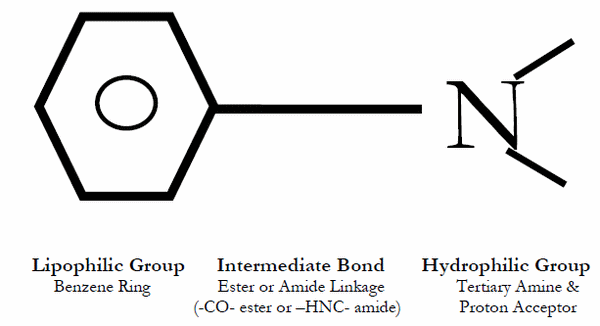
All Local anesthetics contain suffix “-caine”. Local Anesthetics (LA) can be classified as: Esters and Amides.
Esters vs Amides
A mnemonic device is that the names of amides contain 2 “i”s compared with only 1 “i” seen in esters.
Remember: One-eyed ester or Amide word has an “i” in it and hence an extra “i”.
Amides – Contains 2 “i”
Properties:
- Longer acting than esters
- Metabolized by liver enzymes
- Excreted in urine
Medicines:
- Lignocaine
- Lidocaine (Xylocaine)
- Prilocaine
- Mepivacaine
- Bupivacaine (Marcaine/Sensoricaine)
- Etidocaine
- Ropivacaine
- Dibucaine
- Articaine
- Trimecaine
- Dexivacaine
- Butanilacaine
Exceptions:
Amides with only single “i” are –
- Oxetacaine
- Tolycaine
- Pyrrocaine
- Rodocaine
Amide without suffix “caine” – Diperodon
Esters – Contains single “i”
Properties:
- Short acting
- Metabolized in plasma and tissue fluids
- Excreted in urine
- More propensity for allergic reactions
Medicines:
- Amethocaine
- Benzocaine
- Chlorprocaine
- Procaine (Novocaine)
- Cocaine
- Hexylcaine
- Proparacaine
- Tetracaine
Exceptions:
Ester with double “i” –
- Primacaine
- Piperocaine
- Dimethocaine
Ester without suffix “-caine” –
- Butamben
- Butethamine
- Naepaine
Rate of systemic absorption of Local Anesthetics
Mnemonic: In descending order – ICE BALLS
- Intravenous > Tracheal > Intercostal
- Caudal
- Epidural
- Brachial plexus
- Axillary
- Lower extremity (femoral)
- Subcutaneous

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.