Boundaries
- Anteriorly and Laterally: Greater and lesser wings of sphenoid
- Posteriorly: Clivus
- Posteromedially: Petrous part of temporal bone
- Floor: Greater wings of sphenoid and Petrous part of temporal bone
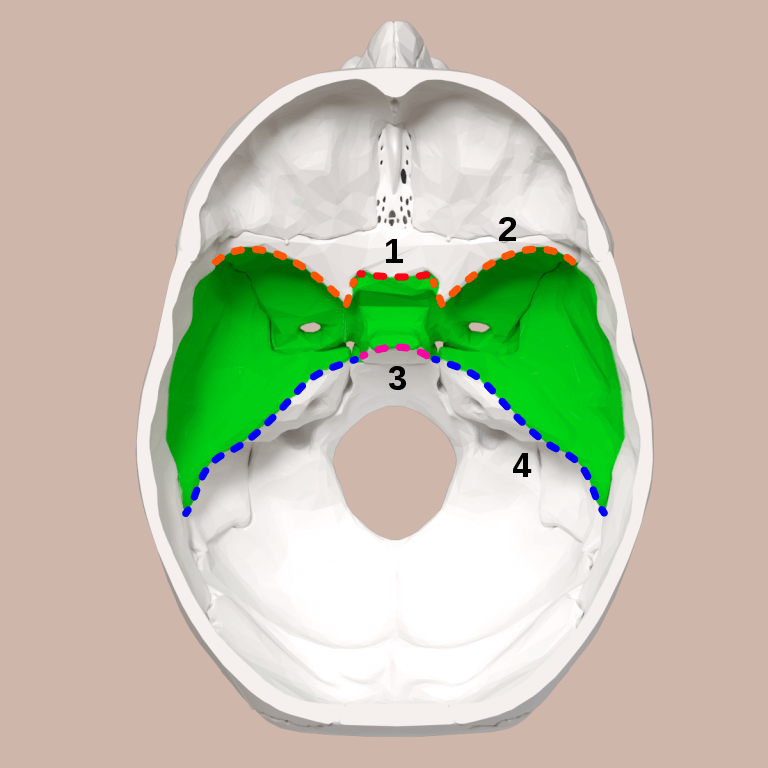
1. Sphenoidal limbus
2. Lesser wing of sphenoid
3. Dorsum sellae of sphenoid bone
4. Petrous part of temporal bone
The body of the sphenoid makes up the central portion of the middle fossa and houses the sella turcica, bounded by the anterior and posterior clinoid processes.
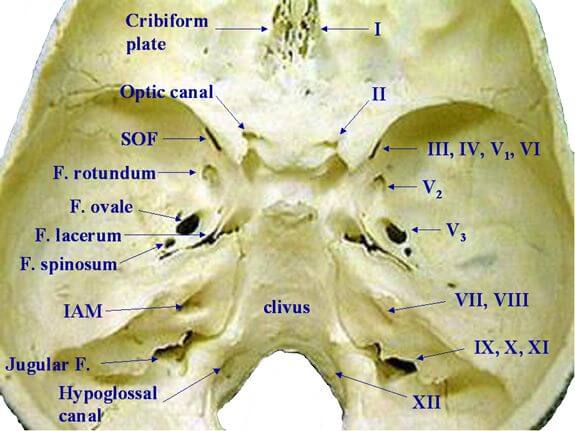
List of Foramina from Anterior to Posterior
Mnemonic: Old Rotund Owls Spin Lazily

- Orbital fissure (Superior orbital fissure, i.e. SOF)
- foramen Rotundum
- foramen Ovale
- foramen Spinosum
- foramen Lacerum
These foramina are in the Sphenoid bone.
Contents of Foramina
1. Superior orbital fissure:
Mnemonic: Everything related to Eyes (LR6 SO4 Rest 3 + CN V1)
- CN III (Occulomotor nerve)
- CN IV (Trochlear nerve)
- CN V1 (Ophthalmic nerve – Lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary branches)
- CN VI (Abducens nerve)
- Ophthalmic vein
2. Foramen rotundum:
Mnemonic: RoMax (CN V2)
- CN V2 (Maxillary nerve)
3. Foramen ovale:
Mnemonic: O-Man/O-MALE including CN V3
- Otic ganglion
- CN V3 (Mandibular nerve)
- Accessory meningeal artery
- Lesser petrosal nerve (parasympathetic fibers from glossopharyngeal nerve which receives a connecting branch from the facial nerve and then joins the otic ganglion)
- Emissary vein
4. Foramen spinosum:
Mnemonic: MMS
- Middle meningeal artery
- Meningeal branch of mandibular artery
5. Foramen lacerum/Carotid canal:
Mnemonic: LIP
- Internal carotid artery
- Pterygoid canal (Vidian canal) artery and nerve
- Vidian artery: branch of maxillary artery
- Vidian nerve: Greater superficial petrosal nerve + Deep petrosal nerve (ends in pterygopalatine ganglion)
Contents
- Temporal lobe
- Pituitary gland
- Trigeminal or Gasserian ganglion
- Greater superficial petrosal nerve (GSPN)
- Intracranial portion of ICA
- Cavernous sinus
Clinical considerations
Medial meningeal artery (MMA):
- Ascends across the pterion (thin sheet of bone)
- Auriculotemporal nerve wraps around it
- Injury results in Extradural hemorrhage
Basilar skull fracture: can result to a carotid-cavernous fistula, manifesting with proptosis, chemosis, and pulsating exophthalmos
Vidian nerve: landmark for safe identification of petrous part of ICA
Greater petrosal nerve: reliable lateral landmark of Kawase triangle (laterally – GPN, anteriorly – CN V1, posteriorly – arcuate eminence)