Mnemonic: C BIG K D
Calcium gluconate (Cardiac stabilizer)
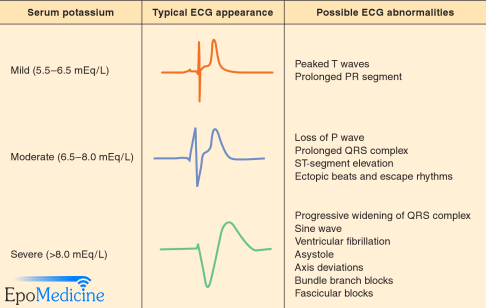
It is generally accepted that calcium should be given when there are ECG changes associated with hyperkalaemia.
Calcium gluconate 10% 10-30 ml IV (1-3 gm) over 5-10 minutes (Can be repeated after 5 minutes if ECG changes persistent)
0.5 ml/kg in children
Onsent of action: Immediate
Duration of action: 30-60 minutes
Calcium chloride contains 3 times more elemental calcium than calcium gluconate but must be given through central line due to high osmolarity.
Hyperkalaemic patients taking digoxin should be given calcium as a slow infusion over 20 to 30 minutes. This avoids hypercalcaemia that may potentiate the myocardial toxicity of digitalis.
Beta agonists (Drives K+ into cell)
Salbutamol
Onset of action: Within 30 minutes
IV: 0.5 mg (0.4 mcg/kg in children)
IV administration reduces K+ by ~1 to 1.5 mEq/l
Maximum effect for IV: 30 minutes
Nebulization: 10 mg (in children 2.5 mg if <25 kg and 5 mg if >25 kg) in 4 ml of NS over 10 minutes
Nebulization reduces K+ by 0.5 to 1 mEq/l
Maximum effect for nebulization: 90 minutes
Insulin with Glucose (Drives K+ into cell)
10 Units Soluble Insulin in 1-2 amp D50W IV over 5 minutes (Insulin 0.1-0.2 U/kg with 1ml/kg D50W)
Onset of action: 20 minutes
Maximum effect: 30-60 minutes
Duration: 4-6 hours
K+ drop by 0.6-1 mEq/L
Kayexalete (Gastrointestinal K+ binder)
1-2 gm/kg
Per Oral: Sodium polystyrene sulfonate 15-30 g in 100-200 ml 30% sorbitol (Sorbitol increases fecal excretion) or 10% glucose (repeated every 4-6 hours)
Per Rectal: 50 g with 150 ml tap water and left for atleast 60 minutes.
It may be indicated if haemodialysis is delayed (>2–3 hours).
Onset of action: 1-2 hours
Maximum effect: may take upto 6 hours
One gram resin exchanges 1mEq Na for 1mEq K
Adverse effect: Bowel necrosis
Diuretics (Renal K+ Excretor)
Can be used if patient is hypervolemic or normovolemic.
Furosemide 40 mg-80 mg (1-2 mg/kg) IV push
40 mg Furosemide = 1 mg Bumetanide
Onset of action: 15 minutes
Duration: 2-3 hours
Dialysis (Definitive management)
Indications:
- Severe hyperkalemia
- Drug measures have failed
K+ drops by 1 mEq/L in 1st hour and 2 mEq/L after 3 hours.
Can available 598 fact’s of high yielding & mnemonics.
I will be very thankful.