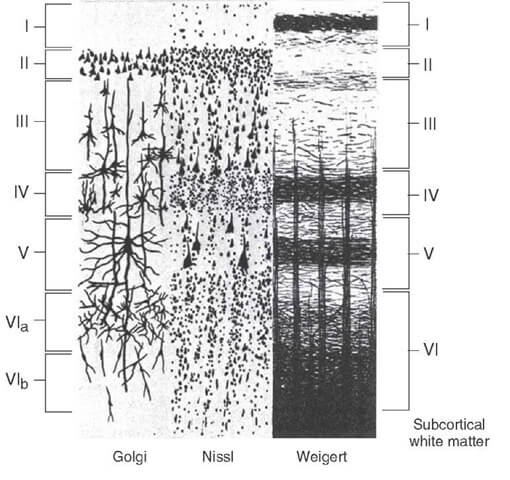
The neocortex have 6 layers and allocortex have only 3 layers.
The 6 layers of Neocortex:
Orientation of layers:
- Outer: Towards meaninges
- Inner: Towards white matter
Idea about the layers:
- Molecular or plexiform: Only cell processes
- Granular layer: Densely packed stellate cells
- Pyramidal layer: Medium and Large pyramidal cells
- Multiform layer: Different types of cells
- Pyramidal cells are absent in inner granular layer
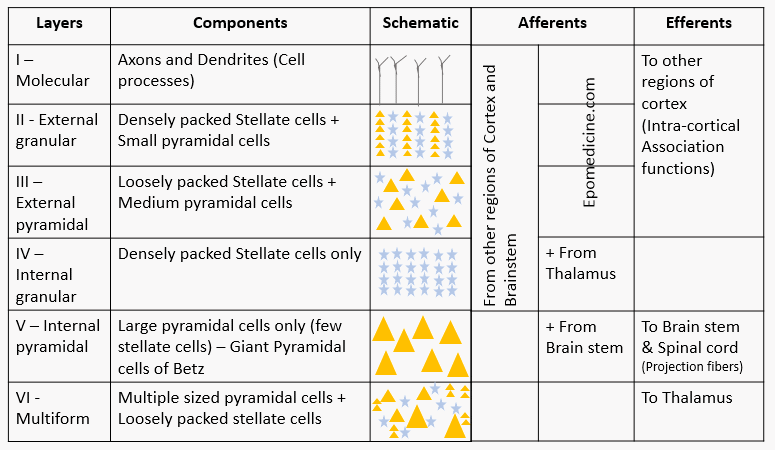
| Layers | Components | Afferents | Efferents | |
| I – Molecular | Axons and Dendrites (Cell processes) | From other regions of Cortex and Brainstem | To other regions of cortex
(Intra-cortical Association functions) |
|
| II – External granular | Densely packed Stellate cells + Small pyramidal cells | |||
| III – External pyramidal | Loosely packed Stellate cells + Medium pyramidal cells | |||
| IV – Internal granular | Densely packed Stellate cells only | + From Thalamus | ||
| V – Internal pyramidal | Large pyramidal cells only (few stellate cells) – Giant Pyramidal cells of Betz | + From Brain stem | To Brain stem & Spinal cord (Projection fibers) | |
| VI – Multiform | Multiple sized pyramidal cells + Loosely packed stellate cells | To Thalamus | ||
The 3 layers of allocortex:
- Molecular layer
- Pyramidal layer
- Multiform layer
Allocortex is found in: Limbic system
- Olfactory cortex
- Hippocampal formation
- Subiculum
Mesocortex: A transitional type of 3 to 6-layered cortex between neocortex and allocortex –
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Pre- and Para-subiculum
- Insula
Neurons of the cortex:
- Pyramidal cells:
- Large layer V pyramidal cells project axons to brainstem and spinal cord.
- Smaller layer II and III pyramidal cells project axons to other cortical areas.
- Stellate cells: Interneurons whose axons remain within the cortex
- Fusiform cells (in deeper layers): Gives rise to corticothalamic projections
- Horizontal cells of Cajal
- Cells of Martinotti
Bands of Baillarger: Formed by high concentration of horizontally arranged nerve fibers.
- External band: In layer IV
- Internal band: In layer V

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.


Clear and Concise- thanks!