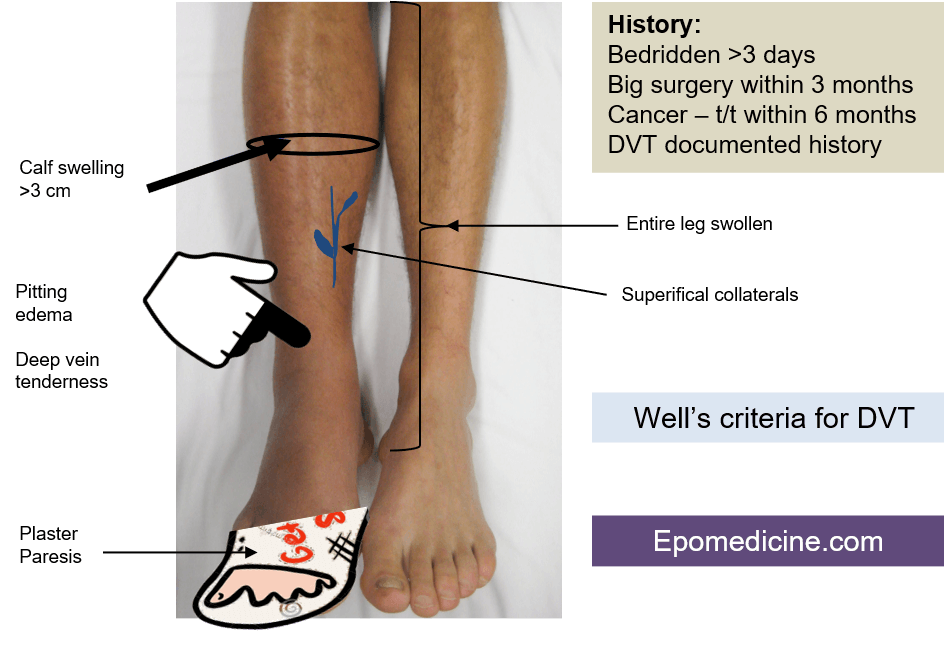
Well’s criteria for DVT with Mnemonic
Mnemonic: ABCD(CD)E(CDE) – 4P A: Alternate diagnosis of DVT more likely (-2) B: Bedridden recently >3 days or Big (major) surgery within 3 months (+1) C: Cancer – treatment or palliation within 6 months (+1) D: Deep venous involvement: Mnemonic – CD Collateral (non-varicose) superficial veins present (+1) Deep venous…