ASBURY CRITERIA FOR GUILLAIN BARRE SYNDROME (GBS)
Required Criteria
Mnemonic: AIDP
1. Areflexia
2. Include in differential and rule out other causes
3. Duration < 4 weeks
4. Progressive weakness of 2 or more limbs due to neuropathy
Supportive criteria
Mnemonic: AIDPS
1. Afebrile
2. Involvement:
- Mild sensory involvement
- Facial or other cranial nerve involvement
3. Demyelinating electrophysiologic evidence
4. Protein in CSF (100-1000 mg/dl) + Low WBC (Albumino-cytologic dissociation)
5. Symmetrical distribution relatively
Why protein is increased in CSF in GBS?
Intense inflammation at the junction of the dorsal and ventral roots leads to breakdown in the blood-brain barrier and the transudation of plasma proteins into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Management of GBS
Mnemonic: AIDP
1. Supportive:
- Analgesia: e.g. NSAIDs
- Airway: may need ventilation in ITU
- Autonomic: may need a urinary catheter
- Antithrombotic: TED stockings, LMWH
2. IVIG 0.4 g/kg/day for 5 days
3. Dexamethasone (corticosteroid): No significant role
4. Plasma exchange (Plasmapheresis): Alternative to IVIG; 5 times during 2 weeks
At about 6 weeks after treatment with IVIG, 5-10% deteriorate after initial stabilization or improvement due to wearing off of therapeutic effect of IVIG in patients in whom immune response is prolonged.
Variants of GBS
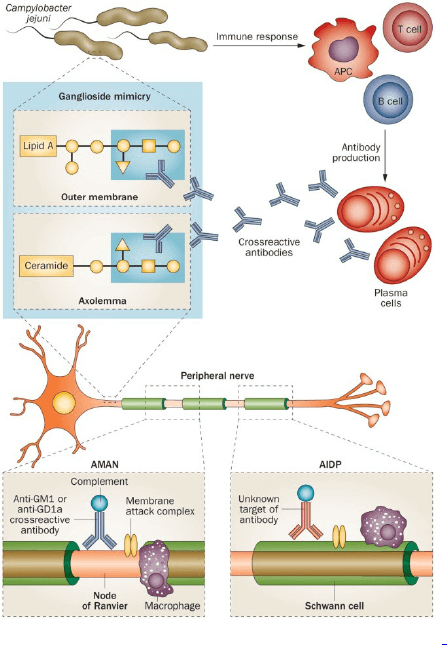
AIDP (Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy): commonest; antecedent viral or bacterial infection
AMAN (Acute motor axonal neuropathy): pure motor form; 60% are seropositive for campylobacter; pediatric
AMSAN (Acute motor sensory axonal neuropathy): adults
Miller Fisher syndrome: Ophthalmoplegia + Ataxia + Areflexia
Acute panautonomic neuropathy: rarest
Pathogenesis of GBS
Molecular mimicry and cross-reactivity: Lipo-oligosaccharide (LOS) of C.jejuni mimic carbohydrate of ganglioside, i.e. anti-ganglioside antibodies.
Very nice
Difference between asbury and brighton criteria?