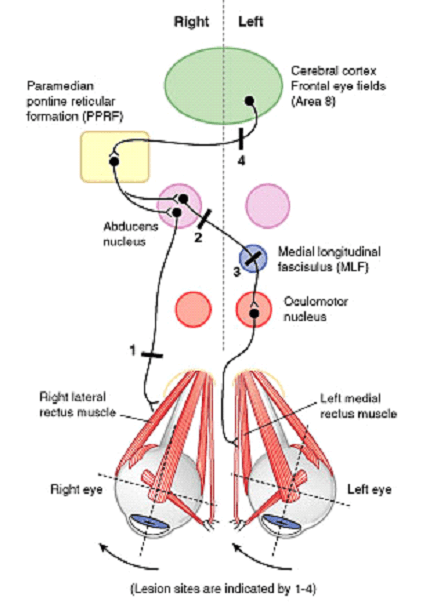
Components of Pathway
For both eyes to look at a side:
- Contralateral Frontal Eye Field (Brodmann area 8)
- Ipsilateral PPRF (Paramedial Pontine Reticular Formation)
- Ipsilateral CN VI Nucleus
- Contralateral Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF)
- Contralateral CN III Nucleus
Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway
Lesions of Conjugate Gaze Pathway
Abducens (CN VI) nerve:
Affected side cannot abduct
Lesion site 1 in figure – Right abducens nerve
- Right eye cannot look right
Abducens (CN VI) nucleus or PPRF:
Both the eyes cannot look towards the affected side (Lateral gaze paralysis)
Lesion site 2 in figure – Right abducens nucleus
- Right eye cannot look right or abduct (Right Lateral rectus dysfunction)
- Left eye cannot look right or adduct (Left Medial rectus dysfunction – as abducens nucleus activates contralateral CN III through contralateral MLF)
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF):
Eye on affected side cannot adduct when the eye on unaffected side abducts (Internuclear ophthalmoplegia)
Lesion site 3 in figure – Left MLF
- Left eye cannot adduct or look right when right eye looks to the right
- Convergence intact
- Right eye exhibits nystagmus
Can be differentiated from the Occulomotor nerve lesion by the absence of ptosis and mydriasis seen with occulomotor nerve lesion.
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: Lack of communication such that when CN VI nucleus activates ipsilateral lateral rectus, contralateral CN III nucleus does not stimulate medial rectus to contract. Abducting eye displays nystagmus (CN VI overfires to stimulate CN III). Convergence is normal.
If the left eye is able to abduct and shows nystagmus, the pathway involves –
- Ipsilateral (left) structures – Pontine structures (PPRF and CN VI)
- Contralateral (right) structures – Structures above pons (MLF, CN III and frontal eye field)
- Diagnosis – Right Intranuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) because right MLF is involved
Mnemonic:
- INO – Impaired adduction and Nystagmus Opposite (i.e. Left INO = Left impaired adduction and Right nystagmus)
Frontal Eyefield:
Eyes cannot look to the side opposite to the lesion
Lesion site 4 in figure – Left Frontal eye field
- Both the eyes cannot look to the right
- Slowly drift to the left

Concept cleared! It has been so confusing like forever!
Thank you so much. I never knew this concept is this easy. Hats off!