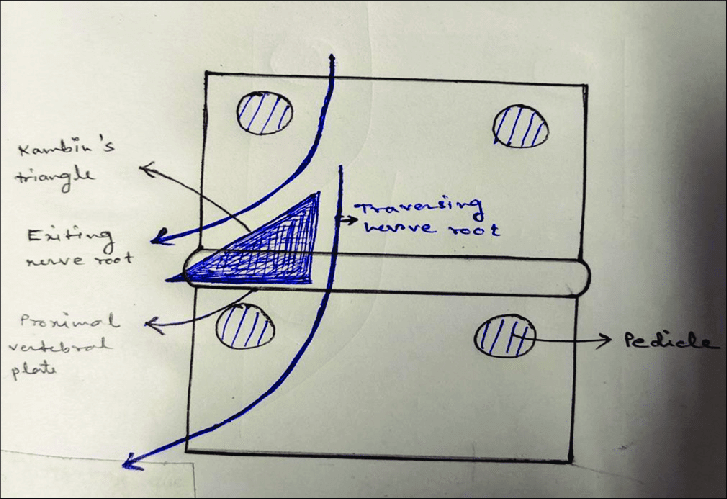
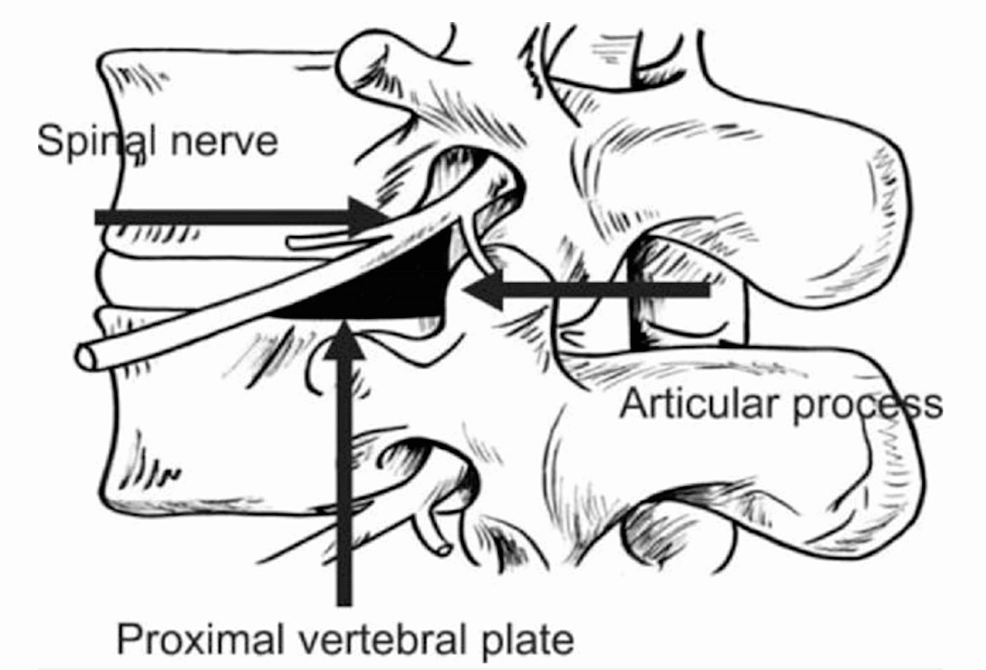
There is confusion regarding the borders of Kambin’s triangle across the literature.
Kambin originally described the borders of this triangular working zone as:
- Anterior: Exiting nerve root
- Inferior: Proximal end plate of lower lumbar vertebra
- Posterior: Superior articular process of lower vertebra
- Medial: Traversing nerve root and dural sac
Though it was named as a “triangle” it was described with 4 borders with 2 triangles (in AP view and Lateral view) which gives a 3D structure more appropriately a “prism”.
Uses of Kambin’s triangle:
Kambin’s triangle is regarded as a “safe” space because it is devoid of important neurovascular structures. It is an anatomical corridor useful in:
- Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection (TFESI)
- Diagnostic discograms
- Access disc space in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF)
- Access disc space in Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD)

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.