Rule of 3s
The measured hemoglobin concentration is 3 times the RBC count, and the calculated hematocrit is 3 times the Hb level. A significant deviation means artifacts in the value estimated or the RBCs are smaller or larger than the normal.
- HCt = 3 X Hb
- RBC count = Hb/3
The units
- Hematocrit: Percentage (%)
- MCV: fL (femtolitres i.e. 10^-15 litres)
- MCH: pg (picogram i.e. 10^-12 grams)
- MCHC: g/L
1 ml = 1000 cu.mm
1 L = 1000 ml
1 L = 1000000 cu.mm
Hb (g/dL) X 10 = Hb (g/L)
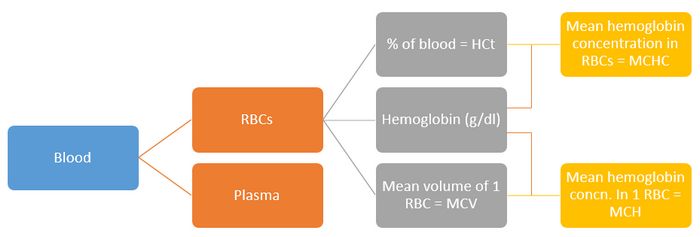
Hematocrit
In simple words, hematocrit is the percentage of your blood that is made up of Red Blood Cells (RBCs).
HCt = (Total blood volume – Total Plasma volume)/Total blood volume
Mean corposcular volume (MCV)
Mean volume of 1 RBC (Total RBC volume/Total number of erythrocytes or RBC)
MCV = (HCt X 10)/RBC count per Litre
Normal: 80-100 fL
Apply rules of 3 in the formula above: MCV = (3 X Hb X 10)/Hb/3 = 90. Hence, MCV is around 90 fL in average. Normal value is 90±10 fL.
HCt = MCV X RBC count X 0.1
Mean corposcular hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean hemoglobin concentration in 1 RBC (Hemoglobin concentration/Total number of erythrocytes or RBC)
MCH = (Hb X 10)/RBC count per Litre
Normal: 27-33 pg
Apply rules of 3 in the formula above: MCH = (3 X RBC count X 10)/RBC count = 30. Hence, MCH is around 30 pg in average. Normal value is 30±3 pg.
Mean corposcular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
Mean hemoglobin concentration in RBCs (Hemoglobin concentration/proportion of RBC)
MCHC = (Hb X 100)/HCt
Normal: 33-37 g/L
Apply rules of 3 in the formula above: (Hb X 100)/(3 X Hb) = 33. Hence, MCHC is around 33g/L in lower limit. Normal range is 35±2 g/L.
Interconversions
MCHC = (MCH X 100)/MCV
MCH = (MCHC X MCV)/100
MCV = (MCH X 100)/MCHC
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
Measure of anisocytosis (variability in RBC size) i.e. standard deviation of MCV
RDW = (Standard deviation of red cell volume X 100)/Mean cell volume
Normal range = 11 to 15%
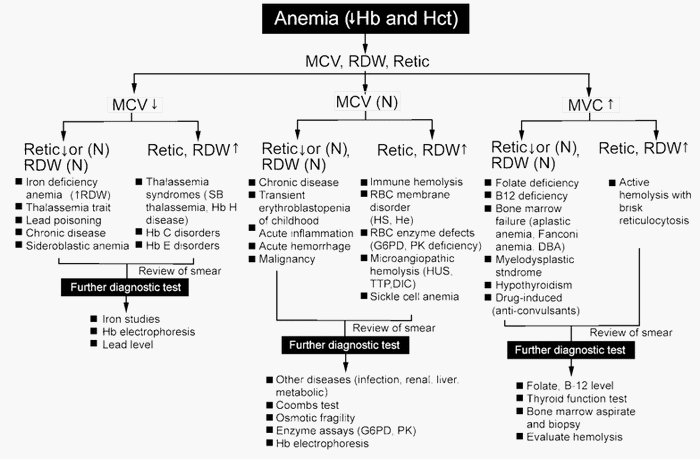
Classification of Anemia based on MCV
MCV low (Microcytic)
Normal RDW
- Thalasemmia trait
- Anemia of chronic disease
- HbH
High RDW
- Iron deficiency
- Beta-thalasemmia
- Sickle/HbC trait
MCV normal (Normocytic)
Normal RDW
- Normal
- Anemia of chronic disease
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Transfusion
- Chemotherapy
- CLL, CML
- Hemorrhage
High RDW
- Mixed deficiency
- Early iron or folate deficiency
- Myelofibrosis
- Sideroblastic anemia
MCV high (Macrocytic)
Normal RDW
- Aplastic anemia
- Pre-leukemia
High RDW
- Folate deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Immune hemoglobin
- Cold agglutinins
- CLL