Deep tendon reflexes are monosynaptic reflexes integrated at lamina IX of the spinal cord. Deep tendon reflexes may be interpreted as:
- Normal
- Diminished or absent (hyporeflexia): Lower motor neuron lesions
- Exaggerated or clonus (hyper-reflexia): Upper motor neuron lesions
- Inverted or paradoxical: Damaged afferent pathway
| Name | Spinal level | Peripheral nerve | Location struck to elicit | Response |
| Upper extremity | ||||
| Biceps | C5-C6 | Musculocutaneous | Examiner’s fingers over biceps tendon | Biceps contraction with slight elbow flexion |
| Brachioradialis or Radial periosteal or Supinator | C6 | Radial | Examiner’s fingers about 10 cm above the wrist on radial aspect of forearm (musculo-tendinous junction) | Elbow flexion with variable supination – Exaggerated: finger and wrist flexion too – Inverted reflex: absent elbow flexion/supination with present finger/wrist flexion |
| Triceps | C7-C8 | Radial | Triceps tendon just above the olecranon insertion | Triceps contraction with elbow extension – Inverted/paradoxical reflex: elbow flexion instead of extension |
| Finger flexor or Warternberg’s sign | C8-T1 | Median and ulnar | Examiner’s fingers on the palmar surface of the patient’s fingers | Flexion of patient’s fingers and distal phalanx of thumb |
| Scapulohumeral | C4-C5 | Dorsal scapular | Tip of scapula at vertebral body | Retraction of scapula with adduction of humerus |
| Deltoid | C5-C6 | Axillary | Examiner’s finger over deltoid insertion on humerus | Slight abduction of upper arm |
| Pectoralis | C5-T1 | Medial and lateral pectoral | Examiner’s finger on deltopectoral groove | – Normal: Contraction of pectoralis major felt but not seen – Hyperactive: Adduction and slight internal rotation of arm at shoulder |
| Clavicle | Lateral aspect of clavicle | Hyperreflexia: Contraction of various muscle groups – Watch for symmetry | ||
| Latissimus dorsi | C6-C8 | Thoracodorsal | Examiner’s finger over latissimus dorsi tendon at intertubercular groove of humerus | Abduction and slight shoulder internal rotation |
| Pronator teres | C6-C7 | Median | Volar surface of distal radius or dorsal aspect of styloid process of ulna | Brief supination followed by pronation of forearm |
| Trunk | Minimal/absent in normal | |||
| Deep abdominal | T5-T12 | Intercostal nerves, Ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves | Anterior rectus abdominal muscle sheath | Contraction of abdominal muscles and deviation of umbilicus towards site of stimuli (weak or absent normally) |
| Iliac | T10-T12 | Lower intercostal nerves | Over iliac crest | Contraction of lower abdominal muscles |
| Symphysis pubis | T11-T12 and upper lumbar | Lower intercostal, ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric | Over symphysis pubis, 1.5-2 cm from midline | Normal ‘upper response’: Contraction of abdominal muscles and downward movement of umbilicus Exaggerated ‘lower response’ or puboadductor reflex: Ipsilateral adductor muscle contracts with some hip flexion |
| Costal periosteal | T5-T9 | Upper intercostal | Xiphoid process, lower rib margins | Contraction of upper abdominal muscles and slight movement of umbilicus towards side of stimulation |
| Lower extremity | ||||
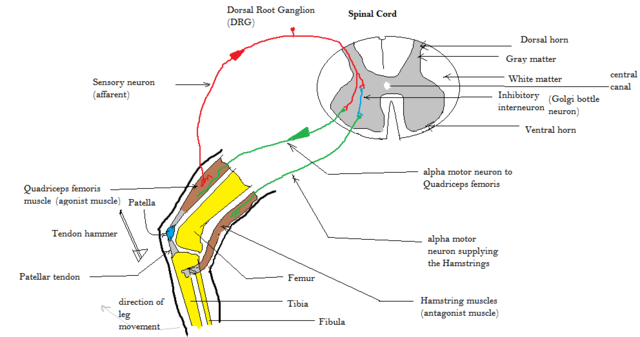
| Knee or Patellar or Quadriceps | L3-L4 | Femoral | Patellar tendon just below patella | Palpated/seen quadriceps contraction with knee extension – Absent: Westphal’s sign – Exaggerated: Response obtained by tapping over examiner’s finger superior to patella (supra-patellar reflex) or Clonus seen – Inverted: Contraction of hamstrings and knee flexion |
| Achilles or Ankle or Triceps surae | S1-S2 | Tibial | Achilles tendon just above its insertion on calcaneus | Hamstring contraction with plantar flexion – Hyperactive: Elicited by tapping other areas of sole of foot (medioplantar reflex) or clonus – Paradoxical: Elicited by tapping anterior aspect of ankle |
| Adductor | L2-L4 | Obturator | Medial epicondyle femur | Contraction of adductors with inward movement of thigh – Exaggerated: Crossed or bilateral adduction of thigs |
| Medial hamstring | L5 | Tibial portion of sciatic nerve | Examiner’s finger over semimembranosus or semitendinosus at insertion of tibia | Hip extension and knee flexion with internal rotation |
| Lateral hamstring | S1 | Tibial portion of sciatic nerve | Examiner’s finger over biceps femoris tendon insertion or fibular head | Knee flexion |
| Peroneal or Tibialis anterior | L4-S1 | Deep and superficial peroneal | Examiner’s finger over distal 1st and 2nd metatarsal of inverted and plantar-flexed foot | Eversion and dorsiflexion of foot |
| Tibialis posterior | L5-S1 | Tibial nerve | Tibialis posterior just above and behind medial malleolus | Foot inversion |
| Tensor lata | L4-S1 | Superior gluteal | Origin of tensor fascia lata near ASIS | Slight thigh abduction |
| Gluteal | L5-S1 | Inferior gluteal | Lower portion of sacrum or posterior aspect of ilium near gluteus maximus insertion | Contraction of gluteus maximus and extension of thigh |
| Head | ||||
| Jaw or Chin | Pons | V3 division of trigeminal nerve | Examiner’s finger on jaw tip | Upward movement of jaw |
References:
- Lin-Wei O, Xian LLS, Shen VTW, Chuan CY, Halim SA, Ghani ARI, Idris Z, Abdullah JM. Deep Tendon Reflex: The Tools and Techniques. What Surgical Neurology Residents Should Know. Malays J Med Sci. 2021 Apr;28(2):48-62. doi: 10.21315/mjms2021.28.2.5. Epub 2021 Apr 21. PMID: 33958960; PMCID: PMC8075597.
- DeJong’s – The Neurologic Examination, 8th Edition