Origin: Dorsal venous network
The 1st 2 letters of the word “biceps” that being the muscle with which the vein is in relation, will give a mnemonic aid to retain the relative position of the basilic and cephalic veins. (B.I., Basilic Internal)
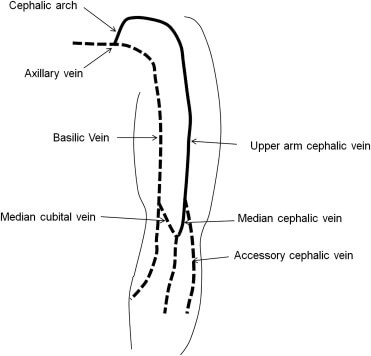
- Basilic vein courses medially
- Cephalic vein course laterally
At the elbow these 2 veins are connected by median cubital vein.
Cephalic vein courses more cephalad.
In the arm, at the lower border of teres major, basilic vein moves deep, combines with the brachial veins (venae comitantes) to form axillary vein. Cephalic vein travels to shoulder in deltopectoral groove and enters the axilla via clavipectoral triangle to terminate into axillary vein.
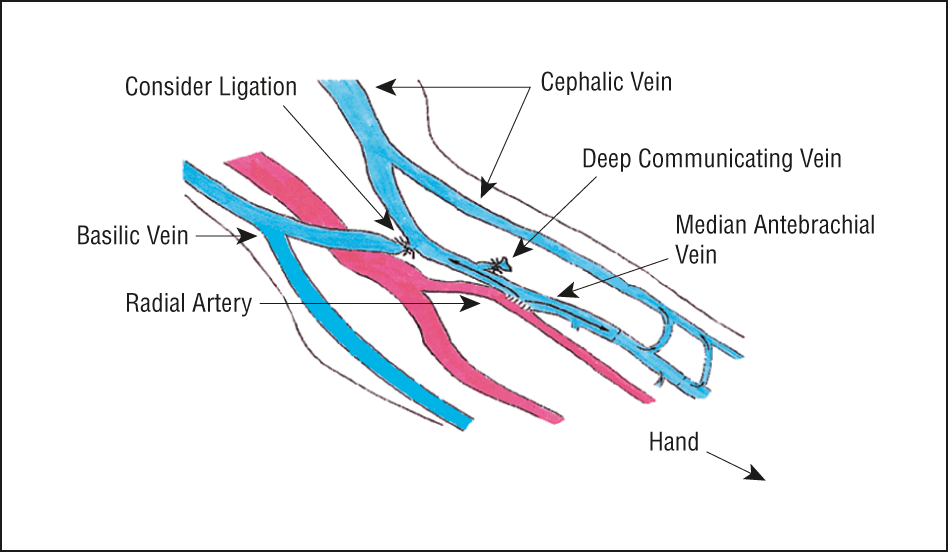
In approximately 20% of people, the median antebrachial vein (median vein of the forearm) divides into a median basilic vein, which joins the basilic vein, and a median cephalic vein which joins the cephalic vein. In these cases, a clear “M” formation is produced by the cubital veins.
It is important to observe and remember that either the median cubital vein or the median basilic vein, which ever pattern is present, crosses superficial to the brachial artery, from which it is separated by the bicipital aponeurosis. These veins are good sites for drawing blood but are not ideal for injecting an irritating drug because of the danger of injecting it into the brachial artery.
Clinical correlation:
1. Cephalic vein has a tortuous course in shoulder and has acute junction with axillary vein. Hence, basilic vein is better for insertion of SVC catheter.
2. The median cubital vein is a common site of venepuncture. It is a superficial vein that is located anteriorly to the cubital fossa region. It is thought to be fixed in place by perforating veins, which arise from the deep venous system and pierce the bicipital aponeurosis. Its ease of access, fixed position and superficial position make the median cubital vein a good site for venepuncture in many individuals.