While historically, NS and RL have been thought to be generally equivalent for resuscitation, there has been an associated risk of hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis with large-volume resuscitation using normal saline. Hyperchoremic metabolic acidosis has been found to increase the risk of acute kidney injury. This is thought to be due to the vasoconstrictive effects of hyperchloremia and a consequent reduction in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
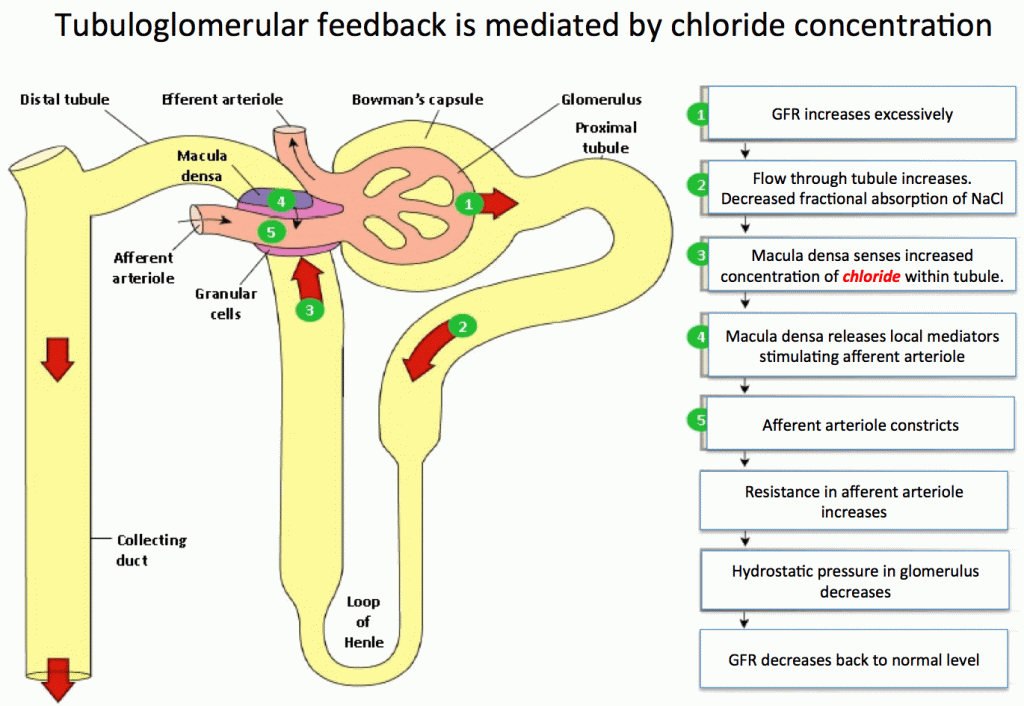
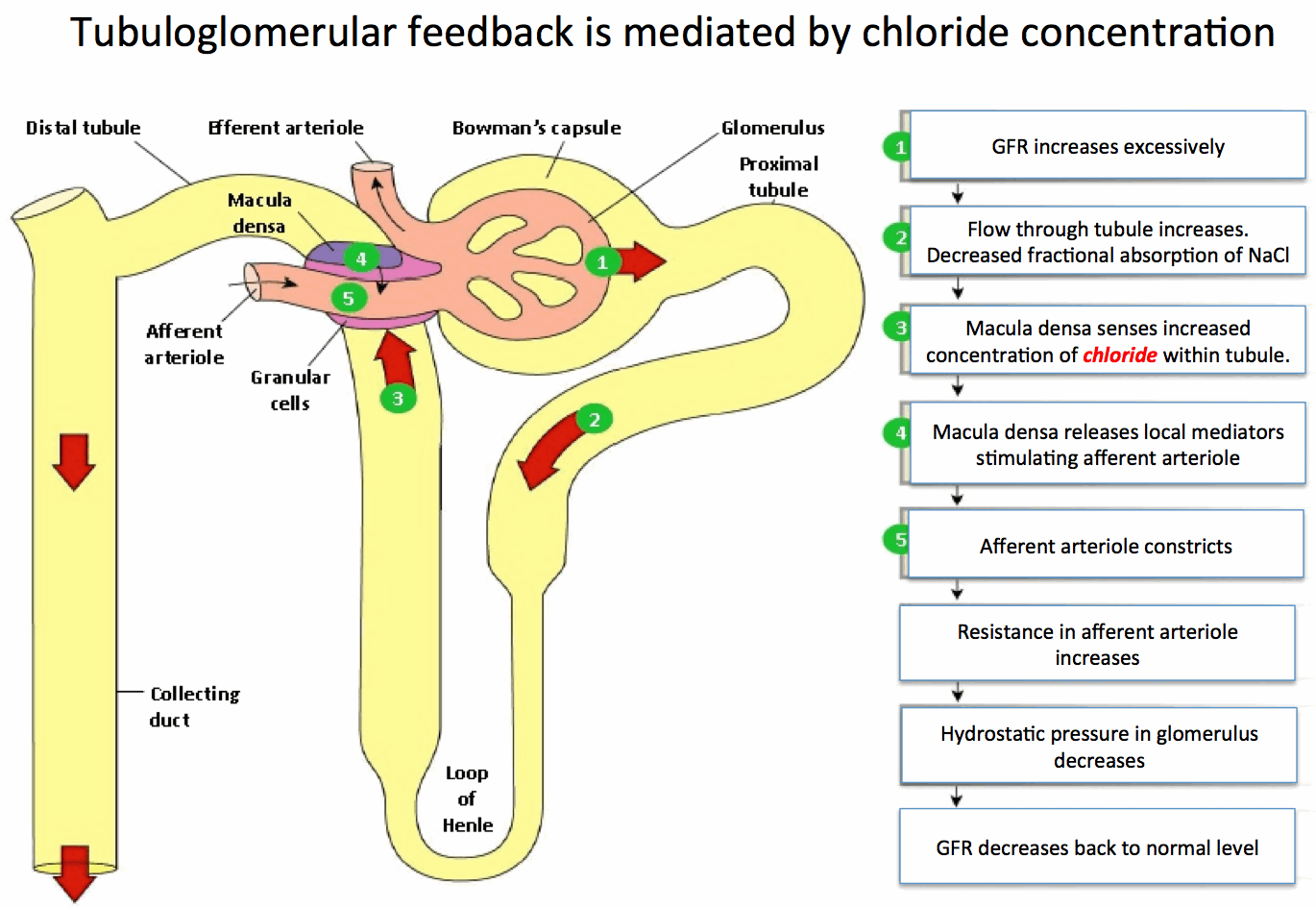
Hyperchloremia causes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles of the kidney. However, this is a side effect of how the kidneys auto-regulate renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Recall that blood flows into the glomerulus of the kidney via afferent arterioles. The renal blood flow determines the GFR or the flow of plasma filtered into the kidney. Chloride concentration at the macula densa within the distal tubule is one way the kidney can sense and adjust the glomerular filtration rate. How does this work?
Under normal circumstances, the increased chloride concentration at the distal tubule is due to impaired absorption in the proximal tubule. This indicates to the kidney’s sensory mechanisms that GFR is too high, and the proximal tubule cannot absorb the chloride quickly enough. Increased chloride then triggers vasoconstriction to decrease the GFR. Conversely, low perfusion will result in hypochloremia at the macula densa, leading to vasodilation to increase GFR.
However, in iatrogenic hyperchloremia due to high-volume NS infusion, the underlying issue is not increased GFR. However, the feedback mechanism is the same, stimulating vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole with inappropriate (in this case) reduction in GFR. In this case, a decrease in GFR worsens the hypoperfusion.