Factor Va and VIIIa are different in coagulation cascade. They are the co-factors for factor Xa and IXa respectively.
Another mnemonic: protein C Cuts Coagulation by Cutting Cofactors (Va and VIIIa)
Protein S is cofactor for protein S.
Protein C and S pathway using the mnemonic:
- Time To: Thrombin (factor IIa) – Thrombomodulin complex
- Play Counter Strike: Protein C and S
- 5 and 8 o’clock: Va and VIIIa
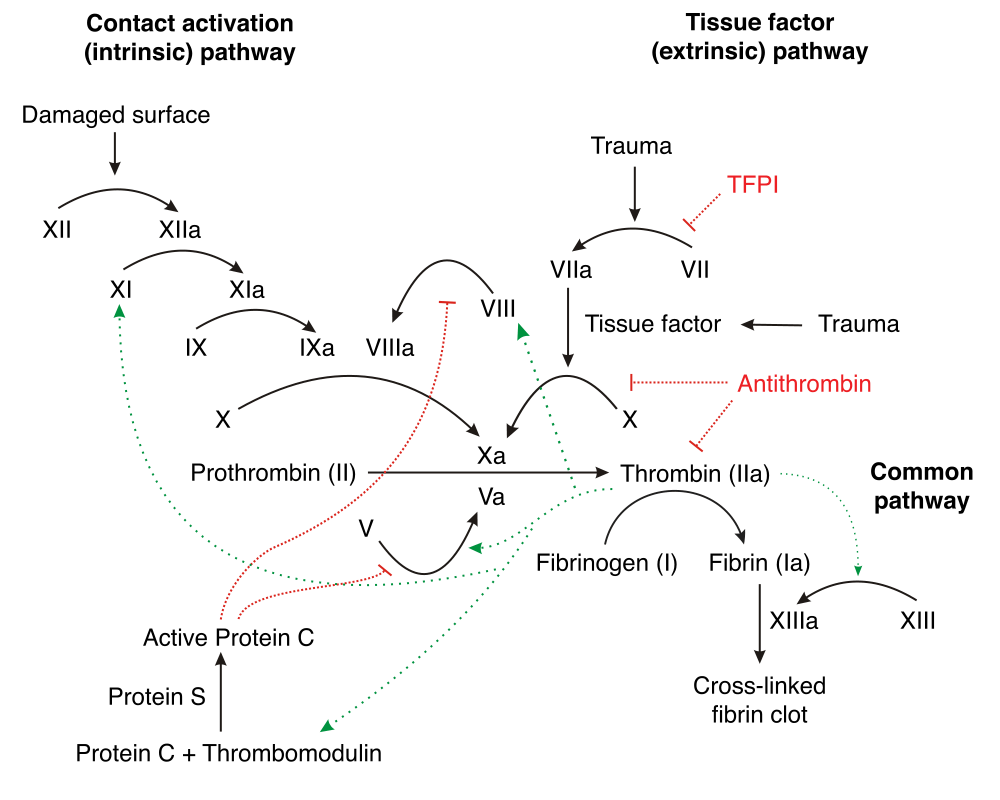
Clinical implications:
a. Factor V leiden mutation: Factor V resistant to inhibition by activated protein C (APC) leading to hypercoagulability.
b. Warfarcin induced Paradoxical hypercoagulability: The half-life of protein C is relatively short 6-8 hours. With inhibition of vitamin K, level of protein C falls before that of vitamin K dependent pro-coagulant factors like II, VII, IX and X, which have a half life of 5-7 days. This results in loss of protein C anticoagulant effect before inhibition of coagulation pathway achieved, and for a short time the patient becomes paradoxically more hypercoagulable.
- This can lead to skin or subcutaneous necrosis secondary to thrombosis.
- Heparin is co-administered with warfarin initially in cases of DVT to prevent this complication.
Review simplified coagulation cascade.

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.