Mnemonic: Boat starts and PRASaD DIVEs
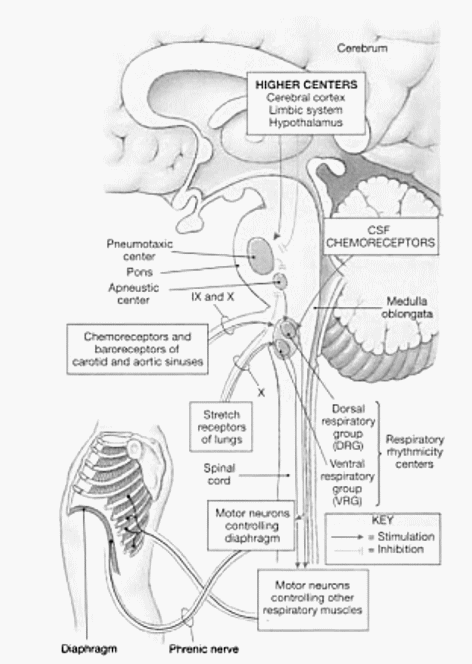
1. pre-Botzinger complex Starts respiratory rhythm (pacemaker): Boat Starts
- Location: Between nucleus ambiguus and lateral reticular nucleus (upper medulla)
2. Pneumotaxic center Represses Apneustic center: PR-A
- Location: Upper pons (Nucleus parabrachialis and Kolliker-fuse nucleus)
3. Apneustic center Stimulates DRG: A-SaD
- Location: Lower pons
4. Dorsal respiratory group (DRG) for Inspiration (tidal): DI
- Location: Dorsal medulla (Nucleus Tractus Solitarius)
5. Ventral respiratory group (VRG) for Expiration (forced): VE
- Location: Ventrolateral medulla (Nucleus ambiguus and Nucelus retro-ambiguus)
In summary:
- Rhythmic cycle of breathing originates in medulla (pre-botzinger complex).
- Voluntary respiration is controlled by cerebral cortex. Limbic system and hypothalamus alter pattern of breathing in emotional stress such as fear and rage.
- Involuntary respiration is controlled by upper brainstem.
- DRG (NTS) is Inspiratory center (receives CN 9 and 10 afferents from peripheral chemoreceptors, airways and lungs)
- VRG (Nucleus ambiguus and retro-ambiguus) is Expiratory center (however, it has both inspiratory and expiratory neurons)
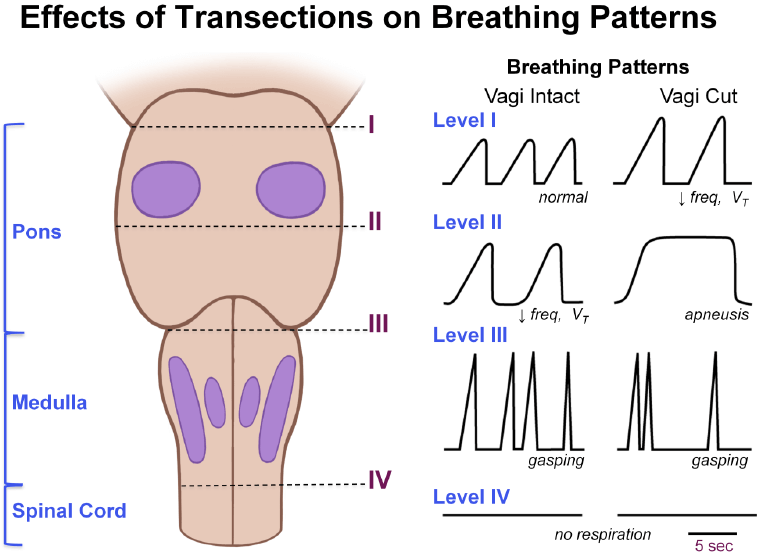
- Apneustic center stimulates DRG (inspiratory center) and causes inspiration (Apneusis = Prolonged inspiratory gasps).
- Pneumotaxic center (Nucleus parabrachialis and Kolliker fuse nucleus) and CN 10 inhibit Apneustic center to limit inspiration (volume) and increase the rate of respiration. Under normal conditions, after 2 seconds, apneustic center is inhibited by pneumotaxic center.
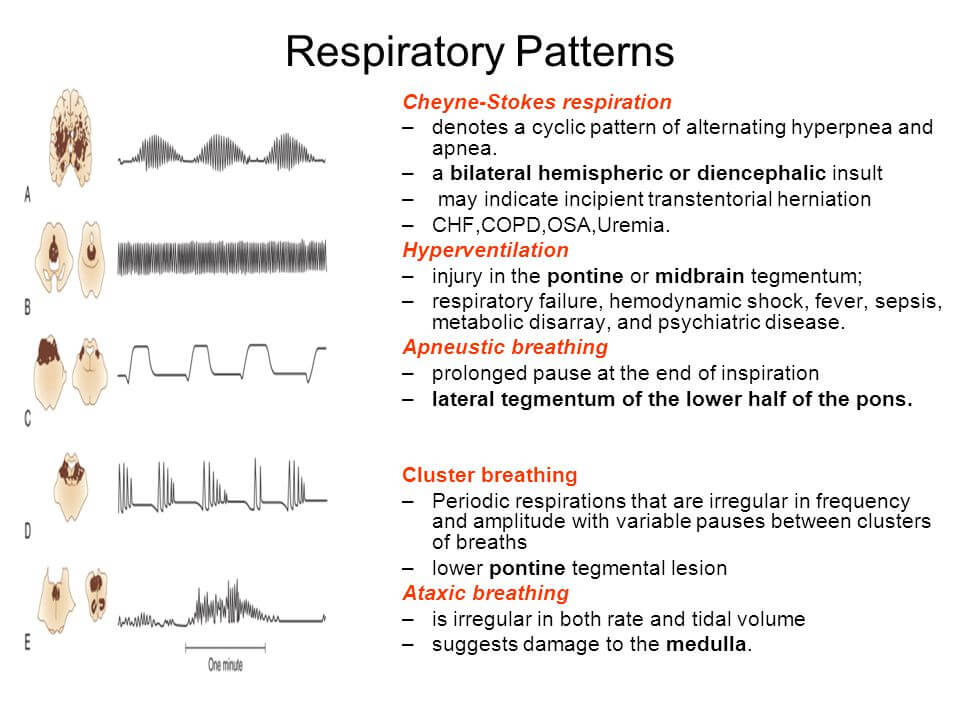
Effect of lesion/transection:
From superior to inferior: