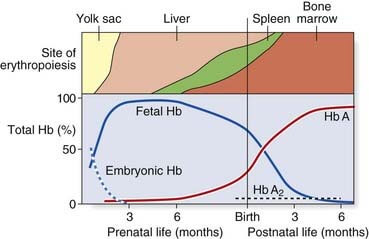
Hemoglobin Switching mnemonics
1st to appear: Embryonic hemoglobin (Gower and Portland)
Switch from fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin: “Gamma goes, Beta becomes, Alpha always”
- Fetal hemoglobin: α2γ2
- Adult hemoglobin: α2β2
| ζ chain | α chain | |
| ε chain | HbE Gower 1 | HbE Gower 2 |
| γ chain | HbE Portland I | HbF |
| β chain | HbE Portland II | HbA |
| δ chain | N/A | HbA2 |
Mnemonic for 4 sites of erythropoiesis
“Young Liver Synthesizes The Blood”
- Yolk sac: 3-8 weeks
- Liver: 6-30 weeks
- Spleen and Thymus: 9-28 weeks
- Bone marrow: 28 weeks to adult
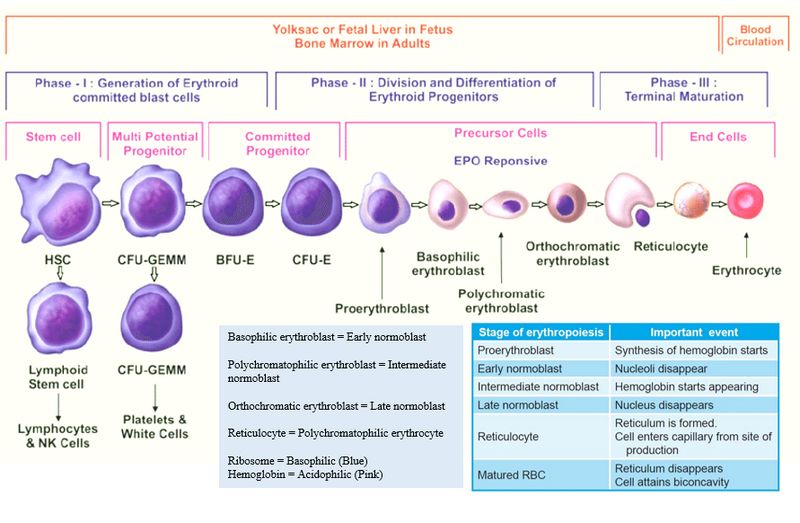
Erythropoiesis Stages Mnemonic
“Powerful Businesses Pollute Our Reeling Environment” OR
Just remember “PB PORE”
- Proerythroblast or Pronormoblast (Rubriblast)
- Basophilic normoblast (Macroblast or Early normoblast or rubricyte)
- Polychromatic normoblast (Intermediate normoblast)
- Orthochromatic normoblast (Normoblast or Late normoblast or metarubricyte)
- Reticulocyte (Polychromatic erythrocyte)
- Erythrocyte
Remember the duration of erythropoiesis from proerythroblast to erythrocyte is 6-8 days (average 7 days).
- Proerythroblast to Reticulocyte = 4 days (1 day for each)
- Reticulocyte to erythrocyte = 2 to 4 days (reticulocyte spends 1-2 days in marrow and circulates for 1-2 days in peripheral blood before maturing to erythrocyte)
As the cell matures the following morphological changes take place progressively:
- Cell Size: Decreases
- Nucleus: Size decreases, chromatin becomes more clumped and the nucleoli disappear
- Cytoplasm: Shrinks
- Cytoplasmic basophilia decreases:
- Ribosome (basophilic because of RNA content, i.e. stains blue) appears first
- Ribosome synthesizes Hemoglobin (acidophilic, i.e. stains pink)
- As the haemoglobin content approaches the desired levels the number of ribosomes decreases.
- As erythropoiesis progressess the cytoplasm changes from deep blue (mainly ribosomes) in basophilic normoblast to polychromatophilic (ribosomes and haemoglobin) in polychromatophilic normoblast and resembling that of a erythrocyte (mainly haemoglobin) in orthochromatophilic normoblast.
- Cell number: The earliest nucleated stages are least numerous and the later stages the most numerous.
AWESOME SUMMARY OR ERYTHROPOIESIS!