Location
Alpha = Arteries and smooth muscles
Beta = Beats or Breaths
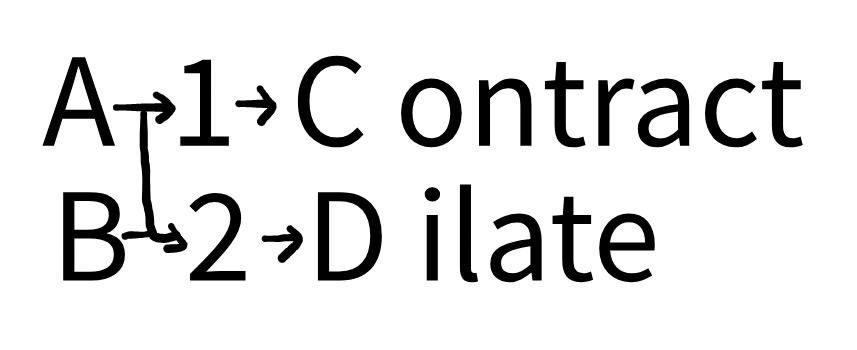
Types and Action
1 = Contract
2 = Dilate
Receptors
Alpha 1:
- Vasoconstriction
- Mydriasis (contraction of iris dilator muscles)
- Bladder sphincter contraction
- Uterus contraction
Alpha 2:
- Smooth muscle dilation
- Presynaptic terminal inhibition (negative feedback)
Beta 1:
Mnemonic: We have 1 HEART
- Increase heart rate and contraction
Beta 2:
Mnemonic: We have 2 LUNGS
- Dilate smooth muscles including bronchioles
Beta 3:
Mnemonic: 3 = Triglyceride
- Lipolysis
Excellent mnemonics, thank you for teaching and sharing. God bless you ❤️❤️❤️❤️
You’ve helped a soul🙏🙏