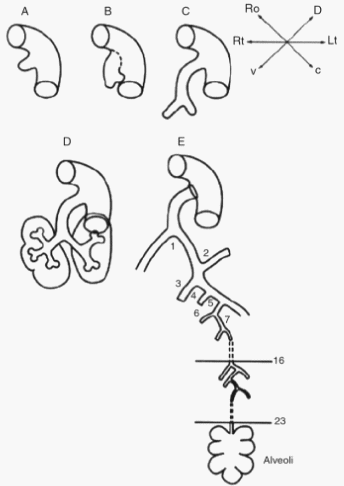
Remember the mnemonic – “Every Premature Child Takes Air“. The development of lungs comprises of 5 distinct stages: Embryonic (3-8 weeks, i.e. embryonic period) Pseudoglandular (5-16 weeks) Canalicular (16-26 weeks) Terminal saccular (26-36 weeks) Alveolar (36 weeks to 40 weeks and continues to childhood) The first and last stages, i.e….
Author: Epomedicine
Diaphragm and Body Cavities Development – Embryology Made Easy
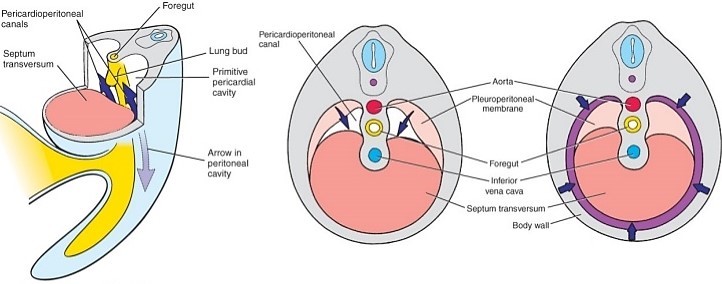
Let’s go back to the 4th week during the development of heart. The primitive intraembryonic coelom forms in the lateral and cardiogenic mesoderm during 4th week of development. Like the heart fields, the intraembryonic coelom has a horse-shoe configuration during this period: A thick mesodermal plate called “septum transversum” lies…
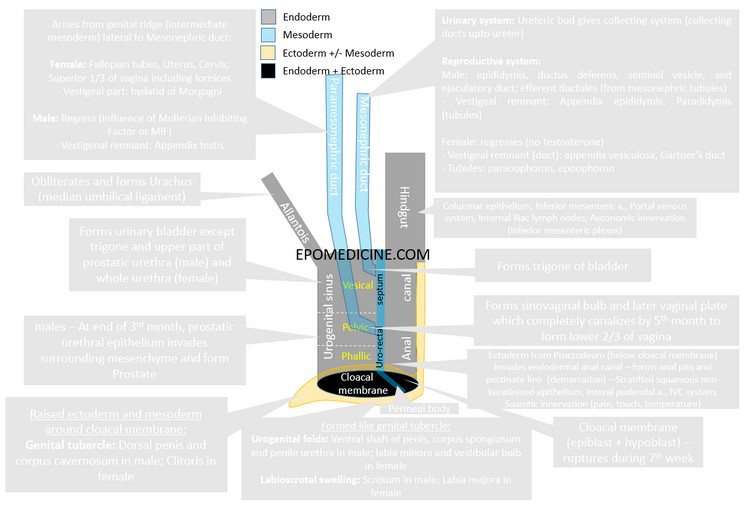
Cloaca in Embryology – Urogenital and Anal Development
Cloaca literally meas a “sewer” – a coduit for carrying of drainage water and waste matter. The cloaca in human fetus have the same function, i.e. carries waste porducts in the from of urine and stool. Cloaca: Common chamber for the hindgut and urinary systems. Formation of cloaca: Endodermal – incorporation…
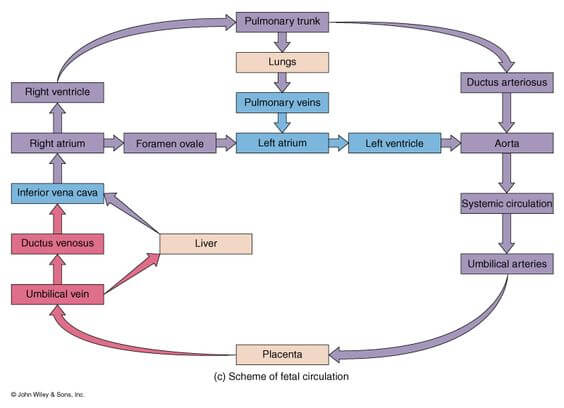
Fetal Circulation Made Easy
Following are the important features of fetal circulation: 1. Placenta plays the role of lungs; lungs are not functional: Like pulmonary veins, left umbilical vein carries highly oxygenated blood from placenta to heart. Like pulmonary artery, right and left umbilical arteries braing deoxygenated blood to placenta. 2. Mixing potentially occurs…
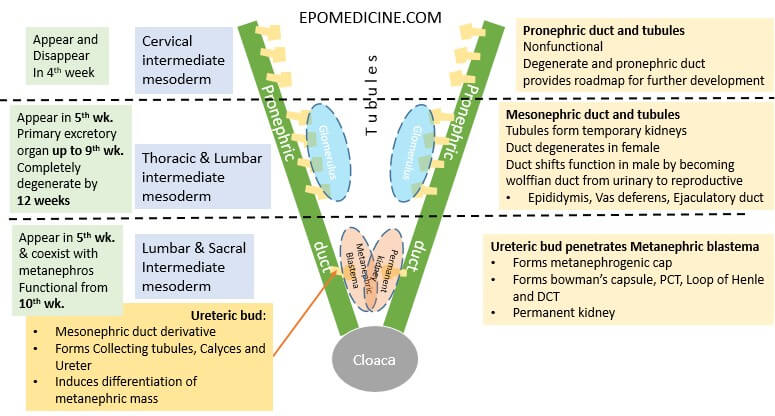
Renal (Kidney) Development – Embryology Made Easy
Kidney development occurs chronologically from cranial to caudal direction from urogenital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) in 3 different phases. Intermediate mesoderm → urogenital ridge (longitudinal elevation along dorsal body wall) → nephrogenic cord → Pronephros, Mesonephros and Metanephric mesoderm/blastema Remember the embryology of brain – from cranial to caudal, the primordial…
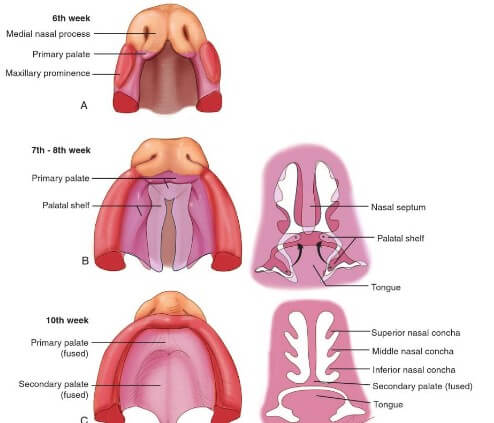
Face and Palate Development – Embryology made Easy
4 week embryo 5 mesenchymal prominences (facial primordia) appear in relation to the stomodeum (a depression in the surface ectoderm which marks the future mouth and oral cavity): Cranially: Frontonasal prominence (unpaired) Laterally: Maxillary prominence (paired; 1st pharyngeal arch) Caudally: Mandibular prominence (paired; 1st pharyngeal arch) 5 week embryo Localized…
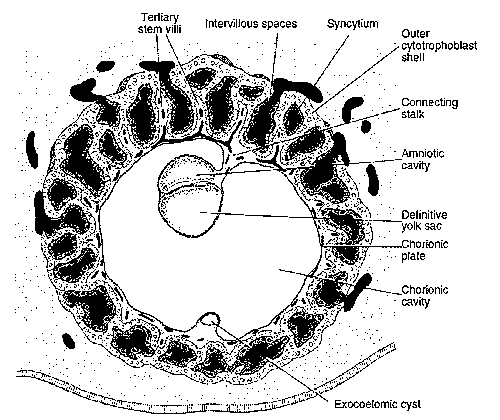
Embryology Week 3: Trimalinar Germ Disc
In the Week 2, we had a bilaminar germ disc with 2 cavities (amniotic cavity and yolk sac) suspended in the chorionic (extraembryonic cavity) by a connecting stalk (future umbilical cord). In the 3rd week, the embryo will have 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) following a process called…
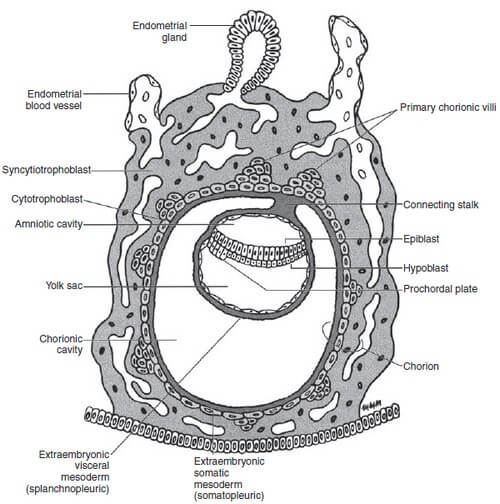
Embryology Week 2: Rule of Twos
Starting from Day 8, blastocyst progressively invades into the endometrial stroma and there is formation of: 2 layers in Trophoblast: 1. Inner mononulcear Cytotrophoblast (Cellular) Mitotic figures are found in the cytotrophoblast – hence generate primary chorionic villi into the syncytiotrophoblast. 2. Outer multinucleated Syncytiotrophoblast (Syncytium – cells have fused) Mitotic…