Structure of erythropoietin (EPO)
- Glycoprotein hormone
- 165 amino acids
- Molecular mass – 30 kDa
Site of production/synthesis of erythropoietin (EPO)
- Kidneys (75-90%): Peritubular interstitial cells
- Liver (15%; chief source in fetus and neonates): Centrilobular hepatocytes
After birth, erythropoietin is not detectable until 8-12 weeks after birth leading to physiological anaemia of the newborn.
Gene for erythropoietin is on chromosome 7.
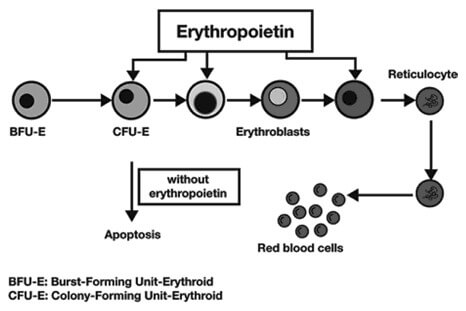
Mechanism of action of erythropoietin (EPO)
1. Receptor: Tyrosine-kinase (JAK/STAT pathway)
2. Functions in hematopoiesis:
- Poerthyroblast production:
- Proliferation: Stimulates mitosis in committed erythroid progenitor cells; it doesn’t act on pluripotent stem cells
- Differentiation (major): Prevents DNA breakdown
- Speeds up RBC maturation: Shortens time between recrutiment of precursor stem cells and release of reticulocytes
- Hemoglobin synthesis: Erythropoietin stimulates the rate-limiting step in hemoglobin synthesis, i.e. formation of ALA from glycine and succininc acid by ALA synthase
Increase in circulating RBCs triggered by erythropoietin takes 2-3 days to appear, since red cell maturation is a slow process.
3. Proposed functions outside bone marrow:
- Blood vessels: Angiogenesis
- Brain: Neurotrophic and neuroprotective
Stimulation of erythropoietin (EPO) production
1. Hypoxia sensed by kidney (renal hypoxia): Hypoxia increases the abundance of the α subunit of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) which would otherwise undergo ubiquitin-proteasome degradation under normoxic conditions. Abundance of HIF-1α enchances production of erythropoietin mRNA. This can be due to hypoxemia or renal vasoconstriction.
2. Hormones: Androgens, Thyroxine, Growth hormone, Prolactin, ACTH, Adrenocortical steroids
3. Hemolysates: Products released following hemolysis of RBCs
Mnemonic: Remember 3 “H” that stimulate erythropoietin production.
Erythropoietin (EPO) metabolism
- Principal site of inactivation is liver.
- Half-life in circulation is about 5 hours.
Clinical uses of erythropoietin (EPO)
- Anemia of chronic renal failure
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Anemia associated with malignancy
- Anemia of chronic disease
- AIDS
- Anemia of prematurity
- Presurgical uses (Jeovah’s witness)
Erythropoietin abuse
In blood doping to increase endurance and physical fitness in sports
References
- Kumar and Clark’s Clinical Medicine By Parveen Kumar, Michael L Clark
- Principles of Physiology for the Anaesthetist, Second edition By Peter Kam, Ian Power
- Ganong’s review of Medical Physiology, 24th edition
- Medical Physiology, 2nd Edition by Walter Boron Emile Boulpaep