Micturition (Urination) is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is a type of reflex with voluntary control. The micturition cycle occurs in 2 phases:
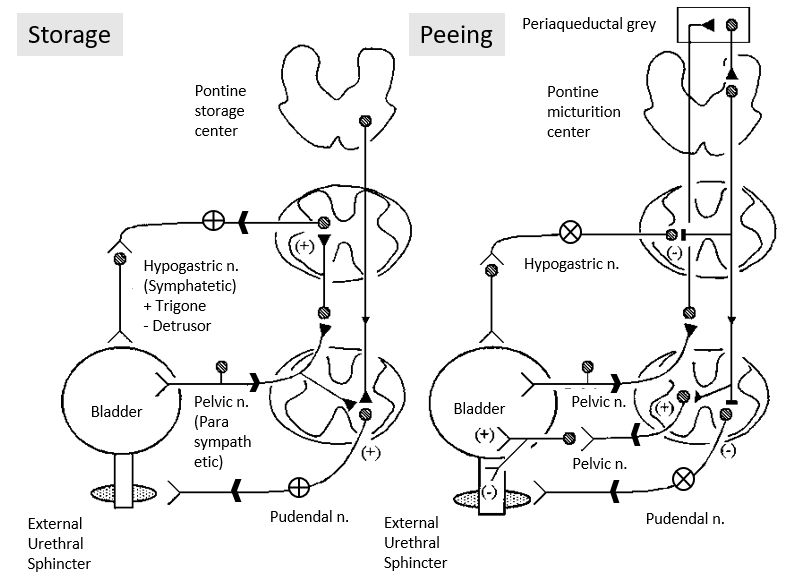
Urinary Storage
Mnemonic: Storage = Sympathetic
1. Stimulus: Urine filling until tension in the wall of urinary bladder rises above the threshold
2. Receptor: Stretch receptors in bladder wall
3. Afferent: Pelvic parasympathetic
4. Center: S2-S4
5. Efferent: Hypogastric sympathetic (lumbar)
6. Effectors:
- Detrusor muscle: relaxation
- Trigone muscle: contraction (internal urethral sphincter)
Micturition Reflex
Mnemonic: Peeing = Parasympathetic
1. Stimulus: Volume of urine that initiates micturition reflex is 300-400 ml
2. Receptor: Stretch receptors in bladder wall
3. Afferent: Pelvic parasympathetic
4. Centre: S2–S4
5. Efferent: Pelvic parasympathetic
6. Effectors:
- Derusor muscle: contraction
- Trigone muscle: relaxation (internal urethral sphincter)
Voluntary Control
Because the external urethral sphincter is composed of skeletal muscle, its contraction and relaxation can be consciously controlled until the decision to urinate is made. This control is aided by nerve centers in the brain stem and cerebral cortex that can partially inhibit the micturition reflex throught the pudendal nerve. Nerve centers within the pons and hypothalamus function to make the micturition reflex more effective.
Higher control of micturition reflex
1. The reflex is controlled by facilitatory and inhibitory higher centres.
- Facilitatory centers:
- a) Pontine centers and
- b) Posterior hypothalamus
- Inhibitory centers: Midbrain
2. The higher centers exert final control of micturition
- They partially inhibit the reflex except when micturition is desired.
- They can prevent micturition by contraction of external urethral sphincter.
- When it is time to urinate, the cortical areas facilitate the sacral center to initiate micturition reflex and inhibit the external urethral sphincter.
Neurogenic Bladder
1. Suprapontine lesion: Uninhibited bladder
2. Infra-pontine suprasacral spinal cord lesion: Automatic bladder
3. Sacral spinal cord lesion: Autonomous bladder
4. Lesion involving afferent sensory neurons: Sensory neurogenic bladder
5. Lesion involving efferent motor neurons: Motor paralytic bladder
| Supra-pontine lesion | Infra-pontine suprasacral lesion | Sacral lesion | |
| History/Bladder diary | Urgency, frequency, urgency incontinence | Urgency, frequency, urgency incontinence, hesitancy, retention | Hesitancy, retention |
| Post-void residual urine (PVR) | No PVR | +/- Elevated PVR | PVR >100 ml |
| Uroflowmetry | Normal flow | Interrupted flow | Poor/absent flow |
| Urodynamics | Detrusor overactivity | Detrusor overactivity; Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia | Detrusor underactivity; Sphincter insufficiency |