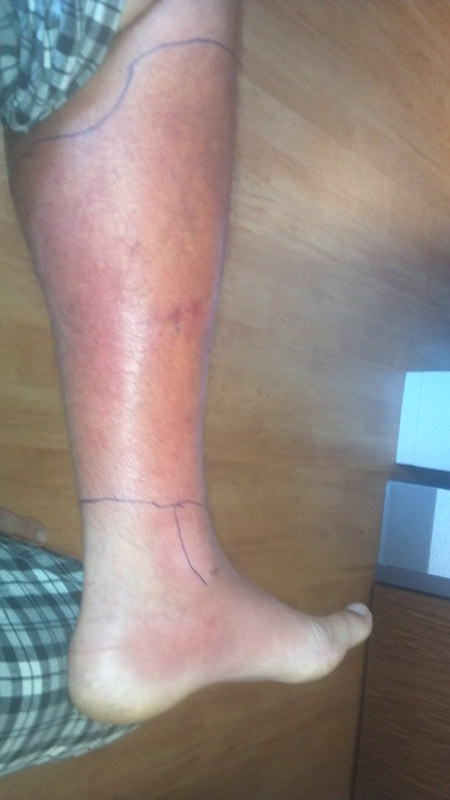
Cellulitis is a rapidly spreading acute inflammation with infection of skin and subcutaneous tissue that spreads widely through tissue spaces. It is commonly caused by either Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus. Erysipelas is a superficial form of cellulitis involving lymphatics; it has a peau d’orange appearance and a sharp border. It characteristically appears on the face. Since,…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
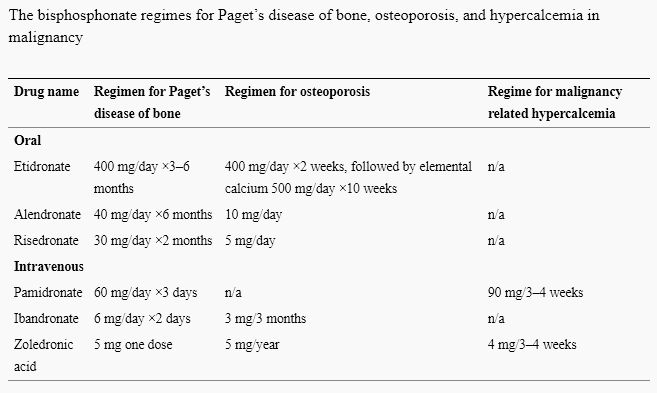
Bisphosphonate Pharmacology
Classification Non-nitrogen containing (1st generation): Etidronate Clodronate Tiludronate Nitrogen containing (2nd and 3rd generation): a. 2nd generation (alky-amino nitrogen containing): Pamidronate Alendronate Ibadronate Olpadronate b. 3rd generation (heterocyclic nitrogen containing): Risedronate Zoledronate Chemical structure Stable derivatives of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) Mechanism of action Strong attachment to hydroxyapatite mineral found in…
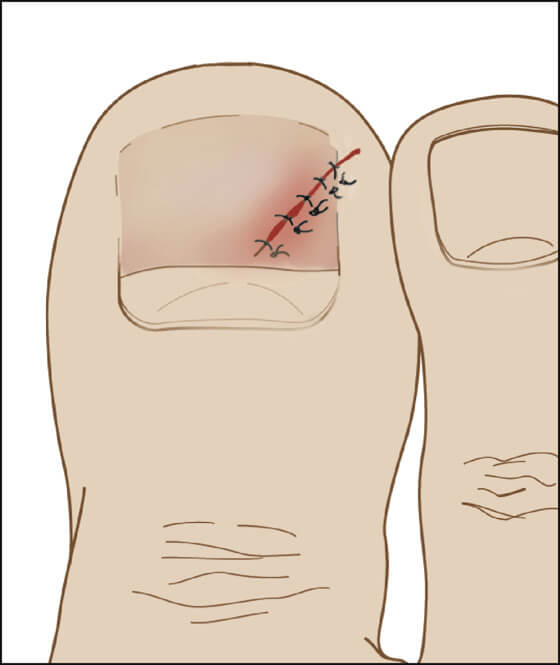
Nail Bed Injuries : Van Beek Classification and Management
Clinically, the Van Beek classification system denominates 5 principal nail bed injuries, subclassified by location within the nailbed (involving either the sterile and/or germinal matrix, respectively) and the extent of injury. Germinal Matrix Injury GI: Small subungual hematoma proximal nail (<25%) GII: Germinal matrix laceration, large subungual hematoma (>50%) GIII:…
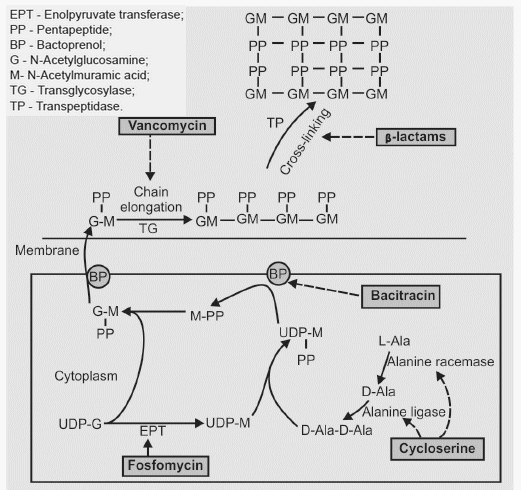
Antimicrobial Mechanism of Actions – Everything you need to know
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors A peptidoglycan monomer consists of 2 joined amino-sugars, N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and N-acetyle muramic acid (NAM), with a pentapeptide coming off of the NAM. So, a peptidoglycan monomer is a NAG-NAM-pentapeptide. These peptidoglycan monomers are synthesized in cytosol and transported across cytoplasmic membrane by Bactoprenols (BP)….
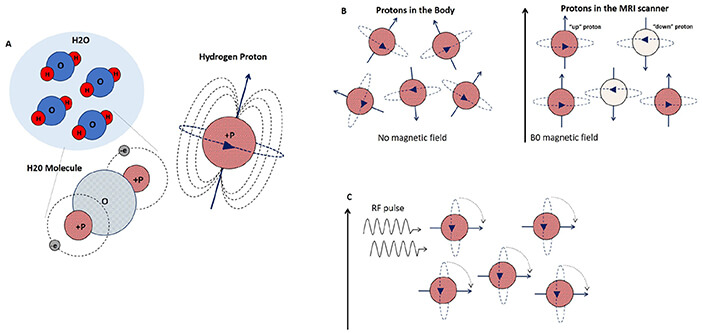
MRI Physics Made Easy
Human body is made up of water, which means a large number of atoms inside our body is hydrogen atoms, the nucleus of which contains a positively charged proton that spins (or precesses) around an axis like a child’s top. This spinning generates its own tiny magnetic field, giving the…

Dog bite wounds : Primary closure or Delayed closure?
A study of 50 dog bite wounds revealed that the commonest colonizing: Aerobic micro-organisms are: Pasteurella (50%), Streptococcus (46%), Staphylococcus (46%), Neisseria (32%), and Corynebacterium (12%), Eikenella corrodens (2%) Anaerobic micro-organisms are: Fusobacterium nucleatum (16%), Bacteroides tectus (14%), Prevotella heparinolytica (14%), Propionibacterium acnes (14%), Prevotella intermedia (8%), Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (8%),…
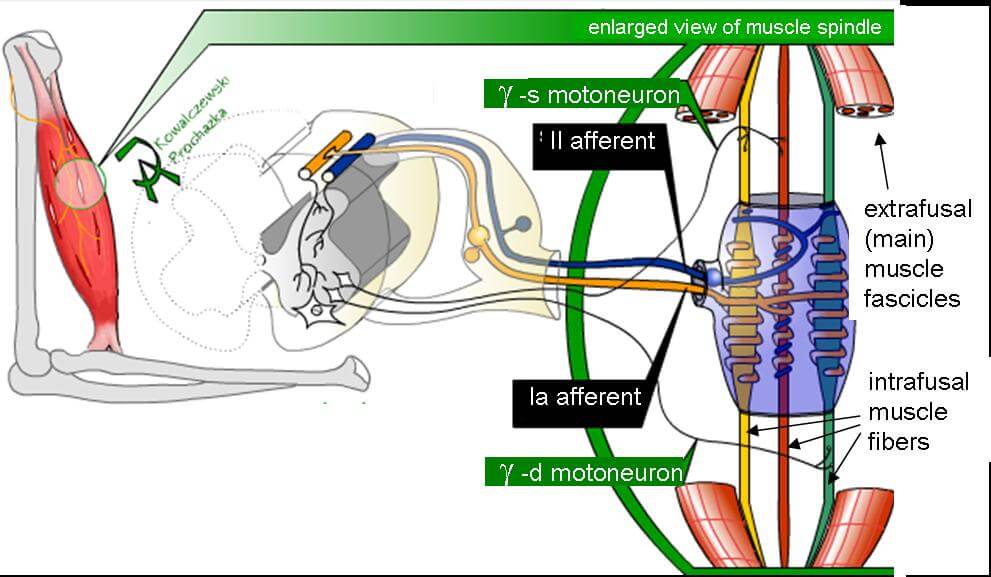
Nerve fibers – Classification
Nerve fibers can be classified as A, B and C and A type fibers can be further classified into alpha, beta, gamma and delta. The size and myelination (thus conduction) progressively decreases in the descending order. A alpha: Efferent (Somatic motor) – To extrafusal fibers (muscle spindle) Afferent (Proprioception): Ia…
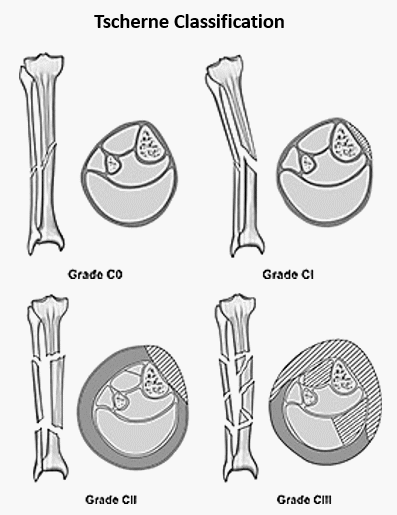
Oestern and Tscherne Classification for Closed fractures
The classification system for closed fractures is based on the physiologic concept that the energy imparted to the bone (and the resultant fracture pattern) directly correlates with the energy transferred to the surrounding soft tissues. Grade Soft tissue injury Fracture Compartment C0 Absent or Negligible Simple (Spiral) Soft and/or Normal…