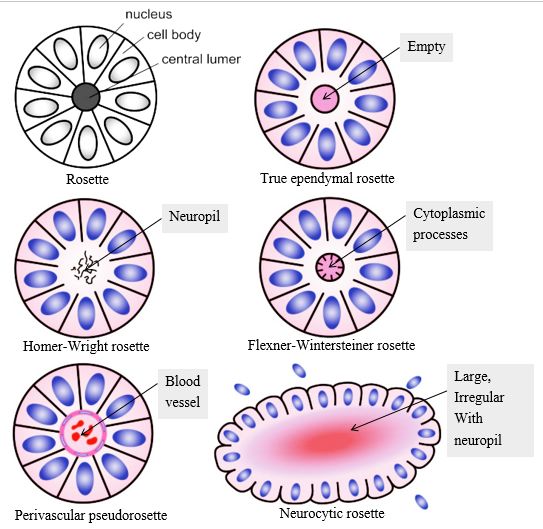
Rosette refers to a decoration or pattern resembling a rose.
In pathology, rosette refers to aa halo or “spoke-wheel” arrangement of cells around a central structure especially in neoplasms of neuroblastic or neuroectoderma origin. The central structure can be:
a. Empty lumen: True ependymal rosette
- Well differentiated ependymomas (minority of cases)
- Ependymoblastoma (rare form of PNET)
b. Meshwork of fibers (Neuropil): Homer-Wright rosette
Remember: It is Neuropil and not neutrophil. Neuropil refers to primitive neuronal processes or neurites.
- Medulloblastoma
- Supratentorial PNETs
- Pineoblastoma
- Retinoblastoma
c. Cytoplasmic extensions of encircling tumor cells: Flexner-Wintersteiner rosette
- Retinoblastoma
- Pineoblastoma
- Medulloepithelioma
Fleurettes: This refers to tumor cell’s attempt for photoreceptor differentiation.
d. Blood vessel: Perivascular pseudorosette
This is pseudorosette because the central structure is not actually formed by the tumor itself, but instead represents an arrangement of cells around native, non-neoplastic element.
- Medulloblastoma
- PNETs
- Central neurocytoma
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
Glomeruloid bodies are like pseudovascular rosette. They are seen in:
- Glioblastoma multiforme
- Schiller-Duval bodies of Endodermal sinus – Yolk sac tumor.
e. Irregular large lumen with neuropil (similar to Homer-Wright rosette): Neurocytic rosette
- Central neurocytoma
Also, rosetting of erythrocytes in peripheral blood smear (PBS) is seen in Malaria (Plasmodium infection).