TB SMEAR (+) CULTURE (–): 4 Ds
D: DEAD: continued expectoration of dead organisms
D: DEGENERATE: non-cultivable non-TB mycobacteria, unable to proliferate on a standard AFB culture
D: DELAY: excessive > 5 days between collection & inoculation
D: DRUGS: sufficient anti TB levels to suppress growth in vitro
TB RISK FACTORS: SHE LOVED RICHES
S: Silicosis
H: HIV & Head and neck cancer
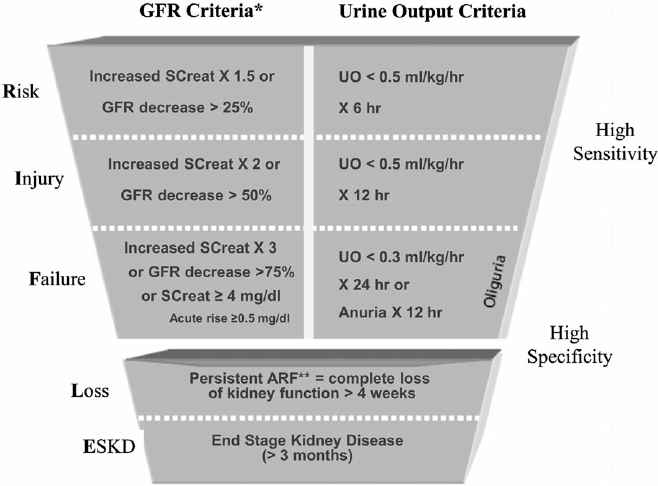
E: ESKD
L: Lupus, Lymphoma, Low BMI
O: Operations (gastrectomy) Organ Transplant
V: VDU
E: EtOH
D: DM
R: Recent TB
I: Incarcerated
C: Closed contact
H: Homeless
E: Emigrants
S: Staying in nursing homes
RISK FACTORS FOR LUNG CANCER: RARITIES
- R: Radon
- A: Asbestos
- R: Radiation (breast cancer)
- I: Ingestion of beta carotene (diet)
- T: Tobacco smoking
- I: Inhaled coal, nickel and vinyl chloride
- E: Exhaust Diesel
- S: Shit Metals & other materials: arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, chromium
MILLIARY OPACITIES DIFFERENTIALS – MILIARY
- M: Metastases [thyroid, renal cell, breast, malignant melanoma, pancreatic, osteosarcoma, trophoblastic.], Multifocal micronodular pneumocytes hyperplasia MMPH [occurs in Tuberous sclerosis; the other one is LAM]
- I: Infections: TB, fungal, Chicken pox (don’t forget the KFC]
- L: Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) ma
- I: Inhalation: silicosis and CWP Coal Worker Pneumoconiosis
- A: Autoimmune: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- R: Reaction to BCG, BCGosis
- Y: Why?
- Mitral stenosis
- Pulmonary hemosiderosis
- Sarcoidosis: miliary sarcoidosis
BRONCHIECTASIS COMPLICATIONS
C: Cor pulmonale
O: On top: brain abscess
M: Massive hemoptysis
P: Pleural effusion
L: Lung abscess
I: Infection – empyema
C: Crash – respiratory failure
A: Amyloidosis
T: Tension, pulmonary HTN
I: Inflammation – pleurisy
O: Omas, Aspergillomas
N: Neumothorax
S: Secondary infection – PNM
RULE OF 50’S: PULMONARY FUNCTION CRITERIA SUGGESTING HIGH RISK IN RESECTIVE SURGERY [LUNG CA]
- FVC < 50% predicted
- FEV1 < 50% of FVC or < 2L
- DLCO < 50% predicted
- MVV maximal voluntary ventilation < 50%
- RV/TLC > 50%
THE C’S DDx OF ASTHMA
- Cord dysfunction (vocal cord: this is an exam question)
- Compression: goiter, other mass
- CCF (cardiac asthma)
- Carvedilol and b-blockers (cause bronchoconstriction)
- Chemicals: diisocyanates, persulfates, aldehydes and amines
- Caca: ascariasis
- Crop: animal dung and wood burn (biomass fuel)
- Common allergens: mold (hypersensitivity PNMitis: precipitins from Micropolyspora faenii – Moldy Hay; Malt workers Aspergillus clavatus)
- Colonization with Aspergillus fumigatus
- Cotton mill: byssinosis
- Carcinoid: Kulchitsky’s cells
- Cancer
- Cold & Cold (cold environment and flues)
- COPD
- Chronic bronchitis
- Cough post infectious
- Constrictive bronchiolitis: Iraqi and Afghanistan burn pit combustion and explosion blasts
- Complicated exercise
- Converting enzyme: ACEI (causes angioneurotic edema)
- C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency (congenital & acquired lymphoproliferative disorders; Rx FFP)
- Ca2+ increase
ASTHMA PHENOTYPES: high risk P11 RULE = admit the px please
- P: Patient Phenotypes.
- FAB: Female (á30 xs) Adult (á7xs) Black
- IBM: Inner-city Black Male
- P: Pediatric < 5 years
- P: Poor perceiver
- P: Presenting at night (á 10 xs)
- P: Previous ICU or intubation
- P: Past month: > 1H/ED, > 2MDI
- P: Past year: > 2H, > 3ED visits
- P: Prednisone
- P: PNM or other complication
- P: Persistent asthma (>1 week)
- P: Pumpkin like: leptin resistance (obesity) is associated with poor steroid response
COPD CONTROL (DYSPNEA)
| Controlled | Partial control | Uncontrolled | |
| DaY time | < 2 wk | > 2 wk | 3 out of 6 criteria |
| SABA | < 2 wk | > 2 wk | |
| PEF (i.e. FEV1) | > 80% | < 80% | |
| Night time | 0 / month | any | |
| Exacerbation | 0 / year | > 1 / year | |
| ADL limitations | 0 | any |
DISGRACE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA
| BRONCHITIS | EMPHYSEMA | |
| Dyspnea DLCO | Mild late Normal | Severe early Decreased |
| Infections | common | occasional |
| Symptoms | Copious cough early | Scanty sputum late |
| Gamma, ie X Rays | Large heart | Small heart |
| Respiratory insufficiency | repeated | terminal |
| Age Airway resistance | 40-45 Increased | 50-75 Normal/slight increased |
| Cor pulmonale | Common | Rare Terminal |
| Elastic recoil | Normal | Decreased |
SARCOIDOSIS EYE/FUNDI CHANGES: remember Land, Bock & Mutton
- Landers sign: retinal granulomas
- Busacca nodules (over the iris)
- Optic disc granulomas
- Candle wax dripping [periphlebitis]
- Koeppe nodules (pupil margins)
- Mutton fat keratic precipitates appearing on Arlt’s triangle (anterior segment of the eye; not on the fundi)
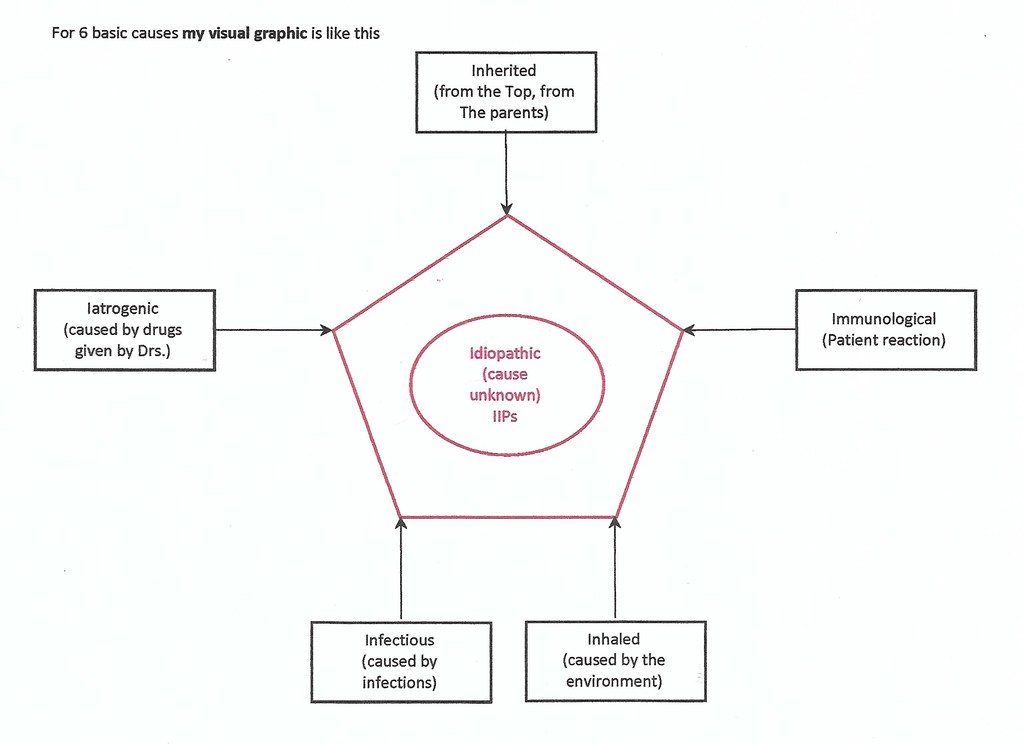
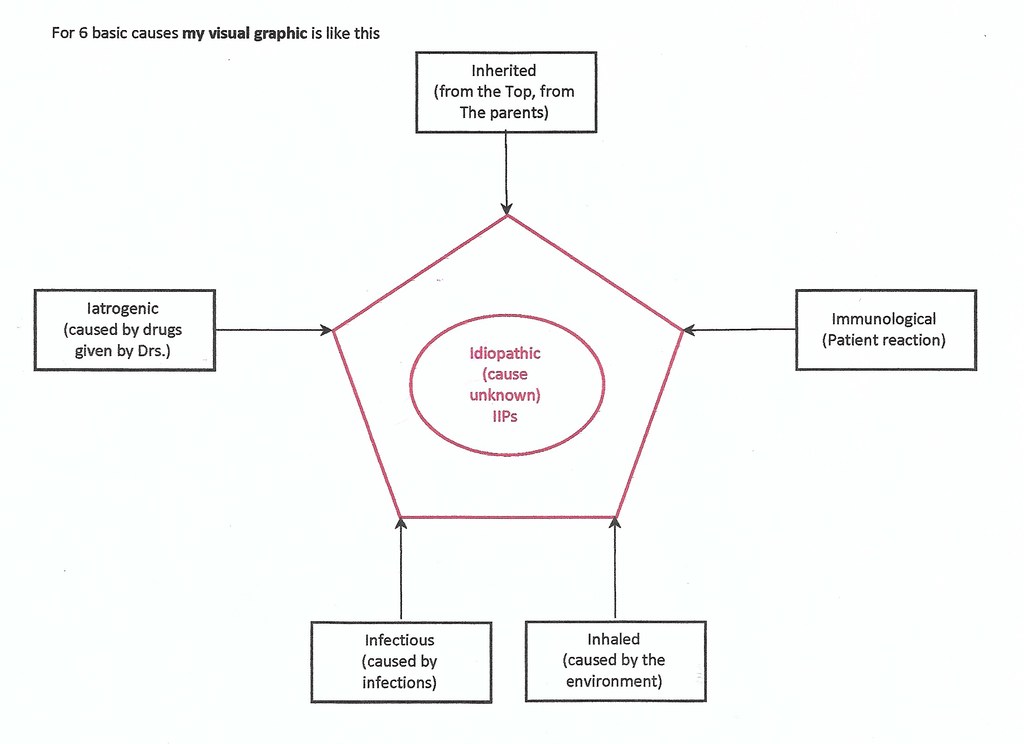
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES
6 Is of ILDs
- I: Inherited: Neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis, lymphangiomyomatosis
- I: Iatrogenic: DXT, meds (MTX, nitrofurantoin, amiodarone, Chemio: bleomycin)
- I: Infections: TB
- I: Inhaled: Asbestos, Silicosis, Berylliosis, EAA [Farmer’s lung or Mold hay, etc.]
- I: Immunological: RA, SLE, SS, Sjögren’s, Dermatomyositis, Sarcoid
- I: Idiopathic (Inside circle): cause unknown [IPF: UIP, NSIP, DIP, COP, RB, AIP, LIP]
Visual mnemonic for 6 Basic Causes

Hard worker, Reliable, Team player, Family man.
MBChB (O’Porto Univ.), Dip HIV Man (CMSA), DTM&H (Wits), DipPEC (CMSA), Dip Internal Medicine (CMSA), M. Med. Clinical Pharm [Cum Laude] (Univ. Pretoria), FCP (CMSA)
Thank you for the helpful mnemonics.