Peculiarities of cerebral circulation: 1. Brain and spinal cord is isolated from endothelium by BBB composed of continuous capillaries that limits movement of proteins and electrolytes 2. Fluid movement is primarily determined by osmolar gradient (in contrast to peripheral tissues – transcapillary gradient of large macromolecules) 3. Hence, administration of…
Category: Clinical Skills and Approaches
History taking and examination skills and Flowchart approaches to commonly encountered medical conditions and diseases.
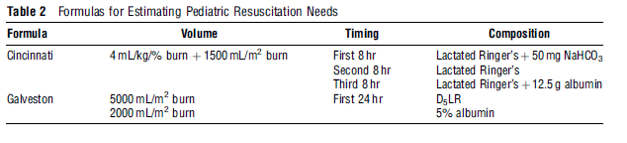
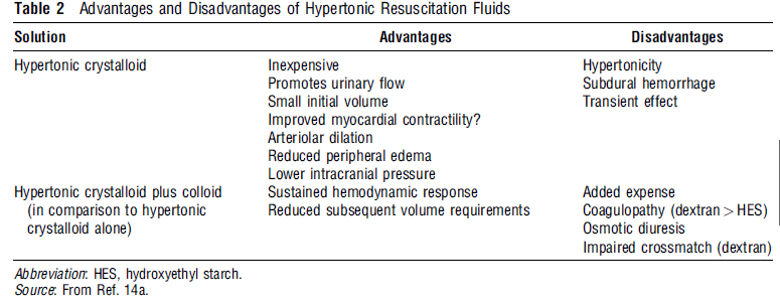
Burn Fluid Resuscitation
A) Clinical endpoints suggesting adequacy of burn fluid resuscitation: B) Pathophysiology of Burn:
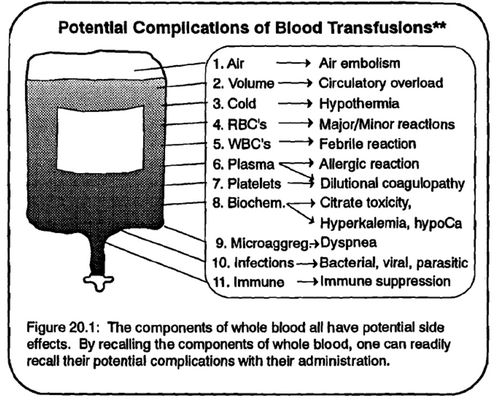
Perioperative Fluid Management
Author: Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, KISTMCTH A) RELEVANT ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Details of the body fluid compartments are described here Microvessels for fluid exchange: The Exchange Vessels – capillaries and most proximal part of the venules Sinusoidal capillaries (liver, spleen, bone marrow): freely permeable to all solutes Fenestrated capillaries (glands, glomeruli, GIT):…
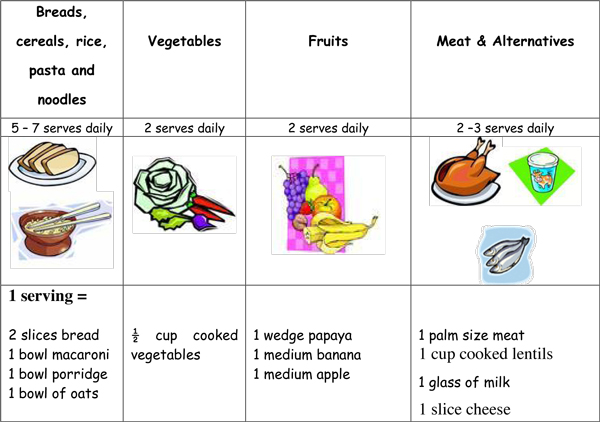
Nutritional History Made Easy
Energy Requirement 1. For a child with normal body weight: 100 Kcal/kg for 1st 10 kg Add 50 Kcal/kg for next 10 kg Add 20 Kcal/kg for body weight additional to 20 kgs 2. By age: For ≤ 1 year: 100 Kcal/kg/day Every additional years till puberty: Add 100 Kcal/year…

History and Examination in Ophthalmology
A) HISTORY Besides chief complaints, other portion of history is similar to the one you prepare in internal medicine. 1. Description of symptom (SOCRATES): S – Site (Unilateral or Bilateral) O- Onset C – Character R – Radiation (if applicable) A – Aggravating and relieving factors T – Timing and…
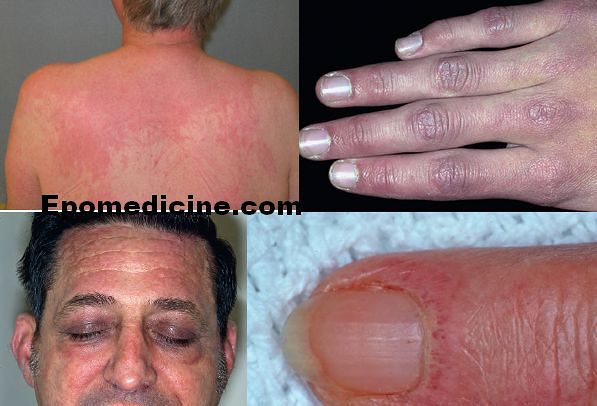
Skin signs of Dermatomyositis: Heliotrope rash, Grotton papules and Shawl sign
Dermatomyositis is a connective tissue disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of voluntary muscles and skin. It is more common in women and the age of onset is 50-70 years. A) Heliotrope Rash: It is a macular, confluent, purple or purple/red rash over both eyelids and periorbital tissue present with or…
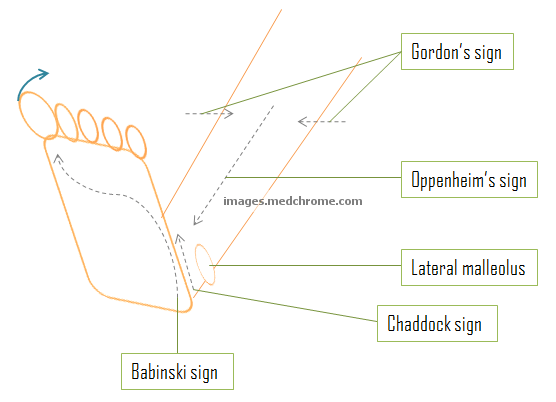
Pathological reflexes – Variations of Babinski
Normally, the pathological reflexes are not evident because they are suppressed by cerebrum at brainstem or spinal cord level by 6 months of age. Importance: Up-going (dorsiflexion) toe can be elicited at various sites and all indicated Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) lesion. Use a blunt-pointed object like fingernail or tip…
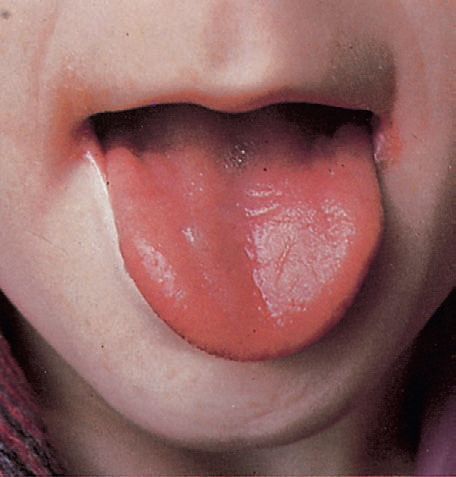
Hematological Signs – Angular Stomatitis and Atrophic Glossitis
ANGULAR STOMATITIS/CHEILITIS Definition: Maculopapular and vesicular lesions grouped on the skin at the corners (or ‘angles’) of the mouth and the mucocutaneous junction. It is made worse by licking the lips. Causes: 1. Oral candidiasis 2. Poorly fitting dentures 3. Bacterial infection 4. Less common Nutritional deficiencies (especially riboflavin, iron and pyridoxine) Iron…