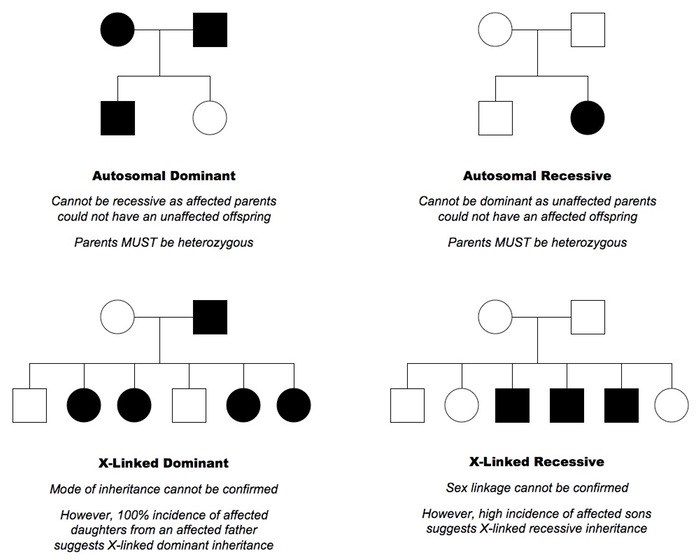
First: Look for Mitochondrial Inheritance
- Female transmits disease to all the offsprings (both males and females).
- Male doesn’t transmit the disease and only the females transmit the disease.
If Mitochondrial inheritance is absent, go to second step.
Second: Look if the gene is Dominant, Recessive
- Dominant:
- Atleast one member in all generations will have the disease.
- Both affected parents can produce normal offsprings. Parents must be heterozygous.
- Recessive inheritance:
- There will be some generations without the disease also (skips generation).
- Both normal parents can produce affected offsprings. In such case, parents must be heterozygous.
Third: Look if the disease is X-linked or Autosomal or Y-linked
- X-linked dominant:
- Male transmits disease only to the daughters (all daughters).
- Female transmits disease to half of sons and half of daughters.
- X-linked recessive:
- If only males are affected, it is likely to be X-linked recessive.
- Female only acts as carriers and remain unaffected.
- Autosomal dominant:
- No sex predilection
- Affected individual transmits disease to 1/2 of offsprings.
- Autosomal recessive:
- No sex predilection
- Affected individual transmits disease to 1/4 of offsprings.
- Consanguinity increases risk of autosomal recessive disorders.
- Y-linked (Holandric):
- Never skips generation
- Only males are affected (father transmits the disease to son).
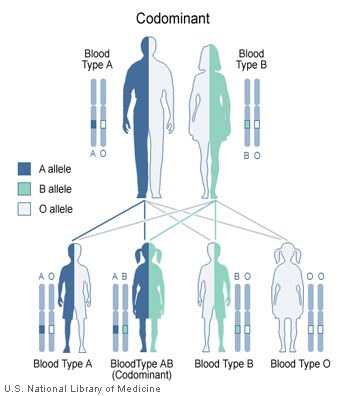
Codominant Inheritiance
This is similar to autosomal dominant inheritance but in codominant inheritance, two different versions (alleles) of a gene can be expressed, and each version makes a slightly different protein. e.g. Blood group, HLA.
amazing
its really Osm
Thanks for the author
Wow. Thank you sir for explaining this concept with such good language.
Outstanding tricks
Thank you so much, amazing trick.
I’m super grateful.