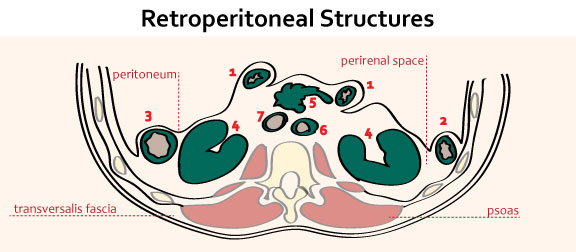
Retroperitoneal organs are partly covered on one side with parietal peritoneum. They are immobile or fixed. The classification of retroperitoneal organs divides primary and secondary retroperitoneal organs due to the embryonic development –
- Primary retroperitoneal organs: Never had mesentery
- Secondary retroperitoneal organs: Initially intraperitoneal but lost their mesentery during development
Retroperitoneal structures
Mnemonic: SAD PUCKER
- Suprarental glands
- Aorta and Inferior venacava
- Duodenum (except 1st part)
- Pancreas (except tail)
- Ureters and bladder
- Colon (Ascending and Descending only), Cysterna chyli
- Kidneys
- Esophagus (Anterior and Left covered)
- Rectum (except upper 1/3)
Primary retroperitoneal structures
Mnemonic: SAUKER
- Suprarenal glands
- Aorta and inferior venacava
- Ureters and bladder
- Kidneys
- Esophagus
- Rectum
Secondary retroperitoneal structures
- Duodenum (descending and horizontal part)
- Pancreas (head, neck and body)
- Colon
Clinical significance
Kocher maneuver (access to retroperitoneum): Performed by first identifying the duodenum, and then making an incision in the peritoneum along its immediate lateral (right) aspect, allowing the duodenum and head of the pancreas to be separated from their peritoneal attachments and reflected 180 degrees medially (to the patient’s left) to gain access to retroperitoneal structures.
Extended Kocher maneuver: If greater exposure is required, the incision can then be extended caudally along the white line of Toldt, allowing the ascending colon to be reflected medially and more access to the more inferiorly lying retroperitoneal structures.
Retroperitoneal fibrosis:
- Uncommon collagen vascular disease
- Often presents initially with ureteric obstruction
- Idiopathic (70%), Bening and malignant conditions, Medications
Eponymous signs of retroperitoneal hemorrhage:
- Grey-turner’s sign (flank ecchymosis): development of a hematoma along the lateral abdominal wall secondary to perirenal space bleeding tracking along with the quadratus lumborum
- Cullen’s sign (periumbilical ecchymosis): when retroperitoneal bleeding dissects along the falciform ligament anteriorly
- Fox’s sign (anteromedial thigh ecchymosis): from blood tracking along the psoas and iliacus muscles’ fascial planes

I think most of the issues were tackled
🙏
Why don’t you have an app please