Components of Coomb’s test:
Mnemonic: ABCD
- A: Antibody (to be detected)
- B: Blood antigen (RBC)
- C: Coomb’s reagent (Anti-antibody)
- D: Detect agglutination
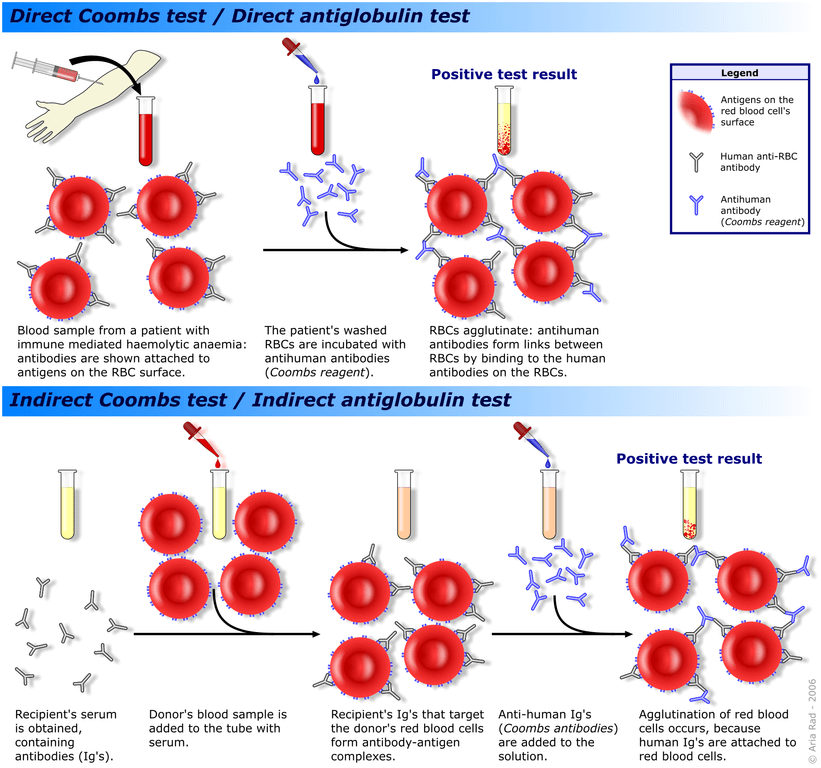
Direct Coomb’s/Antiglobulin test (DAT or DCT):
Mnemonic: In DAT/DCT we take A+B from patient and add C [(A+B) + C]
Another Mnemonic: DCBA (Direct Coomb’s detect Blood Bound Antibody)
- Patient component: RBC +/- Antibody
- Coomb’s reagent: Anti-antibody
- Result: Agglutinates if Antibody bound to RBC (Positive)
Indirect Coomb’s/Antiglobulin test (IAT):
Mnemonic: In IAT, we take A from patient and add B+C [A+(B+C)]
- Patient component: +/- Antibody (serum)
- Reagent: donor RBC + Coomb’s reagent (Anti-antibody)
- Result: Agglutinates if Antibody present in serum (Positive)
Clinical Examples
a. Direct Coomb’s test (DCT):
- Mix infant’s RBC with Coomb’s reagent: if cells agglutinate, maternal antibody is present
b. Indirect Coomb’s test (IAT):
- Prenatal testing: Mix mother’s serum with Rh (D)+ cells (antigen) and add Coomb’s reagent: cells agglutinate if there is anti-D antibody is present in mother (this may be due to Rh+ fetus or Rh+ blood transfusion)
- Rho-gam (anti-D antibody) is given to Rh- mother to neutralize circulating Rh antigen preventing the formation of antibody.
- Cross-matching: Mix recipient’s serum with donor’s blood with antigens and add Coomb’s reagent: cells agglutinate if there is antibody to donor blood antigen in recipeint’s serum.

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.