Tests the function of: Posterior or Dorsal column which may be impaired in:
- Subacute combined degeneration (SCD) of spinal cord (Vitamin B12 deficiency)
- Posterior cord syndrome (Posterior spinal artery infarction)
- Hemisection of spinal cord (Brown Sequard syndrome)
Pathophysiologic basis: When the patient is standing with the eyes open, visual, proprioceptive, and vestibular information is used to maintain postural stability. With the eyes closed, the patient must rely on proprioception and vestibular function.
Technique
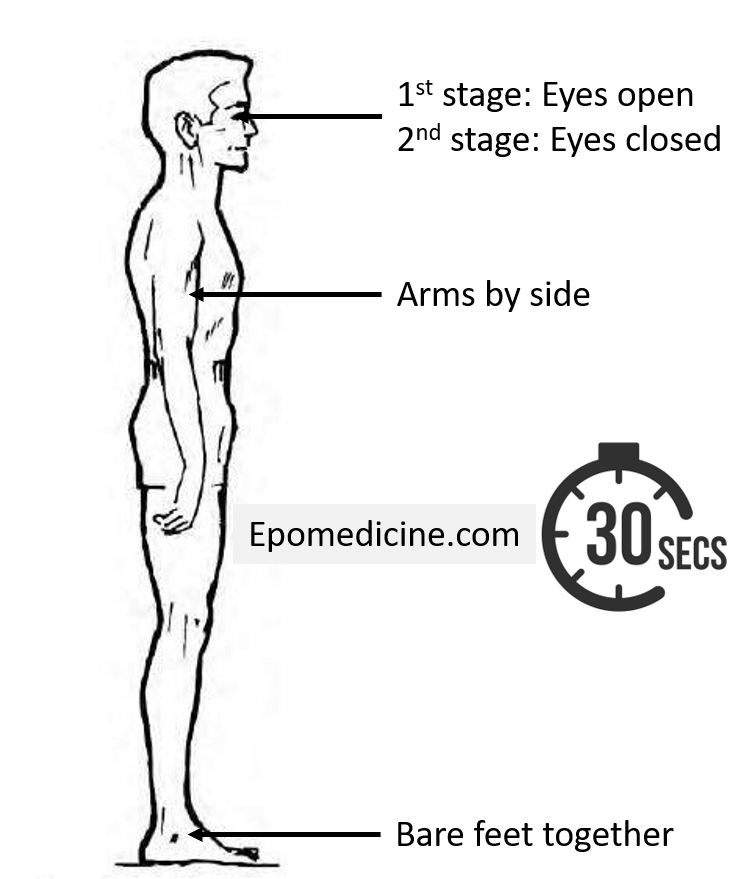
Romberg position:
1. Feet position: 2 feet together without shoes on a firm, flat surface
2. Arm position: At the sides or folded across chest or outstretch forwards (can simultaneously check pronator drift and finger-nose test)
Failed test: Different interpretations used across various literatures –
- Swaying at ankles rather than at hip
- Taking a corrective step to the side
- Use of upper extremities to stabilize the body
- Significant sway with the patient nearly falling
False positive: Histrionic sway
1. Swaying at hip
2. Patient may take a step with eyes closed (not possible in true Romberg positive)
3. Instability can often be eliminated by diverting the patient’s attention (ask to detect numbers the examiners write with his/her fingers on patient’s forehead, to wiggle the tongue or to perform finger to nose testing)
4. Toes are extended (toes are strongly flexed to grip the floor in true Romberg positive)
Stage 1: Romberg position with eyes open for 30 seconds
- Patient must be stable
- Failed test: Romberg is not applicable
- Widen the stance to the point where they are stable before proceeding to Stage 2
Stage 2: Romberg position with eyes closed for 30 seconds
- Patient is stable: Romberg negative
- Failed test: Romberg positive
Modifications
1. Sharpened or Tandem Romberg test: Similar to the Romberg test but the patient is asked to stand with one foot directly in front of the other (heel touching toe)
2. Ropper’s refined Romberg test: Turning the head side to side eliminates vestibular clues and increases the reliance on proprioception
Further testing
1. Failed Romberg test with eyes closed: Sensory ataxia; confirm with –
- Impaired conscious proprioception and vibratory sense
- Diminished or absent ankle reflex
2. Failed Romberg test with eyes open: Indicates cerebellar problem; confirm with –
- Vibratory sense, proprioception and ankle reflexes are normal
References:
- DeJong’s – The Neurologic Examination (8th Edition)
- Fundamentals of Tests and Measures for the Physical Therapist Assistant By Stacie J. Fruth, Carol Fawcett
- Forbes J, Cronovich H. Romberg Test. [Updated 2021 Dec 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563187/