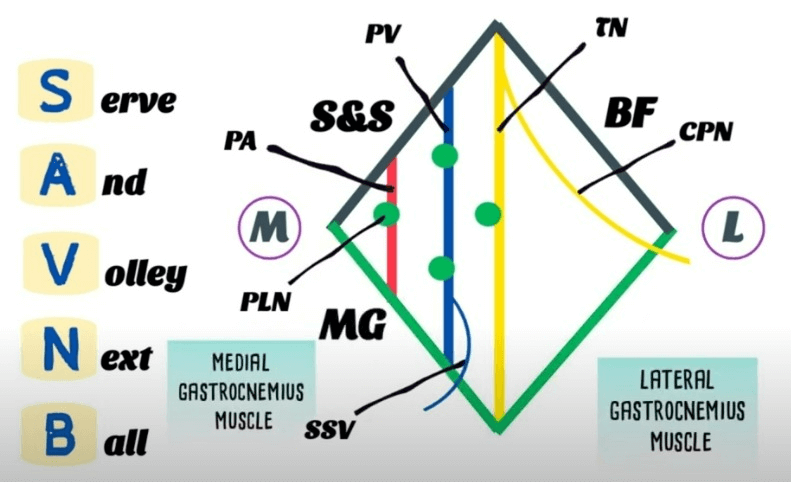
Mnemonic: Serve And Volley Next Ball
- Semimembranosus/Semitendinosus
- Artery – Popliteal artery
- Vein – Popliteal vein
- Nerve – Tibial nerve and Common peroneal nerve
- Biceps femoris
Think of popliteal fossa as a diamond-shaped space. The floor is formed by Popliteus muscle.
Membranosus = Medial (The 2 “Semis” go together – hence medial border is formed by semimembranosus, semitendinosus and medial head of gastrocnemius)
Therefore, biceps femoris and lateral head of gastrocnemius has to be lateral.
The tibial nerve lies superior to the vessels in the inferior aspect of the popliteal fossa. In the upper part of the fossa, the tibial nerve lies lateral to the vessels, it then passes superficial to them to lie medially. The popliteal artery is the deepest structure in the popliteal fossa.
Causes of lump/swelling in popliteal fossa
Mnemonic: ABCD
- Aneurysm
- Benign and malignant neoplasms:
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS)
- Synovial hemangioma
- Cysts:
- Baker’s cyst (Synovial cyst)
- Ganglionic cyst
- Meniscal cyst
- DVT