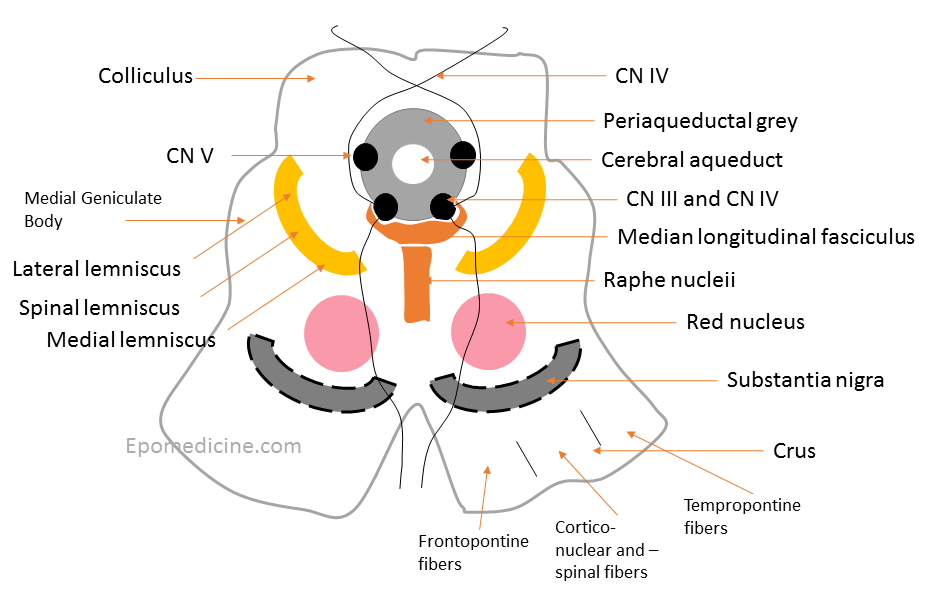
The cross-section of midbrain can be compared to the “upside down striped face of a red-eyed demon“. Using this analogy of a demon face, lets assign the structures found on the cross-section of midbrain: Ear = Crus cerebri Medial – frontopontine fibers Middle – corticonuclear and corticospinal tract Lateral –…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
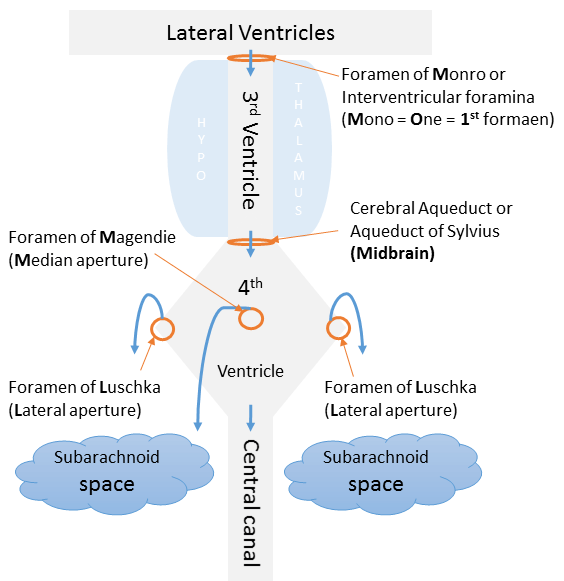
CSF Circulation Made Simple
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Production and Absorption CSF is produced by the choroid plexus that lines the ventricles. Choroid plexus = Infoldings of blood vessels of piamater + Modified ciliated ependymal cells Tight junctions of the choroid plexus cells form Blood-CSF barrier. CSF is reabsorbed by arachnoid granulations to enter dural…
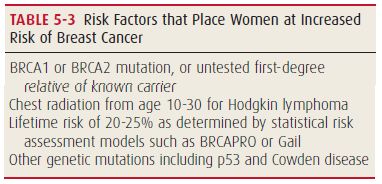
Breast Cancer Screening
ACS recommendations (2015) For women with average risk: 40-44 years: mammogram on patient’s choice 45-54 years: mammogram yearly >54 years: mammogram 2 yearly or yearly based on patient’s choice Women must be informed on the benefits and harms of mammographic screening Regular clinical breast exam and breast self-exam are not…
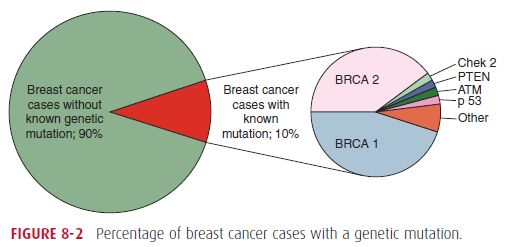
Breast Cancer Risk Factors with Mnemonics
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BREAST CANCER Incidence: In general, less industrialized nations tend to have lower rates of breast cancer, with Japan being an exception to this rule. The highest rates are seen in Europe and North America. Age at onset: Race: incidence is higher among white women than African- American woman, but the mortality is higher…
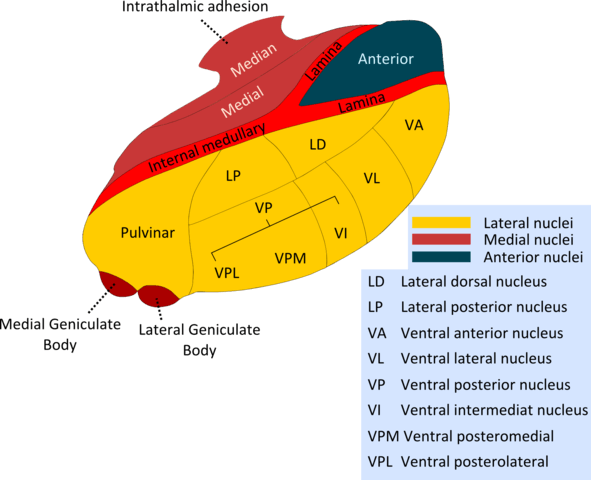
Thalamic Connections Mnemonic
Structure of Thalamus A vertical “Y” shaped white mater – internal medullary lamina divides thalamus into: In anatomical position: Pulvinar = Posterior end or posterior pole of thalamus Thalamic Connections Picture mnemonic Remember the schematic diagram drawn below showing important parts of thalamus in an anticlockwise fashion: Now, we assign…
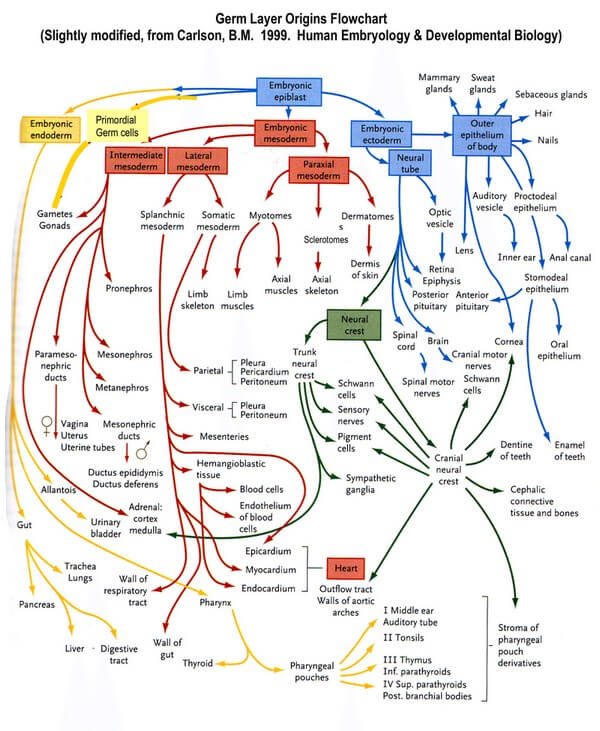
Germ Layer Derivatives – Mnemonics
Principle of Germ Layer Segmentation Ectoderm gives further rise to neuroectoderm and neural crest cells. Endoderm remains intact. Mesoderm gives further rise to paraxial mesoderm (somitomeres and 35 pairs of somites), intermediate mesoderm, and lateral mesoderm: General Rule for Germ Layer Derivatives Ectodermal derivatives: 1. Everything that makes you attractive: Skin, hair,…
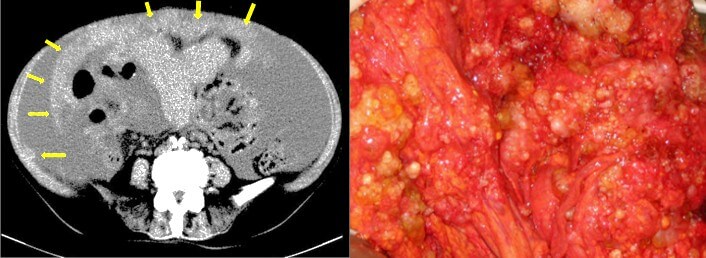
Omental Cake
Definition of Omental Caking Thickening of the omentum resulting from localized or diffuse infiltration of omental fat by soft tissue density mass is referred as “omental caking”. It is a radiological sign, which is often identified in CT scan. Involved Anatomical Structure in Omental Caking Greater Omentum – an extension of…
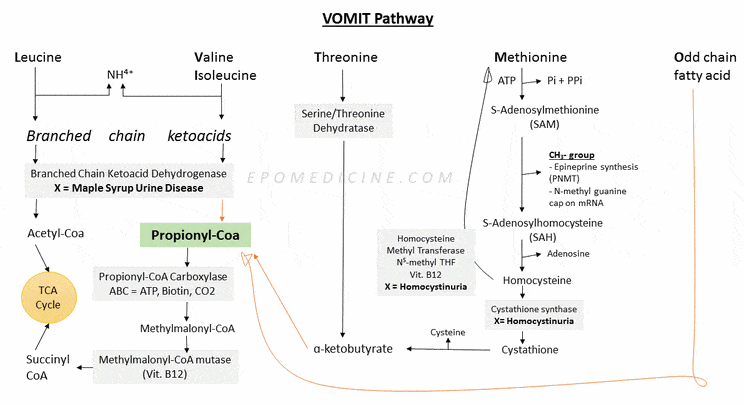
VOMIT Pathway – Propionyl CoA Intermediate
Propionyl CoA is a common intermediate in catabolism of essential amino acids and odd chain fatty acids. It is also called VOMIT pathway which stands for: Valine Odd chain fatty acids Methionine Isoleucine Threonine They enter TCA cycle – using PMS pathway: Propionyl CoA Methylmalonyl CoA Succinyl CoA Defects in…