Synonyms: Obscured margin sign, Loss of outline sign
Silhouette refers to the shadow and derived it’s origin from shadow papercuts done by Etienne de Silhouette.
Principle of Silhouette sign
On a normal Chest X-ray the well-defined borders of the heart and the domes of the diaphragm are visualised because the adjacent normal air containing radiolucent lung.
Silhouette sign is based on the principle that if the two structures have approximately the same radiographic density, an are in intimate contact with each other, then the interface between them is obliterated.
If a lesion effaces one of these interfaces then the sharp margin (heart or diaphragm) is lost. The CXR appearance of a blurred or effacement is referred to as the silhouette sign.
Application of silhouette sign
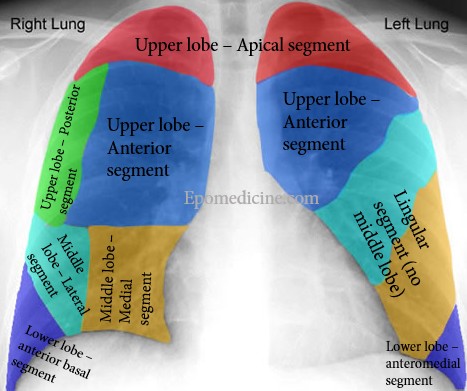
It is used in localization of intrathoracic opacity like: consolidation, mass, fluid, atelectasis, etc. that are in contact with mediastinum or diaphragm.
| Silhouette structure | Lung segment |
| Ascending aorta | Right upper lobe – Anterior segment |
| Aortic knob/knuckle | Left upper lobe – apicoposterior segment |
| Right heart border | Right middle lobe – medial segment |
| Left heart border | Left upper lobe – lingular segment |
| Right hemidiaphragm | Lower lobe – anterior segment |
| Left hemidiaphragm |
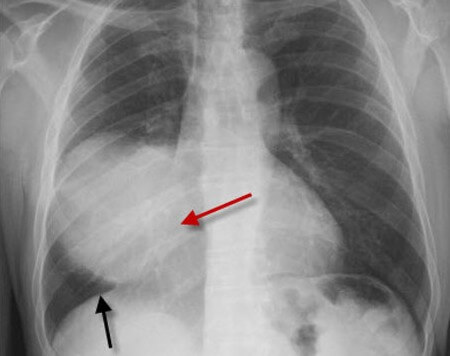
Ans: Right middle lobe
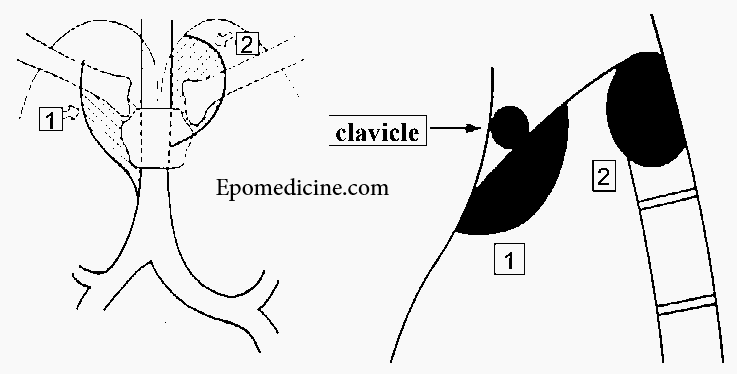
Cervico-thoracic pass sign
Upper most border of the mediastinum:
- Anterior mediastinum: Ends at the level of clavicle
- Middle and posterior mediastinum: Projects above the clavicle
Interpretation:
- The external and superior edges of the mediastinal opacity disappear above the clavicles: opacity is anterior in the superior mediastinum
- The superior edge of the opacity is visible in the pulmonary air: the opacity is posterior
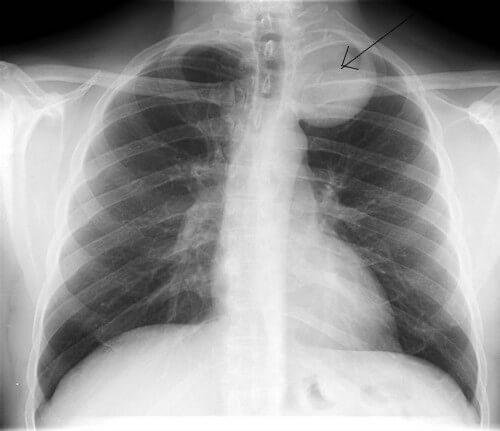
Ans: Posterior (because the opacity projects above the ipsilateral clavicle)