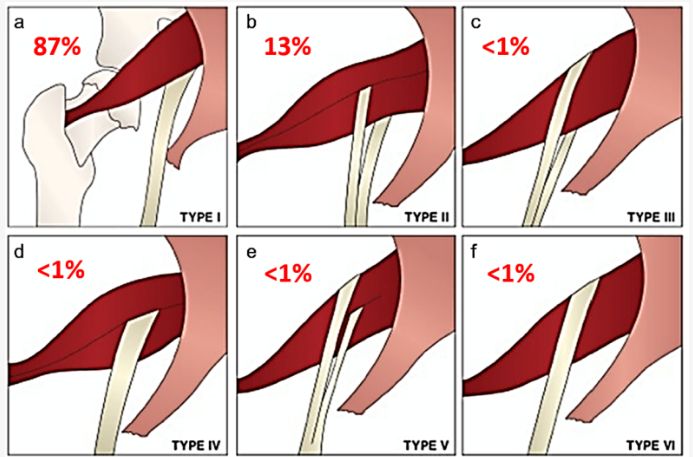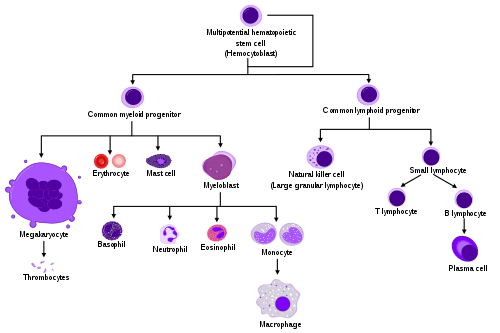
a. SCF (Steel factor): Multipontent stem cells
b. IL-3: Myeloid stem cells (“3” turned down looks like “m“)
c. IL-7: Lymphoid stem cell (“L” turned up looks like “7“)
d. GM-CSF (Granulocyte macrophage Colony stimulating factor): Myeloid lineage (Erythrocytes, Thrombocytes, Granulocytes and Monocytes)
Pharmaceutical: Sargramostim
e. G-CSF: Granulocytes (Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophil)
Pharmaceutical: Filgrastim, peg-filgrastim
f. M-CSF: Monocytes
g. EPO (Erythropoietin): Erythrocytes
Pharmaceutical: Epoietin-alpha, Darbepoietin
h. TPO (Thrombopoietin): Thrombocytes
i. IL-11: Thrombocytes (11 letters in THROMBOCYTE)
Pharmaceutical: Oprelvekin
j. IL-5: Eosinophil (E is the 5th letter)
k. IL-2: T-cells (“T” for “Two” and “T-lymphocytes”)
l. IL-4: B-cells (B4 – Basophill secrete IL-4 → B cell growth)
m. IL-6: Plasma cells (6 letters in PLASMA)
n. IL-15: NK cells (15 letters in GRANULAR KILLERS)
Some other roles of cytokins:
1. IL-8: Neutrophil chemotactic factor
2. IL-12: TH1 differentiation and NK cell activation
3. IFN-gamma: Inhibits TH2 differentiation
4. IL-4: TH2 differentiation and class switching to IgE and IgG
5. IL-5: Class switching to IgA
6. IL-10: Cytokine synthesis inhibition in NK and TH1 cells
7. IL-1: Lymphocyte activating factor

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.