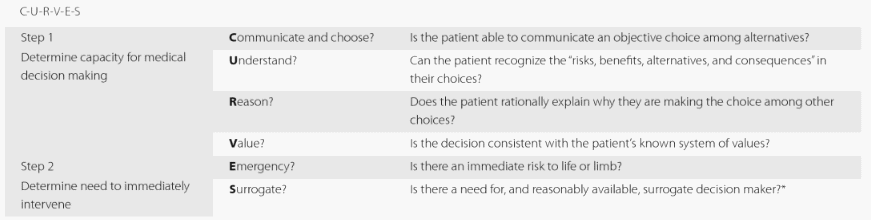
a. Choose and communicate
- Can the patient make a choice and communicate that choice?
b. Understand
- Does the patient understand the risks, benefits, alternatives and consequences of the decision?
c. Reason
- Can the patient provide logic or reason behind his/her decision?
d. Value
- Is the choice the patient makes consistent with their values?
e. Emergency
- Is there an impending, emergent risk to the life or limb?
f. Surrogate
- Is there a decision maker available or advanced directives of the patient?
The first 4 letters (C-U-R-V) assess the Decision-Making Capacity of the patient. A paitent lacks capacity if any of these pre-requisite abilities are absent.
The last 2 letters (E-S) sssess whether emergency treatment can be delivered without Informed Consent. Treating with implied consent is only appropriate when the patient does not have capacity to make the decision (C-U-R-V), it is an Emergency (E), and there is no surrogate decision maker (S) available, i.e. lack all the 6 points of CURVES.
Reference:
Chow GV, Czarny MJ, Hughes MT, Carrese JA. CURVES: a mnemonic for determining medical decision-making capacity and providing emergency treatment in the acute setting. Chest. 2010 Feb;137(2):421-7. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-1133. PMID: 20133288.
This is excellent piece of information, very helpful in clinical practice
Thank you very much. Thank you so much for explaining in such a beautiful way. Looking forward to your next post