GRUNTING
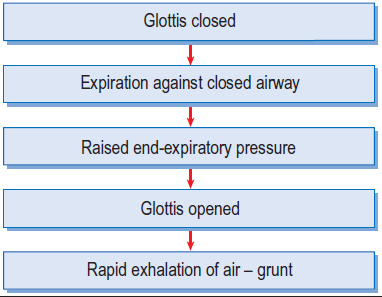
Definition: A short, explosive, moaning or crying sound heard on expiration (Child and neonates)
Cause: Any cause of respiratory distress
Mechanism: In attempt to increase FRC which helps to keep narrowed or collapsing airways open, creating a longer time for alveolar gas exchange
STERTOR
Definition: Non-musical, low pitched, snoring sound
Cause: Supra-laryngeal obstruction
STRIDOR
Definition: Loud, intense, monophasic sound with constant pitch
Cause: Upper airway obstruction at and below level of vocal cord
Types:
- Inspiratory (Supra-glottic)
- Biphasic (Sub-glottic/glottic to tracheal ring)
- Expiratory (Tracheo-bronchial)
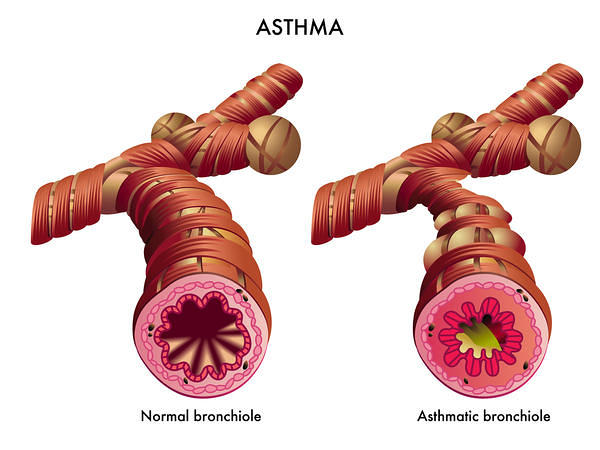
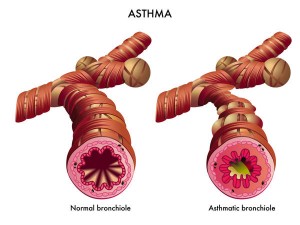
WHEEZE
Definition: Continual, high-pitched musical sound heard at the end of inspiration or start of expiration
Cause: Asthma, RTI, COPD, Foreign Body aspiration, Cardiac asthma, Bronchiolitis
Mechanism: Vibration of airway wall due to increased velocity of air through narrowed airway
Types:
- Monophonic: Fixed single pitch resulting from localized narrowing of a single airway (Bronchial tumor, Fixed Foreign Body)
- Polyphonic: Multiple simultaneous different pitched sound occurs during expiration and implies diffuse disease of different sized airways