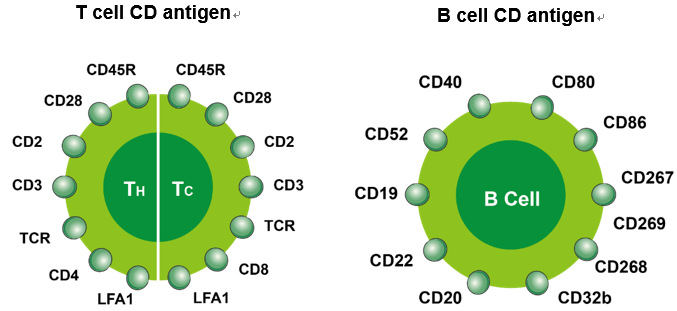
“CD” in immunology stands for Cluster of Differentiation and includes cell surface markers that can be detected by lab technique called flow cytometry. Well, we will just focus on the ones you need to remember at undergraduate level. If you wish to go into further details, there are plenty of resources available in the internet.
CD45 = Leukocyte Common Antigen (LCA) i.e. expressed in all except erythrocytes and platelets.
CD3 = Pan-T cell marker
CD19 = Pan-B cell marker
CD13, CD33 and CD11b = Pan-myeloid markers
T cells and B cells
T cells: Tiny numbers
- CD2
- CD4 (T-helper cells)
- CD8 (Cytotoxic T cells; i.e. 2 X 4 = 8)
- CD28 (Costimulatory molecule needed to activate T cells) – has “2” and “8”
- Also: CD1, CD3, CD5 and CD7
B cells: Big numbers
- CD10 or CALLA (Common ALL Antigen): Pre-B cells and derivatives
- CD21 (EBV receptor)
- CD19, 20, 22, 23
- CD 40 (Competence signal molecule needed for isotype switching and formation of memory cells)
- Mnemonic: CD 19 + CD 21 = CD40
Receptors present in Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) including B cells:
- CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2): Cosimulatory molecules present in Antigen Presenting Cells (APC)
- MHC class II
Wannabe T cells: Add 1 in front of CD4 and CD8
- Macrophages (CD14)
- Neutrophils (CD18)
Remember in sequence: 34, 45, 56 (Stem cells, Lymphoid pecursor and then NK cells)
Stem cells: CD34
Stem cell markers are CD34, tDT and HLA-DR.
Leukocyte common antigen or LCA: CD45
NK cells (that come from lymphocyte precursors): CD56 (also CD16)
- This can also be remembered as 1 + 5 = 6 (CD16 and CD56)
Dendritic cells: CD1 and CD11
- Langerhans cells (Dendritic cells of skin that are APCs): CD1a (Used in Langerhans cell histiocytosis)
- Dendritic cells including Langerhans cells: CD11c (Integrins that interact with ICAMs)
Hairy cell leukemia: A type of mature B-cell CLL
- Early B cells: CD19, CD20, CD22 (CD21 is early B cell marker and absent in hairy cell leukemia)
- CD11c
- CD103 (Regulatory T cells and Intestinal mucosal dendritic cells)