Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine-producing tumor arising from chromaffin cells of the sympathetic nervous system derived embryologically from the primitive neural crest cells.
Sites:
- Adrenal medulla (most common)
- Organ of Zuckerkandl, i.e. ganglia at bifurcation of aorta (second most common)
- Paragangliomas (anywhere along parasympathetic chain)
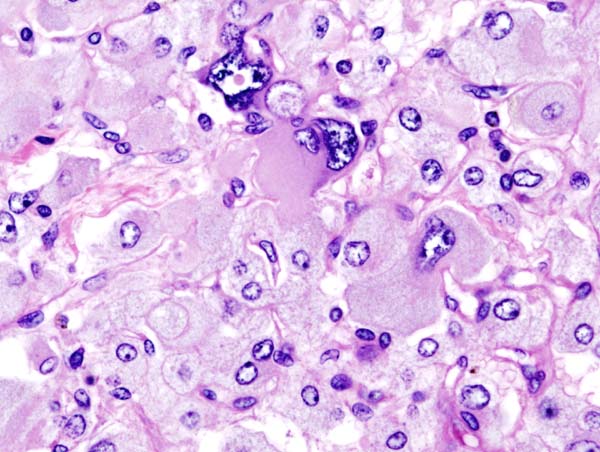
Clinical features
Mnemonic: 5 H or 7 P’s
| 5 H | 7 P |
| Hypertension | Paroxysmal rise in pressure (BP) |
| Headache | Pain (headache) |
| Hyperhidrosis | Perspiration (hyperhidrosis) |
| Hyperglycemia | Pallor |
| Hypermetabolism | Palpitation |
| Pain (abdomen) | |
| PMV in urine |
Rule of 10s
- 10% are bilateral
- 10% are extra-adrenal
- 10% are malignant (higher in extra-adrenal – upto 40%)
- 10% are familial
- 10% are pediatric
- 10% are calcified
Inherited syndromes of (Familial) Pheochromocytoma
1 – NF 1
2 – MEN 2
3 – VHL (3 letter word and Chromosome 3) and MEN 3