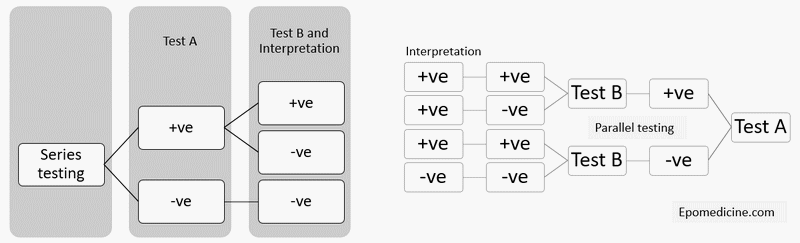
A. Parallel testing
2 screening tests are applied simultaneously:
- Disease positives: Test positive in either of the two tests (If one test is negative, still the other test can prove positive)
- Disease negatives: Test negative in both the tests (If one test is negative, the other test must also be negative)
So, this test will have:
- Less false negatives (increased sensitivity and increased negative predictive value or NPV)
- More false positives (decreased specificity and decreased positive predictive value or PPV)
B. Series testing
After the 1st screening test is conducted, those who test positive are only tested with the 2nd screening test:
- Disease positives: Those who test positive in both the tests (If 1st test is positive, he must test positive in 2nd test as well)
- Disease negatives: Those who test negative in either of the tests
So, this test will have:
- Less false positives: Increased specificity and PPV
- More false negatives: Decreased sensitivity and NPV
Formulae for combined specificity and sensitivity
A. Parallel testing:
- Combined specificity = Specificity of test A X Specificity of test B
- Combined sensitivity = Sensitivity of test A + Sensitivity of test B – [Sensitivity of test A X Sensitivity of test B]
B. Series testing:
- Combined specificity = Specificity of test A + Specificity of test B – [Specificity of test A X Specificity of test B]
- Combined sensitivity = Sensitivity of test A X Sensitivity of test B
Mnemonic:
Remember:
1. Sensitivity is True Positive rate
2. Specificity is True Negative rateIn probability testing, AND = multiplication and OR = Addition
Example: Probability of getting head in coin and/or 1 in dicea. Head and 1 = P (head) X P (1)
b. Head or 1 = P (head) + P (1) – P (head and 1)In parallel testing:
1. Negative (A and B) = Specificity A X Specificity B
2. Positive (A or B) = Sensitivity A + Sensitivity B – [Sensitivity A X Sensitivity B]
In series testing:
1. Negative (A or B) = Specificity A + Specificity B – [Specificity A X Specificity B]
2. Positive (A and B) = Sensitivity A X Sensitivity B
Mnemonic:
“P” letter words decrease in Parallel.
Series Parallel Sensitivity Decrease Increase Specificity Increase Decrease PPV Increase Decrease NPV Decrease Increase

A parallel testing:
Shouldn`t it be correctly:
1. Less false negatives (incresed seinsitivity……)
2. More false positives (decresed SPECIFICITY….)?
Yes you are correct.
Correction done. Thank you Mirjam.