TNM Classification for Breast Cancer
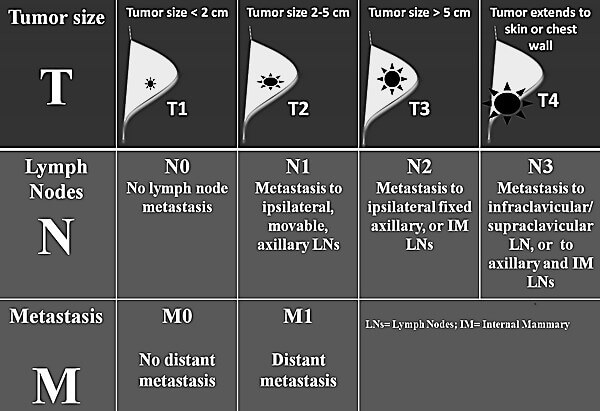
Primary Tumor (T)
- T1: ≤2 cm (20 mm)
- mi: ≤1 mm
- a: 1-5 mm
- b: 5-10 mm
- c: 10-20 mm
- T2: 2-5 cm
- T3: >5 cm
- T4: Direct extension to chest wall and/or skin
- a: Chest wall (exclude only pectoralis muscle adherence/invasion)
- b: Ipsilateral ulceration, satellite nodules or peau’d orange
- c: Both a and b
- d: Inflammatory carcinoma
Regional Lymph Node (N)
- N1: Ipsilateral and mobile level I and II axillary nodes
- N2:
- a: Ipsilateral and matted level I and II axillary nodes
- b: Ipsilateral internal mammary nodes only
- N3:
- a: Ipsilateral level III axillary nodes (infraclavicular node)
- b: Ipsilateral internal mammary nodes + level I, II nodes
- c: Ipsilateral supraclavicular nodes
Distant Metastasis (M)
- cMo (i+): Clinically and radiologically normal but ≤ 0.2 mm tumor cells in blood, bone marrow or other nonregional nodal tissues
- M1: >0.2 mm metastases
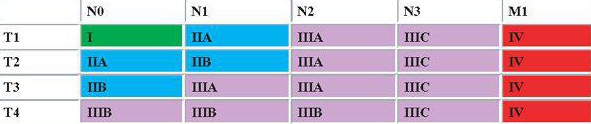
Trick or Mnemonic to remember AJCC Breast Cancer Staging
M1 = Stage IV
T4 = Stage III – b or c
N3 = Stage III – c
N2 = Stage III – a or b
- From above, we know that T4 is either Stage III – b or c (cannot be “a” and cannot be “c”)
- T4N2 = Stage IIIb
- Remaining T 1-3 is Stage IIIa
- T 1,2,3 N2 = Stage IIIa
With remaining T 1-3 and N0-1, add them up:
- Add upto make 1: Stage I (T1No)
- Add upto make 2: Stage IIa (T1N1 or T2N0)
- Add upto make 3: Stage IIb (T3N0 or T2N1)
- Add upto make 4: Stage IIIa (T3N1)
Nottingham Prognostic Index (NPI) Score
NPI score is an indicator of breast cancer outcome based on:
1. Nodal score (N)
- No positive nodes = 1
- 1-3 positive nodes = 2
- ≥4 positive nodes = 3
2. Modified Bloom and Richardson Grade (G): 1-3
3. Tumor invasive size in cm (S)
NPI Score = (0.2 x Invasive Size) + Grade + Nodes
Interpretation:
| NPI Score | Prognostic Group |
|---|---|
| ≤2.4 | Excellent Prognostic Group (EPG) |
| 2.4 – 3.4 | Good Prognostic Group (GPG) |
| 3.4 – 4.4 | Moderate Prognostic Group 1 (MPG1) |
| 4.4 – 5.4 | Moderate Prognostic Group 2 (MPG2) |
| >5.4 | Poor Prognostic Group (PPG) |
Nottingham Prognostic Index Plus (NPI+) Score
NPI+ works by using a panel of biomarkers to assess the biological behaviour of an individual’s tumour by measuring protein expression levels. Combined with a novel bioinformatic and expert system, it can then can sub-classify patients into one of seven clinically distinct biological classes. Importantly, this approach has the potential to predict both clinical outcomes and relevant therapeutic options in breast cancer more accurately than existing methods.1

A good and detailed blog on TNM, alongside stages of breast cancer. Very helpful and informative.
Simple to understand and easy to reproduce
Thank you, very helpful for last minute revision.
Well illustrated TNM classification,
easy to grasp and understand,
Thank you for your effort in simplifying these important clinical areas.